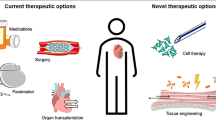
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases remain the first cause of morbidity and mortality in the developed countries and are a major problem not only in the western nations but also in developing countries. Current standard approaches for treating patients with ischemic heart disease include angioplasty or bypass surgery. However, a large number of patients cannot be treated using these procedures. Novel curative approaches under investigation include gene, cell, and protein therapy. This review focuses on potential growth factors for cardiac repair. The role of these growth factors in the angiogenic process and the therapeutic implications are reviewed. Issues including aspects of growth factor delivery are presented in relation to protein stability, dosage, routes, and safety matters. Finally, different approaches for controlled growth factor delivery are discussed as novel protein delivery platforms for cardiac regeneration.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ang:
-
Angiopoietin
- C-GSF:
-
Colony granulocyte stimulating factor
- CHF:
-
Chronic heart failure
- cMLCK:
-
Cardiac-specific myosin light-chain kinase
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular diseases
- EC:
-
Endothelial cell
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EPC:
-
Endothelial progenitor cell
- EPO:
-
Erythropoietin
- ErbB:
-
NRG tyrosine kinase receptor
- FDA:
-
US Food and drug administration
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- FGF-1:
-
Acidic fibroblast growth factor
- FGF-2:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- FGFR:
-
FGF tyrosine kinase receptor
- G-CSF:
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
- GF:
-
Growth factor
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1α
- HSPGs:
-
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans
- IHD:
-
Ischemic heart disease
- LAD:
-
Left anterior descending coronary artery
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricle ejection fraction
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NRG:
-
Neuregulin
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- PDGFR:
-
PDGF tyrosine kinase receptor
- PEG:
-
Poly(ethylene glycol)
- PEO:
-
Poly(ethylene oxide)
- Shh:
-
Sonic hedgehog
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- Tie:
-
Ang tyrosine kinase receptor
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR:
-
VEGF tyrosine kinase receptor
- VSMC:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cell
- WHF:
-
World Heart Federation
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
WHO (2008) WHO The global burden of disease: 2004 update. http://www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GBD_report_2004update_full.pdf. Last visited March 2011
Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Howard VJ, Rumsfeld J, Manolio T, Zheng ZJ, Flegal K, O’Donnell C, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, Goff DC Jr, Hong Y, Adams R, Friday G, Furie K, Gorelick P, Kissela B, Marler J, Meigs J, Roger V, Sidney S, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wilson M, Wolf P (2006) Heart disease and stroke statistics–2006 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 113(6):e85–e151
Mackay J, Mensah G (2004) Atlas of heart disease and stroke. World Health Organization, Geneva
Kurrelmeyer K, Kalra D, Bozkurt B, Wang F, Dibbs Z, Seta Y, Baumgarten G, Engle D, Sivasubramanian N, Mann DL (1998) Cardiac remodeling as a consequence and cause of progressive heart failure. Clin Cardiol 21(12 Suppl 1):I14–I19
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285(21):1182–1186
Lee SH, Wolf PL, Escudero R, Deutsch R, Jamieson SW, Thistlethwaite PA (2000) Early expression of angiogenesis factors in acute myocardial ischemia and infarction. N Engl J Med 342(9):626–633
Shing Y, Folkman J, Sullivan R, Butterfield C, Murray J, Klagsbrun M (1984) Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science 223(4642):1296–1299
Esch F, Baird A, Ling N, Ueno N, Hill F, Denoroy L, Klepper R, Gospodarowicz D, Bohlen P, Guillemin R (1985) Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82(19):6507–6511
Yun YR, Won JE, Jeon E, Lee S, Kang W, Jo H, Jang JH, Shin US, Kim HW (2010) Fibroblast growth factors: biology, function, and application for tissue regeneration. J Tissue Eng 2010:1–18
Losordo DW, Dimmeler S (2004) Therapeutic angiogenesis and vasculogenesis for ischemic disease. Part I: angiogenic cytokines. Circulation 109(21):2487–2491
Kardami E, Detillieux K, Ma X, Jiang Z, Santiago JJ, Jimenez SK, Cattini PA (2007) Fibroblast growth factor-2 and cardioprotection. Heart Fail Rev 12(3–4):267–277
Carmeliet P (2000) Fibroblast growth factor-1 stimulates branching and survival of myocardial arteries: a goal for therapeutic angiogenesis? Circ Res 87(3):176–178
Seghezzi G, Patel S, Ren CJ, Gualandris A, Pintucci G, Robbins ES, Shapiro RL, Galloway AC, Rifkin DB, Mignatti P (1998) Fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) induces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in the endothelial cells of forming capillaries: an autocrine mechanism contributing to angiogenesis. J Cell Biol 141(7):1659–1673
Claffey KP, Abrams K, Shih SC, Brown LF, Mullen A, Keough M (2001) Fibroblast growth factor 2 activation of stromal cell vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis. Lab Invest 81(1):61–75
Kano MR, Morishita Y, Iwata C, Iwasaka S, Watabe T, Ouchi Y, Miyazono K, Miyazawa K (2005) VEGF-A and FGF-2 synergistically promote neoangiogenesis through enhancement of endogenous PDGF-B-PDGFRbeta signaling. J Cell Sci 118(Pt 16):3759–3768
Fujii T, Yonemitsu Y, Onimaru M, Tanii M, Nakano T, Egashira K, Takehara T, Inoue M, Hasegawa M, Kuwano H, Sueishi K (2006) Nonendothelial mesenchymal cell-derived MCP-1 is required for FGF-2-mediated therapeutic neovascularization: critical role of the inflammatory/arteriogenic pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26(11):2483–2489
Ferrara N, Henzel WJ (1989) Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161:851–858
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) VEGF receptor signalling—in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(5):359–371
Grunewald M, Avraham I, Dor Y, Bachar-Lustig E, Itin A, Jung S, Chimenti S, Landsman L, Abramovitch R, Keshet E (2006) VEGF-induced adult neovascularization: recruitment, retention, and role of accessory cells. Cell 124(1):175–189
Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers H, Van Oosterom AT, De Bruijn EA (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev 56(4):549–580
Kutryk MJ, Stewart DJ (2003) Angiogenesis of the heart. Microsc Res Tech 60(2):138–158
Fukumura D, Gohongi T, Kadambi A, Izumi Y, Ang J, Yun CO, Buerk DG, Huang PL, Jain RK (2001) Predominant role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(5):2604–2609
Fujio Y, Walsh K (1999) Akt mediates cytoprotection of endothelial cells by vascular endothelial growth factor in an anchorage-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 274(23):16349–16354
Takahashi T, Yamaguchi S, Chida K, Shibuya M (2001) A single autophosphorylation site on KDR/Flk-1 is essential for VEGF-A-dependent activation of PLC-gamma and DNA synthesis in vascular endothelial cells. EMBO J 20(11):2768–2778
Witzenbichler B, Maisonpierre PC, Jones P, Yancopoulos GD, Isner JM (1998) Chemotactic properties of angiopoietin-1 and -2, ligands for the endothelial-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. J Biol Chem 273(29):18514–18521
Davis S, Yancopoulos GD (1999) The angiopoietins: Yin and Yang in angiogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 237:173–185
Harfouche R, Hassessian HM, Guo Y, Faivre V, Srikant CB, Yancopoulos GD, Hussain SN (2002) Mechanisms which mediate the antiapoptotic effects of angiopoietin-1 on endothelial cells. Microvasc Res 64(1):135–147
Eklund L, Olsen BR (2006) Tie receptors and their angiopoietin ligands are context-dependent regulators of vascular remodeling. Exp Cell Res 312(5):630–641
Teichert-Kuliszewska K, Maisonpierre PC, Jones N, Campbell AI, Master Z, Bendeck MP, Alitalo K, Dumont DJ, Yancopoulos GD, Stewart DJ (2001) Biological action of angiopoietin-2 in a fibrin matrix model of angiogenesis is associated with activation of Tie2. Cardiovasc Res 49(3):659–670
Matsunaga T, Warltier DC, Tessmer J, Weihrauch D, Simons M, Chilian WM (2003) Expression of VEGF and angiopoietins-1 and -2 during ischemia-induced coronary angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285(1):H352–H358
Oh H, Takagi H, Suzuma K, Otani A, Matsumura M, Honda Y (1999) Hypoxia and vascular endothelial growth factor selectively up-regulate angiopoietin-2 in bovine microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 274(22):15732–15739
Holash J, Maisonpierre PC, Compton D, Boland P, Alexander CR, Zagzag D, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ (1999) Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Science 284(5422):1994–1998
Gerhardt H, Golding M, Fruttiger M, Ruhrberg C, Lundkvist A, Abramsson A, Jeltsch M, Mitchell C, Alitalo K, Shima D, Betsholtz C (2003) VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol 161(6):1163–1177
Betsholtz C (2004) Insight into the physiological functions of PDGF through genetic studies in mice. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15(4):215–228
Cao R, Brakenhielm E, Pawliuk R, Wariaro D, Post MJ, Wahlberg E, Leboulch P, Cao Y (2003) Angiogenic synergism, vascular stability and improvement of hind-limb ischemia by a combination of PDGF-BB and FGF-2. Nat Med 9(5):604–613
Hao X, Mansson-Broberg A, Gustafsson T, Grinnemo KH, Blomberg P, Siddiqui AJ, Wardell E, Sylven C (2004) Angiogenic effects of dual gene transfer of bFGF and PDGF-BB after myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315(4):1058–1063
Zhang J, Cao R, Zhang Y, Jia T, Cao Y, Wahlberg E (2009) Differential roles of PDGFR-alpha and PDGFR-beta in angiogenesis and vessel stability. FASEB J 23(1):153–163
Li X, Tjwa M, Moons L, Fons P, Noel A, Ny A, Zhou JM, Lennartsson J, Li H, Luttun A, Ponten A, Devy L, Bouche A, Oh H, Manderveld A, Blacher S, Communi D, Savi P, Bono F, Dewerchin M, Foidart JM, Autiero M, Herbert JM, Collen D, Heldin CH, Eriksson U, Carmeliet P (2005) Revascularization of ischemic tissues by PDGF-CC via effects on endothelial cells and their progenitors. J Clin Invest 115(1):118–127
Li X, Kumar A, Zhang F, Lee C, Li Y, Tang Z, Arjunan P (2010) VEGF-independent angiogenic pathways induced by PDGF-C. Oncotarget 1(4):309–314
Britsch S (2007) The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling system in development and disease. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 190:1–65
Meyer D, Yamaai T, Garratt A, Riethmacher-Sonnenberg E, Kane D, Theill LE, Birchmeier C (1997) Isoform-specific expression and function of neuregulin. Development 124(18):3575–3586
Kuramochi Y, Cote GM, Guo X, Lebrasseur NK, Cui L, Liao R, Sawyer DB (2004) Cardiac endothelial cells regulate reactive oxygen species-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through neuregulin-1beta/erbB4 signaling. J Biol Chem 279(49):51141–51147
Zhao YY, Sawyer DR, Baliga RR, Opel DJ, Han X, Marchionni MA, Kelly RA (1998) Neuregulins promote survival and growth of cardiac myocytes. Persistence of ErbB2 and ErbB4 expression in neonatal and adult ventricular myocytes. J Biol Chem 273(17):10261–10269
Fukazawa R, Miller TA, Kuramochi Y, Frantz S, Kim YD, Marchionni MA, Kelly RA, Sawyer DB (2003) Neuregulin-1 protects ventricular myocytes from anthracycline-induced apoptosis via erbB4-dependent activation of PI3-kinase/Akt. J Mol Cell Cardiol 35(12):1473–1479
Okoshi K, Nakayama M, Yan X, Okoshi MP, Schuldt AJ, Marchionni MA, Lorell BH (2004) Neuregulins regulate cardiac parasympathetic activity: muscarinic modulation of beta-adrenergic activity in myocytes from mice with neuregulin-1 gene deletion. Circulation 110(6):713–717
Bersell K, Arab S, Haring B, Kuhn B (2009) Neuregulin1/ErbB4 signaling induces cardiomyocyte proliferation and repair of heart injury. Cell 138(2):257–270
Seguchi O, Takashima S, Yamazaki S, Asakura M, Asano Y, Shintani Y, Wakeno M, Minamino T, Kondo H, Furukawa H, Nakamaru K, Naito A, Takahashi T, Ohtsuka T, Kawakami K, Isomura T, Kitamura S, Tomoike H, Mochizuki N, Kitakaze M (2007) A cardiac myosin light chain kinase regulates sarcomere assembly in the vertebrate heart. J Clin Invest 117(10):2812–2824
Xu Y, Li X, Liu X, Zhou M (2010) Neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling and chronic heart failure. Adv Pharmacol 59:31–51
Lemmens K, Fransen P, Sys SU, Brutsaert DL, De Keulenaer GW (2004) Neuregulin-1 induces a negative inotropic effect in cardiac muscle: role of nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 109(3):324–326
Iivanainen E, Paatero I, Heikkinen SM, Junttila TT, Cao R, Klint P, Jaakkola PM, Cao Y, Elenius K (2007) Intra- and extracellular signaling by endothelial neuregulin-1. Exp Cell Res 313(13):2896–2909
Jabbour A, Hayward CS, Keogh AM, Kotlyar E, McCrohon JA, England JF, Amor R, Liu X, Li XY, Zhou MD, Graham RM, Macdonald PS (2010) Parenteral administration of recombinant human neuregulin-1 to patients with stable chronic heart failure produces favourable acute and chronic haemodynamic responses. Eur J Heart Fail 13(1):83–92
Gao R, Zhang J, Cheng L, Wu X, Dong W, Yang X, Li T, Liu X, Xu Y, Li X, Zhou M (2010) A Phase II, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, based on standard therapy, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of recombinant human neuregulin-1 in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(18):1907–1914
Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E (1980) Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 287(5785):795–801
Riddle RD, Johnson RL, Laufer E, Tabin C (1993) Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell 75(7):1401–1416
Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, Shen L, Mohler J, McMahon JA, McMahon AP (1993) Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell 75(7):1417–1430
Krauss S, Concordet JP, Ingham PW (1993) A functionally conserved homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in zebrafish embryos. Cell 75(7):1431–1444
Cohen MM Jr (2003) The hedgehog signaling network. Am J Med Genet A 123A(1):5–28
Mimeault M, Batra SK (2010) Frequent deregulations in the hedgehog signaling network and cross-talks with the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway involved in cancer progression and targeted therapies. Pharmacol Rev 62(3):497–524
Farzan SF, Singh S, Schilling NS, Robbins DJ (2008) The adventures of sonic hedgehog in development and repair. III. Hedgehog processing and biological activity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294(4):G844–G849
Zeng X, Goetz JA, Suber LM, Scott WJ Jr, Schreiner CM, Robbins DJ (2001) A freely diffusible form of Sonic hedgehog mediates long-range signalling. Nature 411(6838):716–720
Eaton S (2006) Release and trafficking of lipid-linked morphogens. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16(1):17–22
Bijlsma MF, Borensztajn KS, Roelink H, Peppelenbosch MP, Spek CA (2007) Sonic hedgehog induces transcription-independent cytoskeletal rearrangement and migration regulated by arachidonate metabolites. Cell Signal 19(12):2596–2604
Chinchilla P, Xiao L, Kazanietz MG, Riobo NA (2010) Hedgehog proteins activate pro-angiogenic responses in endothelial cells through non-canonical signaling pathways. Cell Cycle 9(3):570–579
Lavine KJ, Kovacs A, Ornitz DM (2008) Hedgehog signaling is critical for maintenance of the adult coronary vasculature in mice. J Clin Invest 118(7):2404–2414
Bijlsma MF, Groot AP, Oduro JP, Franken RJ, Schoenmakers SH, Peppelenbosch MP, Spek CA (2009) Hypoxia induces a hedgehog response mediated by HIF-1alpha. J Cell Mol Med 13(8B):2053–2060
Agouni A, Mostefai HA, Porro C, Carusio N, Favre J, Richard V, Henrion D, Martinez MC, Andriantsitohaina R (2007) Sonic hedgehog carried by microparticles corrects endothelial injury through nitric oxide release. FASEB J 21(11):2735–2741
Benameur T, Soleti R, Porro C, Andriantsitohaina R, Martinez MC (2010) Microparticles carrying Sonic hedgehog favor neovascularization through the activation of nitric oxide pathway in mice. PloS One 5(9):e12688
Kusano KF, Pola R, Murayama T, Curry C, Kawamoto A, Iwakura A, Shintani S, Ii M, Asai J, Tkebuchava T, Thorne T, Takenaka H, Aikawa R, Goukassian D, von Samson P, Hamada H, Yoon YS, Silver M, Eaton E, Ma H, Heyd L, Kearney M, Munger W, Porter JA, Kishore R, Losordo DW (2005) Sonic hedgehog myocardial gene therapy: tissue repair through transient reconstitution of embryonic signaling. Nat Med 11(11):1197–1204
Pola R, Ling LE, Silver M, Corbley MJ, Kearney M, Blake Pepinsky R, Shapiro R, Taylor FR, Baker DP, Asahara T, Isner JM (2001) The morphogen Sonic hedgehog is an indirect angiogenic agent upregulating two families of angiogenic growth factors. Nat Med 7(6):706–711
Ahmed RP, Haider KH, Shujia J, Afzal MR, Ashraf M (2010) Sonic Hedgehog gene delivery to the rodent heart promotes angiogenesis via iNOS/netrin-1/PKC pathway. PloS One 5(1):e8576
Ueda K, Takano H, Niitsuma Y, Hasegawa H, Uchiyama R, Oka T, Miyazaki M, Nakaya H, Komuro I (2010) Sonic hedgehog is a critical mediator of erythropoietin-induced cardiac protection in mice. J Clin Invest 120(6):2016–2029
Bijlsma MF, Leenders PJ, Janssen BJ, Peppelenbosch MP, Ten Cate H, Spek CA (2008) Endogenous hedgehog expression contributes to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 233(8):989–996
Schumacher B, Pecher P, von Specht BU, Stegmann T (1998) Induction of neoangiogenesis in ischemic myocardium by human growth factors. First clinical results of a new treatment of coronary heart disease. Circulation 97:645–650
Unger EF et al (2000) Effects of a single intracoronary injection of basic fibroblast growth factor in stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 85:1414–1419
Laham RJ, Chronos NA, Marilyn P, Leimbach ME, Udelson JE, Pearlman JD, Pettigrew RI, Whitehouse MJ, Yoshizawa C, Simons M (2000) Intracoronary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) in patients with ischemic heart disease: results of a Phase I open-label dose escalation study. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:2132–2139
Simons M, Annex BH, Laham RJ, Kleiman N, Henry T, Dauerman H, Udelson JE, Gervino EV, Pike M, Whitehouse MJ, Moon T, Chronos NA (2002) Pharmacological treatment of coronary artery disease with recombinant fibroblast growth factor-2. Double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Circulation 105:788–793
Gibson C, Laham R, Giordano F (1999) Magnitude and location of new angiographically apparent coronary collaterals following intravenous VEGF administration. J Am Coll Cardiol 33(Suppl. A):65A (Abstract)
Hendel RC, Henry TD, Rocha-Singh K, Isner JM, Kereiakes DJ, Giordano FJ, Simons M, Bonow RO (2000) Effect of intracoronary recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor on myocardial perfusion: evidence for a dose-dependent effect. Circulation 101:118–121
Henry TD, Rocha-Singh K, Isner JM et al (2001) Results of intracoronary recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor (rhVEGF) administration trial. Am Heart J 142:872–880
Henry TD, Annex BH, McKendall GR, Azrin MA, Lopez JJ, Giordano FJ, Shah PK, Willerson JT, Benza RL, Berman DS, Gibson CM, Bajamonde A, Rundle AC, Fine J, McCluskey ER (2003) The VIVA trial. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ischemia for vascular angiogenesis. Circulation 107:1359–1365
Meier P, Gloekler S, de Marchi SF, Indermuehle A, Rutz T, Traupe T, Steck H, Vogel R, Seiler C (2009) Myocardial salvage through coronary collateral growth by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in chronic coronary artery disease: a controlled randomized trial. Circulation 120(14):1355–1363
Achilli F, Malafronte C, Lenatti L, Gentile F, Dadone V, Gibelli G, Maggiolini S, Squadroni L, Di Leo C, Burba I, Pesce M, Mircoli L, Capogrossi MC, Di Lelio A, Camisasca P, Morabito A, Colombo G, Pompilio G (2010) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor attenuates left ventricular remodelling after acute anterior STEMI: results of the single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled multicentre STem cEll mobilization in acute myocardial infarction (STEM-AMI) trial. Eur J Heart Fail 12(10):1111–1121
Engelmann MG, Theiss HD, Theiss C, Henschel V, Huber A, Wintersperger BJ, Schoenberg SO, Steinbeck G, Franz WM (2010) G-CSF in patients suffering from late revascularised ST elevation myocardial infarction: final 1-year-results of the G-CSF-STEMI trial. Int J Cardiol 144(3):399–404
Theiss HD, Brenner C, Engelmann MG, Zaruba MM, Huber B, Henschel V, Mansmann U, Wintersperger B, Reiser M, Steinbeck G, Franz WM (2010) Safety and efficacy of SITAgliptin plus GRanulocyte-colony-stimulating factor in patients suffering from acute myocardial infarction (SITAGRAMI-trial)—rationale, design and first interim analysis. Int J Cardiol 145(2):282–284
Wang N, Tong G, Yang J, Zhou Z, Pan H, Huo Y, Xu J, Zhang X, Ling F, Li P (2009) Effect of hepatocyte growth-promoting factors on myocardial ischemia during exercise in patients with severe coronary artery disease. Int Heart J 50(3):291–299
Tang YD, Hasan F, Giordano FJ, Pfau S, Rinder HM, Katz SD (2009) Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin on platelet activation in acute myocardial infarction: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Am Heart J 158(6):941–947
Voors AA, Belonje AM, Zijlstra F, Hillege HL, Anker SD, Slart RH, Tio RA, van’t hof A, Jukema JW, Peels HO, Henriques JP, Ten Berg JM, Vos J, van Gilst WH, van Veldhuisen DJ (2010) A single dose of erythropoietin in ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 31(21):2593–2600
Jacobs J (2007) Combating cardiovascular disease with angiogenic therapy. Drug Discov Today 12(23–24):1040–1045
Eppler SM, Combs DL, Henry TD, Lopez JJ, Ellis SG, Yi JH, Annex McCluskey ER, Zioncheck TF (2002) A target-mediated model to describe the pharmacokinetics and hemodynamic effects of recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:20–32
Cleland JL, Duenas ET, Park A, Daugherty A, Kahn J, Kowalski J, Cuthbertson A (2001) Development of poly-(d, l-lactide–coglycolide) microsphere formulations containing recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor to promote local angiogenesis. J Control Release 72:13–24
Kastrup J (2007) Clinical vascular growth factor therapy for neovascularization in patients with coronary artery disease. In: Deindl E, Kupatt C (eds) Therapeutic neovascularization—quo vadis?. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–22
Udelson JE, Dilsizian V, Laham RJ, Chronos N, Vansant J, Blais M, Galt JR, Pike M, Yoshizawa C, Simons M (2000) Therapeutic angiogenesis with recombinant fibroblast growth factor-2 improves stress and rest myocardial perfusion abnormalities in patients with severe chronic coronary artery disease. Circulation 102:1605–1610
Laham RJ, Rezaee M, Post M, Sellke FW, Braeckman RA, Hung D, Simons M (1999) Intracoronary and intravenous administration of basic fibroblast growth factor: myocardial and tissue distribution. Drug Metab Dispos 27(7):821–826
Wang JS (1996) Basic fibroblast growth factor for stimulation of bone formation in osteoinductive or conductive implants. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 269:1–33
Post MJ, Laham RJ, Sellke FW, Simons M (2001) Therapeutic angiogenesis in cardiology using protein formulations. Cardiovasc Res 49:522–531
Pérez-Ramirez B, Guziewicz N, Simler R (2010) Preformulation research: assessing protein solution behavior during early development. In: Jameel F, Hershenson S (eds) Formulation and process development strategies for manufacturing biopharmaceuticals. Wiley, Hoboken
Arakawa T, Timasheff SN (1985) The stabilization of proteins by osmolytes. Biophys J 47(3):411–414
Cleland JL, Powell MF, Shire SJ (1993) The development of stable protein formulations: a close look at protein aggregation, deamidation, and oxidation. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 10(4):307–377
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25:581–611
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Carmeliet P (2000) VEGF gene therapy: stimulating angiogenesis or angioma-genesis? Nat Med 6(10):1102–1103
Lee H, Chung HJ, Park TG (2007) Perspectives on: local and sustained delivery of angiogenic growth factors. J Bioact Compat Polym 22:89–114
Lee KY, Yuk SH (2007) Polymeric protein delivery systems. Progr Polymer Sci 32(7):669–697
Tabata Y, Miyao M, Ozeki M, Ikada Y (2000) Controlled release of vascular endothelial growth factor by use of collagen hydrogels. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 11(9):915–930
Isner JM (2002) Myocardial gene therapy. Nature 415:234–239
Patel ZS, Ueda H, Yamamoto M, Tabata Y, Mikos AG (2008) In vitro and in vivo release of vascular endothelial growth factor from gelatin microparticles and biodegradable composite scaffolds. Pharm Res 25(10):2370–2378
Epstein SE, Fuchs S, Zhou YF, Baffour R, Kornowski R (2001) Therapeutic interventions for enhancing collateral development by administration of growth factors: basic principles, early results and potential hazards. Cardiovasc Res 49:532–542
Lazarous DF, Shou M, Scheinowitz M, Hodge E, Thirumurti V, Kitsiou AN, Stiber JA, Lobo AD, Hunsberger S, Guetta E, Epstein SE, Unger EF (1996) Comparative effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor on coronary collateral development and the arterial response to injury. Circulation 94:1074–1082
Ehrbar M, Djonov V, Schnell C, Tschanz SA, Martiny-Baron G, Schenk U, Wood J, Burri PH, Hubbell JA, Zisch AH (2004) Cell-demanded liberation of VEGF121 from fibrin implants induces local and controlled blood vessel growth. Circ Res 94:1124–1132
Laurens N, Koolwijk P, de Maat MP (2006) Fibrin structure and wound healing. J Thromb Haemost 4(5):932–939
Peattie RA, Nayate AP, Firpo MA, Shelby J, Fisher RJ, Prestwich GD (2004) Stimulation of in vivo angiogenesis by cytokine-loaded hyaluronic acid hydrogel implants. Biomaterials 25:2789–2798
Peattie RA, Rieke ER, Hewett EM, Fisher RJ, Shu XZ, Prestwich GD (2006) Dual growth factor-induced angiogenesis in vivo using hyaluronan hydrogel implants. Biomaterials 27(9):1868–1875
Cai SS, Liu YC, Shu XZ, Prestwich GD (2005) Injectable glycosaminoglycan hydrogels for controlled release of human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials 26:6054–6067
Elçin YM, Dixit V, Gitnick T (2001) Extensive in vivo angiogenesis following controlled release of human vascular endothelial cell growth factor: Implications for tissue engineering and wound healing. Artif Organs 25(7):558–565
Gu F, Amsden B, Neufeld R (2004) Sustained delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor with alginate beads. J Control Release 96(3):463–472
Jay SM, Saltzman WM (2009) Controlled delivery of VEGF via modulation of alginate microparticle ionic crosslinking. J Control Release 134:26–34
Hao X, Silva EA, Månsson-Broberg A, Grinnemo KH, Siddiqui AJ, Dellgren G, Wärdell E, Brodin LA, Mooney DJ, Sylvén C (2007) Angiogenic effects of sequential release of VEGF-A165 and PDGF-BB with alginate hydrogels after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 75:178–185
Matsusaki M, Sakaguchi H, Serizawa T, Akashi M (2007) Controlled release of vascular endothelial growth factor from alginate hydrogels nano-coated with polyelectrolyte multilayer films. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 18(6):775–783
Silva EA, Mooney DJ (2007) Spatiotemporal control of vascular endothelial growth factor delivery from injectable hydrogels enhances angiogenesis. J Thromb Haemost 5:590–598
Zisch AH, Lutolf MP, Hubbell JA (2003) Biopolymeric delivery matrices for angiogenic growth factors. Cardiovasc Pathol 12:295–310
Draget KI, Skjåk-Bræk G, Smidsrød O (1997) Alginate based new materials. Int J Biol Macromol 21:47–55
Khor E, Lim LY (2003) Implantable applications of chitin and chitosan. Biomaterials 24(13):2339–2349
Fujita M, Ishihara M, Morimoto Y, Simizu M, Saito Y, Yura H, Matsui T, Takase B, Hattori H, Kanatani Y, Kikuchi M, Maehara T (2005) Efficacy of photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel containing fibroblast growth factor-2 in a rabbit model of chronic myocardial infarction. J Surg Res 126(1):27–33
Wang H, Zhang X, Li Y, Ma Y, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Zhou J, Lin Q, Wang Y, Duan C, Wang C (2010) Improved myocardial performance in infarcted rat heart by co-injection of basic fibroblast growth factor with temperature-responsive chitosan hydrogel. J Heart Lung Transplant 29(8):881–887
King TW, Patrick CW (2000) Development and in vitro characterization of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-loaded poly(dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid)/poly(ethylene glycol) microspheres using a solid encapsulation/single emulsion/solvent extraction technique. J Biomed Mater Res 51(3):383–390
Patil SD, Papadmitrakopoulos F, Burgess DJ (2007) Concurrent delivery of dexamethasone and VEGF for localized inflammation control and angiogenesis. J Control Release 117(1):68–79
Rocha FG, Sundback CA, Krebs NJ, Leach JK, Mooney DJ, Ashley SW, Vacanti JP, Whang EE (2008) The efffect of sustained delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor on angiogenesis in tissue-engineered intestine. Biomaterials 29(19):2884–2890
Jaklenec A, Hinckfuss A, Bilgen B, Ciombor DM, Aaron R, Mathiowitz E (2008) Sequential release of bioactive IGF-I and TGF-b1 from PLGA microsphere-based scaffolds. Biomaterials 29:1518–1525
Ennett AB, Kaigler D, Mooney DJ (2006) Temporally regulated delivery of VEGF in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res A 79A(1):176–184
Formiga FR, Pelacho B, Garbayo E, Abizanda G, Gavira JJ, Simon-Yarza T, Mazo M, Tamayo E, Jauquicoa C, Ortiz-de-Solorzano C, Prósper F, Blanco-Prieto MJ (2010) Sustained release of VEGF through PLGA microparticles improves vasculogenesis and tissue remodeling in an acute myocardial ischemia–reperfusion model. J Control Release 147:30–37
Tae G, Scatena M, Stayton PS, Hoffman AS (2006) PEG-cross-linked heparin is an affinity hydrogel for sustained release of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 17(1–2):187–197
Cai SS, Liu YC, Shu XZ, Prestwich GD (2005) Injectable glycosaminoglycan hydrogels for controlled release of human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials 26(30):6054–6067
Norton LW, Tegnell E, Toporek SS, Reichert WM (2005) In vitro characterization of vascular endothelial growth factor and dexamethasone releasing hydrogels for implantable probe coatings. Biomaterials 26(16):3285–3297
Yamaguchi N, Zhang L, Chae BS, Palla CS, Furst EM, Kiick KL (2007) Growth factor mediated assembly of cell receptor-responsive hydrogels. J Am Chem Soc 129(11):3040–3041
Zisch AH, Lutolf MP, Ehrbar M, Raeber GP, Rizzi SC, Davies N, Schmökel H, Bezuidenhout D, Djonov V, Zilla P, Hubbell JA (2003) Cell-demanded release of VEGF from synthetic, biointeractive cell ingrowth matrices for vascularized tissue growth. FASEB J 17:2260–2262
Matsusaki M, Akashi M (2005) Novel functional biodegradable polymer IV: pHsensitive controlled release of fibroblast growth factor-2 from a poly(γ-glutamic acid)-sulfonate matrix for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 6:3351–3356
Layman H, Spiga MG, Brooks T, Pham S, Webster KA, Andreopoulos FM (2007) The effect of the controlled release of basic fibroblast growth factor from ionic gelatin-based hydrogels on angiogenesis in a murine critical limb ischemic model. Biomaterials 28(16):2646–2654
Kavanagh CA, Gorelova TA, Selezneva II, Rochev YA, Dawson KA, Gallagher WM, Gorelov AV, Keenan AK (2005) Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymer films as vehicles for the sustained delivery of proteins to vascular endothelial cells. J Biomed Mater Res A 72(1):25–35
Garbern JC, Minami E, Stayton PS, Murry CE (2011) Delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor with a pH-responsive, injectable hydrogel to improve angiogenesis in infarcted myocardium. Biomaterials 32(9):2407–2416
Engel FB, Hsieh PC, Lee RT, Keating MT (2006) FGF1/p38 MAP kinase inhibitor therapy induces cardiomyocyte mitosis, reduces scarring, and rescues function after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(42):15546–15551
Sellke FW, Li J, Stamler A, Lopez JJ, Thomas KA, Simons M (1996) Angiogenesis induced by acidic fibroblast growth factor as an alternative method of revascularization for chronic myocardial ischemia. Surgery 120(2):182–188
Iwakura A, Fujita M, Kataoka K, Tambara K, Sakakibara Y, Komeda M, Tabata Y (2003) Intramyocardial sustained delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor improves angiogenesis and ventricular function in a rat infarct model. Heart Vessels 18(2):93–99
Shao ZQ, Takaji K, Katayama Y, Kunitomo R, Sakaguchi H, Lai ZF, Kawasuji M (2006) Effects of intramyocardial administration of slow-release basic fibroblast growth factor on angiogenesis and ventricular remodeling in a rat infarct model. Circ J 70:471–477
Sakakibara Y, Tambara K, Sakaguchi G, Lu F, Yamamoto M, Nishimura K, Tabata Y, Komeda M (2003) Toward surgical angiogenesis using slow-released basic fibroblast growth factor. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 24(1):105–111; discussion 112
Scott RC, Rosano JM, Ivanov Z, Wang B, Chong PL, Issekutz AC, Crabbe DL, Kiani MF (2009) Targeting VEGF-encapsulated immunoliposomes to MI heart improves vascularity and cardiac function. FASEB J 23(10):3361–3367
Zhang J, Ding L, Zhao Y, Sun W, Chen B, Lin H, Wang X, Zhang L, Xu B, Dai J (2009) Collagen-targeting vascular endothelial growth factor improves cardiac performance after myocardial infarction. Circulation 119:1776–1784
Wu J, Zeng F, Huang XP, Chung JC, Konecny F, Weisel RD, Li RK (2011) Infarct stabilization and cardiac repair with a VEGF-conjugated, injectable hydrogel. Biomaterials 32(2):579–586
Oh KS, Song JY, Yoon SJ, Park Y, Kim D, Yuk SH (2010) Temperature-induced gel formation of core/shell nanoparticles for the regeneration of ischemic heart. J Control Release 146(2):207–211
Wang T, Jiang XJ, Lin T, Ren S, Li XY, Zhang XZ, Tang QZ (2009) The inhibition of postinfarct ventricle remodeling without polycythaemia following local sustained intramyocardial delivery of erythropoietin within a supramolecular hydrogel. Biomaterials 30(25):4161–4167
Silva AKA, Richard C, Bessodes M, Scherman D, Merten OW (2009) Growth factor delivery approaches in hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 10(1):9–18
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2001) Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem Rev 101:1869–1879
Tabata Y, Hijikata S, Ikada Y (1994) Enhanced vascularization and tissue granulation by basic fibroblast growth factor impregnated in gelatin hydrogels. J Control Release 31:189–199
Pharmacopeia U (2008) USP 31, NF 26. Port City Press, Baltimore
Sakakibara Y, Tambara K, Sakaguchi G, Lu F, Yamamoto M, Nishimura K, Tabata Y, Komeda M (2003) Toward surgical angiogenesis using slow-released basic fibroblast growth factor. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 24(1):105–111
Rask F, Dallabrida SM, Ismail NS, Amoozgar Z, Yeo Y, Rupnick MA, Radisic M (2010) Photocrosslinkable chitosan modified with angiopoietin-1 peptide, QHREDGS, promotes survival of neonatal rat heart cells. J Biomed Mater Res A 95(1):105–117
Lin X, Fujita M, Kanemitsu N, Kimura Y, Tambara K, Premaratne GU, Nagasawa A, Ikeda T, Tabata Y, Komeda M (2007) Sustained-release erythropoietin ameliorates cardiac function in infarcted rat-heart without inducing polycythemia. Circ J 71(1):132–137
Kobayashi H, Minatoguchi S, Yasuda S, Bao N, Kawamura I, Iwasa M, Yamaki T, Sumi S, Misao Y, Ushikoshi H, Nishigaki K, Takemura G, Fujiwara T, Tabata Y, Fujiwara H (2008) Post-infarct treatment with an erythropoietin-gelatin hydrogel drug delivery system for cardiac repair. Cardiovasc Res 79(4):611–620
Jeon O, Ryu SH, Chung JH, Kim BS (2005) Control of basic fibroblast growth factor release from fibrin gel with heparin and concentrations of fibrinogen and thrombin. J Control Release 105(3):249–259
Yoon SJ, Fang YH, Lim CH, Kim BS, Son HS, Park Y, Sun K (2009) Regeneration of ischemic heart using hyaluronic acid-based injectable hydrogel. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 91(1):163–171
Ifkovits JL, Tous E, Minakawa M, Morita M, Robb JD, Koomalsingh KJ, Gorman JH III, Gorman RC, Burdick JA (2010) Injectable hydrogel properties influence infarct expansion and extent of postinfarction left ventricular remodeling in an ovine model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(25):11507–11512
Ishihara M, Obara K, Nakamura S, Fujita M, Masuoka K, Kanatani Y, Takase B, Hattori H, Morimoto Y, Ishihara M, Maehara T, Kikuchi M (2006) Chitosan hydrogel as a drug delivery carrier to control angiogenesis. J Artif Organs 9(1):8–16
Sun G, Shen YI, Kusuma S, Fox-Talbot K, JS C, Gerecht S (2011) Functional neovascularization of biodegradable dextran hydrogels with multiple angiogenic growth factors. Biomaterials 32(1):95–106
Dogan AK, Gümüşderelioglu M, Aksöz E (2005) Controlled release of EGF and bFGF from dextran hydrogels in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 74(1):504–510
Norton LW, Tegnella E, Toporekb SS, Reichert WM (2005) In vitro characterization of vascular endothelial growth factor and dexamethasone releasing hydrogels for implantable probe coatings. Biomaterials 26:3285–3297
Yoon JJ, Chung HJ, Park TG (2007) Photo-crosslinkable and biodegradable Pluronic/heparin hydrogels for local and sustained delivery of angiogenic growth factor. J Biomed Mater Res A 83(3):597–605
Sharon JL, Puleo DA (2008) Immobilization of glycoproteins, such as VEGF, on biodegradable substrates. Acta Biomater 4(4):1016–1023
Davies N, Dobner S, Bezuidenhout D, Schmidt C, Beck M, Zisch AH, Zilla P (2008) The dosage dependence of VEGF stimulation on scaffold neovascularization. Biomaterials 29(26):3531–3538
Murphy WL, Peters MC, Kohn DH, Mooney DJ (2000) Sustained release of vascular endothelial growth factor from mineralized poly(lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 21(24):2521–2527
Richardson TP, Peters MC, Ennett AB, Mooney DJ (2001) Polymeric system for dual growth factor delivery. Nat Biotechnol 19(11):1029–1034
Shea LD, Smiley E, Bonadio J, Mooney DJ (1999) DNA delivery from polymer matrices for tissue engineering. Nat Biotechnol 17:551–554
Mooney DJ, Baldwin DF, Suh NP, Vacanti JP, Langer R (1996) Novel approach to fabricate porous sponges of poly(d, l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) without the use of organic solvents. Biomaterials 17:1417–1422
Payne RG, McGonigle JS, Yaszemski MJ, Yasko AW, Mikos AG (2002) Development of an injectable, in situ crosslinkable, degradable polymeric carrier for osteogenic cell populations. Part 3. Proliferation and differentiation of encapsulated marrow stromal osteoblasts cultured on crosslinking poly(propylene fumarate). Biomaterials 23:4381–4387
Briganti E, Spiller D, Mirtelli C, Kull S, Counoupas C, Losi P, Senesi S, Di Stefano R, Soldani G (2010) A composite fibrin-based scaffold for controlled delivery of bioactive pro-angiogenetic growth factors. J Control Release 142(1):14–21
Peirce SM, Price RJ, Skalak TC (2004) Spatial and temporal control of angiogenesis and arterialization using focal applications of VEGF164 and Ang-1*. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H918–H925
Cohen-Sela E, Chorny M, Koroukhov N, Danenberg HD, Golomb G (2009) A new double emulsion solvent diffusion technique for encapsulating hydrophilic molecules in PLGA nanoparticles. J Control Release 133(2):90–95
Kumar PS, Ramakrishna S, Saini TR, Diwan PV (2006) Influence of microencapsulation method and peptide loading on formulation of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) insulin nanoparticles. Pharmazie 61(7):613–617
Bilati U, Allemann E, Doelker E (2005) Strategic approaches for overcoming peptide and protein instability within biodegradable nano- and microparticles. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 59(3):375–388
Vila A, Sanchez A, Tobio M, Calvo P, Alonso MJ (2002) Design of biodegradable particles for protein delivery. J Control Release 78(1–3):15–24
Garbayo E, Ansorena E, Lanciego JL, Aymerich MS, Blanco-Prieto MJ (2008) Sustained release of bioactive glycosylated glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor from biodegradable polymeric microspheres. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 69:844–851
Lee J, Bhang SH, Park H, Kim BS, Lee KY (2010) Active blood vessel formation in the ischemic hindlimb mouse model using a microsphere/hydrogel combination system. Pharm Res 27(5):767–774
Sun Q, Silva E, Wang A, Fritton JC, Mooney DJ, Schaffler MB, Grossman PM, Rajagopalan S (2010) Sustained release of multiple growth factors from injectable polymeric system as a novel therapeutic approach towards angiogenesis. Pharm Res 27(2):264–271
Golub JS, Kim YT, Duvall CL, Bellamkonda RV, Gupta D, Lin AS, Weiss D, Taylor WR, Guldberg RE (2010) Sustained VEGF delivery via PLGA nanoparticles promotes vascular growth. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298:H1959–H1965
Brar BK, Stephanou A, Wagstaff MJ, Coffin RS, Marber MS, Engelmann G, Latchman DS (1999) Heat shock proteins delivered with a virus vector can protect cardiac cells against apoptosis as well as against thermal or hypoxic stress. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31(1):135–146
Lee J, Tan CY, Lee SK, Kim YH, Lee KY (2009) Controlled delivery of heat shock protein using an injectable microsphere/hydrogel combination system for the treatment of myocardial infarction. J Control Release 137(3):196–202
Zhu XH, Wang CH, Tong YW (2009) In vitro characterization of hepatocyte growth factor release from PHBV/PLGA microsphere scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res A 89(2):411–423
Bittner B, Morlock M, Koll H, Winter G, Kissel T (1998) Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres: influence of the encapsulation technique and polymer purity on microsphere characteristics. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 45(3):295–305
Li SH, Cai SX, Liu B, Ma KW, Wang ZP, Li XK (2006) In vitro characteristics of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres incorporating gelatin particles loading basic fibroblast growth factor. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27(6):754–759
Amsden BG, Timbart L, Marecak D, Chapanian R, Tse MY, Pang SC (2010) VEGF-induced angiogenesis following localized delivery via injectable, low viscosity poly(trimethylene carbonate). J Control Release 145(2):109–115
d’Angelo I, Garcia-Fuentes M, Parajo Y, Welle A, Vantus T, Horvath A, Bokonyi G, Keri G, Alonso MJ (2010) Nanoparticles based on PLGA: poloxamer blends for the delivery of proangiogenic growth factors. Mol Pharm 7(5):1724–1733
Tang DW, Yu SH, Ho YC, Mi FL, Kuo PL, Sung HW (2010) Heparinized chitosan/poly(gamma-glutamic acid) nanoparticles for multi-functional delivery of fibroblast growth factor and heparin. Biomaterials 31(35):9320–9332
Parajó Y, D’Angelo I, Welle A, Garcia-Fuentes M, Alonso MJ (2010) Hyaluronic acid/Chitosan nanoparticles as delivery vehicles for VEGF and PDGF-BB. Drug Deliv 17(8):596–604
Lee J, Bhang SH, Park H, Kim BS, Lee KY (2010) Active blood vessel formation in the ischemic hindlimb mouse model using a microsphere/hydrogel combination system. Pharm Res 27(5):767–774
Sun Q, Silva EA, Wang A, Fritton JC, Mooney DJ, Schaffler MB, Grossman PM, Rajagopalan S (2010) Sustained release of multiple growth factors from injectable polymeric system as a novel therapeutic approach towards angiogenesis. Pharm Res 27(2):264–271
Sheridan MH, Shea LD, Peters MC, Mooney DJ (2000) Bioabsorbable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering capable of sustained growth factor delivery. J Control Release 64:91–102
Saif J, Schwarz TM, Chau DY, Henstock J, Sami P, Leicht SF, Hermann PC, Alcala S, Mulero F, Shakesheff KM, Heeschen C, Aicher A (2010) Combination of injectable multiple growth factor-releasing scaffolds and cell therapy as an advanced modality to enhance tissue neovascularization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30(10):1897–1904
Chung YI, Kim SK, Lee YK, Park SJ, Cho KO, Yuk SH, Tae G, Kim YH (2010) Efficient revascularization by VEGF administration via heparin-functionalized nanoparticle-fibrin complex. J Control Release 143:282–289
Tan ML, Choong PF, Dass CR (2010) Recent developments in liposomes, microparticles and nanoparticles for protein and peptide drug delivery. Peptides 31(1):184–193
Xie Y, Ye L, Zhang X, Cui W, Lou J, Nagai T, Hou X (2005) Transport of nerve growth factor encapsulated into liposomes across the blood-brain barrier: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Control Release 105(1–2):106–119
Verma DD, Levchenko TS, Bernstein EA, Torchilin VP (2005) ATP-loaded liposomes effectively protect mechanical functions of the myocardium from global ischemia in an isolated rat heart model. J Control Release 108(2–3):460–471
Palmer TN, Caride VJ, Caldecourt MA, Twickler J, Abdullah V (1984) The mechanism of liposome accumulation in infarction. Biochim Biophys Acta 797(3):363–368
Lukyanov AN, Hartner WC, Torchilin VP (2004) Increased accumulation of PEG-PE micelles in the area of experimental myocardial infarction in rabbits. J Control Release 94(1):187–193
Oh KS, Han SK, Lee HS, Koo HM, Kim RS, Lee KE, Han SS, Cho SH, Yuk SH (2006) Core/Shell nanoparticles with lecithin lipid cores for protein delivery. Biomacromolecules 7(8):2362–2367
Firestone MA, Wolf AC, Seifert S (2003) Small-angle X-ray scattering study of the interaction of poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(propylene oxide)-b-poly(ethylene oxide) triblock copolymers with lipid bilayers. Biomacromolecules 4(6):1539–1549
Nishiyama N, Kataoka K (2006) Current state, achievements, and future prospects of polymeric micelles as nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. Pharmacol Ther 112:630–648
Lee JS, Go DH, Bae JW, Lee SJ, Park KD (2007) Heparin conjugated polymeric micelle for long-terin delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Control Rel 117:204–209
Torney F, Trewyn BG, Lin VSY, Wang K (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles deliver DNA and chemicals into plants. Nat Nanotechnol 2:295–300
Zhang J, Postovit LM, Wang D, Gardiner RB, Harris R, Abdul MM, Thomas AA (2009) In situ loading of basic fibroblast growth factor within porous silica nanoparticles for a prolonged release. Nanoscale Res Lett 4:1297–1302
Kim J, Cao L, Shvartsman D, Silva EA, Mooney DJ (2011) Targeted delivery of nanoparticles to ischemic muscle for imaging and therapeutic angiogenesis. Nano Lett 11(2):694–700
Tengood JE, Kovach KM, Vescovi PE, Russell AJ, Little SR (2010) Sequential delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor and sphingosine 1-phosphate for angiogenesis. Biomaterials 31(30):7805–7812
Laham RJ, Sellke FW, Edelman ER, Pearlman JD, Ware JA, Brown DL, Gold JP, Simons M (1999) Local perivascular delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor in patients undergoing coronary bypass surgery: results of a phase I randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Circulation 100(18):1865–1871
Mirotsou M, Jayawardena TM, Schmeckpeper J, Gnecchi M, Dzau VJ (2011) Paracrine mechanisms of stem cell reparative and regenerative actions in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 50(2):280–289
Sieveking DP, Ng MK (2009) Cell therapies for therapeutic angiogenesis: back to the bench. Vasc Med 14(2):153–166
Wykrzykowska JJ, Henry TD, Lesser JR, Schwartz RS (2009) Imaging myocardial angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cardiol 6(10):648–658
Fuster V, Sanz J, Viles-Gonzalez JF, Rajagopalan S (2006) The utility of magnetic resonance imaging in cardiac tissue regeneration trials. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 3(Suppl 1):S2–S7
Chen FM, Zhang M, Wu ZF (2010) Toward delivery of multiple growth factors in tissue engineering. Biomaterials 31(24):6279–6308
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII PI050168, PI10/01621, CP09/00333 and ISCIII-RETIC RD06/0014), Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (PLE2009-0116 and PSE SINBAD, PSS 0100000-2008-1), Gobierno de Navarra (Departamento de Educación), Comunidad de Trabajo de los Pirineos (CTP), European Union Framework Project VII (INELPY), Agencia Española de Cooperación Internacional para el Desarrollo (AECID), Caja de Ahorros de Navarra (Programa Tu Eliges: Tu Decides) and the “UTE project CIMA”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Formiga, F.R., Tamayo, E., Simón-Yarza, T. et al. Angiogenic therapy for cardiac repair based on protein delivery systems. Heart Fail Rev 17, 449–473 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-011-9285-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-011-9285-8