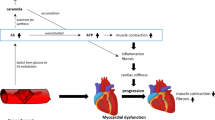
Abstract
The presence of comorbidities significantly influences long-term morbidity and mortality of symptomatic and asymptomatic heart failure (HF) patients. Metabolic syndrome and diabetic cardiomyopathy are two clinical conditions that share multiple pathophysiological mechanisms and that might be both responsible for cardiac dysfunction. However, it is argued whether metabolic syndrome (MS) independently increases HF risk or the association between MS and HF merely reflects the impact of individual risk factors included in its definition on HF development. Similarly, in the context of diabetic cardiomyopathy, many aspects are still challenging starting from the definition up to the therapeutic management. In this clinical review, we focused the attention on molecular pathways, myocyte alterations, and specific patterns of metabolic syndrome and diabetic cardiomyopathy in order to better define the potential diagnostic and therapeutic approaches of these two pathological conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Redfield MM, Jacobsen SJ, Burnett JC Jr, Mahoney DW, Bailey KR, Rodeheffer RJ (2003) Burden of systolic and diastolic ventricular dysfunction in the community: appreciating the scope of the heart failure epidemic. JAMA. 289(2):194–202
Ervin RB (2009) Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among adults 20 years of age and over, by sex, age, race and ethnicity, and body mass index: United States, 2003–2006. Natl Health Stat Rep (13):1–7
Wang J, Sarnola K, Ruotsalainen S, Moilanen L, Lepistö P, Laakso M, Kuusisto J (2010) The metabolic syndrome predicts incident congestive heart failure: a 20-year follow-up study of elderly Finns. Atherosclerosis. 210(1):237–242
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Costa F, American Heart Association, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (2005) Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 112(17):2735–2752
Perrone-Filardi P, Paolillo S, Costanzo P, Savarese G, Trimarco B, Bonow RO (2015) The role of metabolic syndrome in heart failure. Eur Heart J 36(39):2630–2634
Barzilay JI, Kronmal RA, Gottdiener JS, Smith NL, Burke GL, Tracy R, Savage PJ, Carlson M (2004) The association of fasting glucose levels with congestive heart failure in diabetic adults > or =65 years: the Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 43(12):2236–2241
Solang L, Malmberg K, Ryden L (1999) Diabetes mellitus and congestive heart failure. Further knowledge needed. Eur Heart J 20(11):789–795
Gargiulo P, Perrone-Filardi P (2018) Heart failure, whole-body insulin resistance and myocardial insulin resistance: an intriguing puzzle. J Nucl Cardiol 25(1):177–180
Aroor AR, Mandavia CH, Sowers JR (2012) Insulin resistance and heart failure: molecular mechanisms. Heart Fail Clin 8(4):609–617
Bertrand L, Horman S, Beauloye C, Vanoverschelde JL (2008) Insulin signalling in the heart. Cardiovasc Res 79(2):238–248
Saha AK, Xu XJ, Balon TW, Brandon A, Kraegen EW, Ruderman NB (2011) Insulin resistance due to nutrient excess: is it a consequence of AMPK downregulation? Cell Cycle 10(20):3447–3451
Li J, Su S, Zong X (2014) Analysis of the association between adiponectin, adiponectin receptor 1 and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Exp Ther Med 7(4):1023–1027
Bugger H, Boudina S, Hu XX, Tuinei J, Zaha VG, Theobald HA, Yun UJ, McQueen AP, Wayment B, Litwin SE, Abel ED (2008) Type 1 diabetic Akita mouse hearts are insulin sensitive but manifest structurally abnormal mitochondria that remain coupled despite increased uncoupling protein 3. Diabetes. 57(11):2924–2932
Tschope C, Walther T, Escher F et al (2005) Transgenic activation of the kallikrein-kinin system inhibits intramyocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. FASEB J 19(14):2057–2059
Marciano C, Galderisi M, Gargiulo P, Acampa W, D’Amore C, Esposito R, Capasso E, Savarese G, Casaretti L, Iudice FL, Esposito G, Rengo G, Leosco D, Cuocolo A, Perrone-Filardi P (2012) Effects of type 2 diabetes mellitus on coronary microvascular function and myocardial perfusion in patients without obstructive coronary artery disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39(7):1199–1206
Gargiulo P, Marciano C, Savarese G et al (2013) Endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients with normal coronary arteries: a digital reactive hyperemia study. Int J Cardiol 165(1):67–71
Paolillo S, Rengo G, Pagano G, Pellegrino T, Savarese G, Femminella GD, Tuccillo M, Boemio A, Attena E, Formisano R, Petraglia L, Scopacasa F, Galasso G, Leosco D, Trimarco B, Cuocolo A, Perrone-Filardi P (2013) Impact of diabetes on cardiac sympathetic innervation in patients with heart failure: a 123I meta-iodobenzylguanidine (123I MIBG) scintigraphic study. Diabetes Care 36(8):2395–2401
Paolillo S, Rengo G, Pellegrino T, Formisano R, Pagano G, Gargiulo P, Savarese G, Carotenuto R, Petraglia L, Rapacciuolo A, Perrino C, Piscitelli S, Attena E, del Guercio L, Leosco D, Trimarco B, Cuocolo A, Perrone-Filardi P (2015) Insulin resistance is associated with impaired cardiac sympathetic innervation in patients with heart failure. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16(10):1148–1153
Rengo G, Pagano G, Paolillo S, de Lucia C, Femminella GD, Liccardo D, Cannavo A, Formisano R, Petraglia L, Komici K, Rengo F, Trimarco B, Ferrara N, Leosco D, Perrone-Filardi P (2015) Impact of diabetes mellitus on lymphocyte GRK2 protein levels in patients with heart failure. Eur J Clin Investig 45(2):187–195
Iaccarino G, Barbato E, Cipolletta E, de Amicis V, Margulies KB, Leosco D, Trimarco B, Koch WJ (2005) Elevated myocardial and lymphocyte GRK2 expression and activity in human heart failure. Eur Heart J 26(17):1752–1758
Aroor AR, Mandavia C, Ren J, Sowers JR, Pulakat L (2012) Mitochondria and oxidative stress in the cardiorenal metabolic syndrome. Cardiorenal Med 2(2):87–109
Lebeche D, Davidoff AJ, Hajjar RJ (2008) Interplay between impaired calcium regulation and insulin signaling abnormalities in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 5(11):715–724
Tuunanen H, Knuuti J (2011) Metabolic remodelling in human heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 90(2):251–257
Falcao-Pires I, Leite-Moreira AF (2012) Diabetic cardiomyopathy: understanding the molecular and cellular basis to progress in diagnosis and treatment. Heart Fail Rev 17(3):325–344
van de Weijer T, Schrauwen-Hinderling VB, Schrauwen P (2011) Lipotoxicity in type 2 diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 92(1):10–18
Nagoshi T, Yoshimura M, Rosano GM, Lopaschuk GD, Mochizuki S (2011) Optimization of cardiac metabolism in heart failure. Curr Pharm Des 17(35):3846–3853
Barth E, Stammler G, Speiser B, Schaper J (1992) Ultrastructural quantitation of mitochondria and myofilaments in cardiac muscle from 10 different animal species including man. J Mol Cell Cardiol 24(7):669–681
Brown DA, Perry JB, Allen ME, Sabbah HN, Stauffer BL, Shaikh SR, Cleland JGF, Colucci WS, Butler J, Voors AA, Anker SD, Pitt B, Pieske B, Filippatos G, Greene SJ, Gheorghiade M (2017) Expert consensus document: mitochondrial function as a therapeutic target in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol 14(4):238–250
Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral T, Branwood AW, Grishman A (1972) New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol 30(6):595–602
Seferovic PM, Petrie MC, Filippatos GS et al (2018) Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 20(5):853–872
Fang ZY, Prins JB, Marwick TH (2004) Diabetic cardiomyopathy: evidence, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Endocr Rev 25(4):543–567
Jia G, DeMarco VG, Sowers JR (2016) Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol 12(3):144–153
Mandavia CH, Aroor AR, Demarco VG, Sowers JR (2013) Molecular and metabolic mechanisms of cardiac dysfunction in diabetes. Life Sci 92(11):601–608
Anderson EA, Hoffman RP, Balon TW, Sinkey CA, Mark AL (1991) Hyperinsulinemia produces both sympathetic neural activation and vasodilation in normal humans. J Clin Invest 87(6):2246–2252
Vincent MA, Clerk LH, Lindner JR, Klibanov AL, Clark MG, Rattigan S, Barrett EJ (2004) Microvascular recruitment is an early insulin effect that regulates skeletal muscle glucose uptake in vivo. Diabetes. 53(6):1418–1423
Shang Y, Zhang X, Leng W et al (2017) Assessment of diabetic cardiomyopathy by cardiovascular magnetic resonance T1 mapping: correlation with left-ventricular diastolic dysfunction and diabetic duration. J Diabetes Res 2017:9584278
Seferovic PM, Paulus WJ (2015) Clinical diabetic cardiomyopathy: a two-faced disease with restrictive and dilated phenotypes. Eur Heart J 36(27):1718–1727 1727a-1727c
Romano S, Di Mauro M, Fratini S et al (2010) Early diagnosis of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in diabetic patients: a possible role for natriuretic peptides. Cardiovasc Diabetol 9:89
Epshteyn V, Morrison K, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Clopton P, Mudaliar S, Edelman S, Henry R, Maisel A (2003) Utility of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) as a screen for left ventricular dysfunction in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 26(7):2081–2087
Shaver A, Nichols A, Thompson E, Mallick A, Payne K, Jones C, Manne NDPK, Sundaram S, Shapiro JI, Sodhi K (2016) Role of serum biomarkers in early detection of diabetic cardiomyopathy in the West Virginian population. Int J Med Sci 13(3):161–168
Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, Falk V, González-Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GM, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P, Authors/Task Force Members, Document Reviewers (2016) 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail 18(8):891–975
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE (2015) Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 373(22):2117–2128
Fitchett D, Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Hantel S, Salsali A, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE, EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial investigators (2016) Heart failure outcomes with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: results of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME(R) trial. Eur Heart J 37(19):1526–1534
Perrone-Filardi P, Avogaro A, Bonora E, Colivicchi F, Fioretto P, Maggioni AP, Sesti G, Ferrannini E (2017) Mechanisms linking empagliflozin to cardiovascular and renal protection. Int J Cardiol 241:450–456
Tahara A, Kurosaki E, Yokono M, Yamajuku D, Kihara R, Hayashizaki Y, Takasu T, Imamura M, Li Q, Tomiyama H, Kobayashi Y, Noda A, Sasamata M, Shibasaki M (2013) Effects of SGLT2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and obesity in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol 715(1–3):246–255
Radholm K, Figtree G, Perkovic V et al (2018) Canagliflozin and heart failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 138(5):458–468
Kato ET, Silverman MG, Mosenzon O, Zelniker TA, Cahn A, Furtado RHM, Kuder J, Murphy SA, Bhatt DL, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Wilding JPH, Bonaca MP, Ruff CT, Desai AS, Goto S, Johansson PA, Gause-Nilsson I, Johanson P, Langkilde AM, Raz I, Sabatine MS, Wiviott SD (2019) Effect of dapagliflozin on heart failure and mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 139(22):2528–2536
Forcheron F, Basset A, Abdallah P, Del Carmine P, Gadot N, Beylot M (2009) Diabetic cardiomyopathy: effects of fenofibrate and metformin in an experimental model--the Zucker diabetic rat. Cardiovasc Diabetol 8:16
Lu J, Pontre B, Pickup S et al (2013) Treatment with a copper-selective chelator causes substantive improvement in cardiac function of diabetic rats with left-ventricular impairment. Cardiovasc Diabetol 12:28
Turan B (2016) A comparative summary on antioxidant-like actions of timolol with other antioxidants in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Curr Drug Deliv 13(3):418–423
Liu W, Gong W, He M et al (2018) Spironolactone protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Diabetes Res 2018:9232065
Rosen R, Rump AF, Rosen P (1995) The ACE-inhibitor captopril improves myocardial perfusion in spontaneously diabetic (BB) rats. Diabetologia. 38(5):509–517
Wu MS, Liang JT, Lin YD, Wu ET, Tseng YZ, Chang KC (2008) Aminoguanidine prevents the impairment of cardiac pumping mechanics in rats with streptozotocin and nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetes. Br J Pharmacol 154(4):758–764
Dandamudi S, Slusser J, Mahoney DW et al (2014) The prevalence of diabetic cardiomyopathy: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Card Fail 20:304–309
Nichols GA, Hillier TA, Erbey JR, Brown JB (2001) Congestive heart failure in type 2 diabetes: prevalence, incidence, and risk factors. Diabetes Care 24(9):1614–1619
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gargiulo, P., Marsico, F., Renga, F. et al. The metabolic syndrome in heart failure: insights to specific mechanisms. Heart Fail Rev 25, 1–7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-019-09838-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-019-09838-6