Abstract
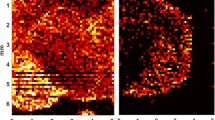
Heroin is an illicit opioid drug which is commonly abused and leads to dependence and addiction. Heroin is considered a pro-drug and is rapidly converted to its major active metabolite 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM) which mediates euphoria and reward through the stimulation of opioid receptors in the brain. The aim of this study was to investigate the distribution and localization of 6-MAM in the healthy Sprague Dawley rat brain following intraperitoneal (i.p) administration of heroin (10 mg/kg), using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging (MALDI-MSI), in combination with quantification via liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). These findings revealed that 6-MAM is present both in plasma and brain tissue with a Tmax of 5 min (2.8 µg/mL) and 15 min (1.1 µg/mL), respectively. MSI analysis of the brain showed high intensities of 6-MAM in the thalamus-hypothalamus and mesocorticolimbic system including areas of the cortex, caudate putamen, and ventral pallidum regions. This finding correlates with the distribution of opioid receptors in the brain, according to literature. In addition, we report a time-dependent distribution in the levels of 6-MAM, from 1 min with the highest intensity of the drug observed at 15 min, with sparse distribution at 45 min before decreasing at 60 min. This is the first study to use MSI as a brain imaging technique to detect a morphine’s distribution over time in the brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen JM, Ripel Å, Boix F, Normann PT, Mørland J (2009) Increased locomotor activity induced by heroin in mice: pharmacokinetic demonstration of heroin acting as a prodrug for the mediator 6-monoacetylmorphine in vivo. J Pharm Exp Ther 331:153–161
Atweh SF, Kuhar MJ (1977) Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res 134:393–405
Baijnath S et al (2015) Evidence for the presence of clofazimine and its distribution in the healthy mouse brain. J Mol Histol 46:439–442
Baijnath S et al (2016a) Neuroprotective potential of Linezolid: a quantitative and distribution study via mass spectrometry. J Mol Histol 47:429–435
Baijnath S, Shobo A, Bester LA, Singh SD, Kruger G, Naicker T, Govender T (2016b) Small molecule distribution in rat lung: a comparison of various cryoprotectants as inflation media and their applicability to MSI. J Mol Histol 47:213–219
Berthoud H-R (2007) Interactions between the “cognitive” and “metabolic” brain in the control of food intake. Physiol Behav 91:486–498
Boix F, Andersen JM, Mørland J (2013) Pharmacokinetic modeling of subcutaneous heroin and its metabolites in blood and brain of mice. Addict Biol 18:1–7
Djurendic-Brenesel M, Pilija V, Mimica-Dukic N, Budakov B, Cvjeticanin S (2012) Distribution of opiate alkaloids in brain tissue of experimental animals. Interdiscip Toxicol 5:173–178
E.M.A (2009) European Medicines Agency, C.H.M.P. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use
Firestone LL, Gyulai F, Mintun M, Adler LJ, Urso K, Winter PM (1996) Human brain activity response to fentanyl imaged by positron emission tomography. Anesth Analg 82:1247–1251
Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Kassed CA, Chang L (2007) Imaging the addicted human brain. Sci Pract Perspect 3:4
Geibprasert S, Gallucci M, Krings T (2010) Addictive illegal drugs: structural neuroimaging. Am J Neuroradiol 31:803–808
Gottås A, Øiestad E, Boix F, Vindenes V, Ripel Å, Thaulow C, Mørland J (2013) Levels of heroin and its metabolites in blood and brain extracellular fluid after iv heroin administration to freely moving rats. Br J Pharmacol 170:546–556
Groeneveld G, de Puit M, Bleay S, Bradshaw R, Francese S (2015) Detection and mapping of illicit drugs and their metabolites in fingermarks by MALDI MS and compatibility with forensic techniques. Sci Rep 5:11716
Hammers A, Lingford-Hughes A (2007) Opioid imaging. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2:67–89
Inturrisi CE, Schultz M, Shin S, Umans J, Angel L, Simon E (1983) Evidence from opiate binding studies that heroin acts through its metabolites. Life Sci 33:773–776
Jones JM, Raleigh MD, Pentel PR, Harmon TM, Keyler DE, Remmel RP, Birnbaum AK (2013) Stability of heroin, 6-monoacetylmorphine, and morphine in biological samples and validation of an LC–MS assay for delayed analyses of pharmacokinetic samples in rats. J Pharm Biomed Anal 74:291–297
Kuhar MJ, Pert CB, Snyder SH (1973) Regional distribution of opiate receptor binding in monkey and human brain. Nature 245:447–450
Le Merrer J, Becker JA, Befort K, Kieffer BL (2009) Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol Rev 89:1379–1412
Lever JR (2007) PET and SPECT imaging of the opioid system: receptors, radioligands and avenues for drug discovery and development. Curr Pharm Des 13:33–49
Magangane P, Sookhayi R, Govender D, Naidoo R (2016) Determining protein biomarkers for DLBCL using FFPE tissues from HIV negative and HIV positive patients. J Mol Histol 47:565–577
Munyeza CF et al (2016) Rapid and widespread distribution of doxycycline in rat brain: a mass spectrometric imaging study. Xenobiotica 46:385–392
NIDA (2016) Heroin. http://www.drugabuse.gov/drugs-abuse/heroin. Accessed 03 Aug 2016
Oldendorf W, Hyman S, Braun L, Oldendorf S (1972) Blood-brain barrier: penetration of morphine, codeine, heroin, and methadone after carotid injection. Science 178:984–986
Paxinos G, Watson C (1994) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Raynor K, Kong H, Chen Y, Yasuda K, Yu L, Bell GI, Reisine T (1994) Pharmacological characterization of the cloned kappa-, delta-, and mu-opioid receptors. Mol Pharmacol 45:330–334
Roda G et al. (2016) Determination of 6-monoacetyl-morphine (6-MAM) in brain samples from heroin fatalities. Pharm Anal Acta 6:451. doi:10.4172/2153-2435.1000451
Rook EJ, Huitema AD, Ree JMv, Beijnen JH (2006) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacokinetic variability of heroin and its metabolites: review of the literature. Curr Clin Pharmacol 1:109–118
Salmon AY, Goren Z, Avissar Y, Soreq H (1999) Human erythrocyte but not brain acetylcholinesterase hydrolyses heroin to morphine. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 26:596–600
Schlaepfer TE et al (1998) Site of opioid action in the human brain: mu and kappa agonists’ subjective and cerebral blood flow effects. Am J Psychiatry 155:470–473
Selley DE, Cao C-C, Sexton T, Schwegel JA, Martin TJ, Childers SR (2001) μ Opioid receptor-mediated G-protein activation by heroin metabolites: evidence for greater efficacy of 6-monoacetylmorphine compared with morphine. Biochem Pharmacol 62:447–455
Shobo A et al (2015a) MALDI MSI and LCMS/MS: towards preclinical determination of the neurotoxic potential of fluoroquinolones. Drug Test Anal 8:832–838
Shobo A et al (2015b) Visualization of time-dependent distribution of rifampicin in rat brain using MALDI MSI and quantitative LCMS/MS. Assay Drug Dev Technol 13:277–284
Shobo A et al (2015c) Tissue distribution of pretomanid in rat brain via mass spectrometry imaging. Xenobiotica 46:247–252
Sim LJ, Childers SR (1997) Anatomical distribution of mu, delta, and kappa opioid-and nociceptin/orphanin FQ-stimulated [35S] Guanylyl-5′-O-(γ-Thio)-triphosphate binding in guinea pig brain. J Comp Neurol 386:562–572
Trescot AM, Datta S, Lee M, Hansen H (2008) Opioid pharmacology. Pain Physician 11:S133–S153
Vorm O, Roepstorff P, Mann M (1994) Improved resolution and very high sensitivity in MALDI TOF of matrix surfaces made by fast evaporation. Anal Chem 66:3281–3287
Wagner CC, Langer O (2011) Approaches using molecular imaging technology—use of PET in clinical microdose studies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:539–546
WHO (2013) Opioid overdose: preventing and reducing opioid overdose mortality. United Nations Office, Austria
Xi ZX, Wu G, Stein EA, Li SJ (2004) Opiate tolerance by heroin self-administration: an fMRI study in rat. Magn Reson Med 52:108–114
Zhang D, Surapaneni S (2012) ADME-enabling technologies in drug design and development. Wiley, Hoboken
Zubieta J-K, Dannals RF, Frost JJ (1999) Gender and age influences on human brain mu-opioid receptor binding measured by PET. Am J Psychiatry 156:842–848
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Research Foundation, SA; Aspenpharmacare, SA; and the University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, SA for having funded this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teklezgi, B.G., Pamreddy, A., Baijnath, S. et al. Post heroin dose tissue distribution of 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM) with MALDI imaging. J Mol Hist 48, 285–292 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-017-9726-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-017-9726-3