Abstract
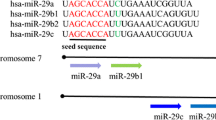
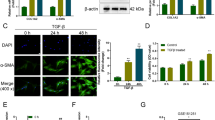
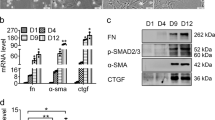
Recent studies have reported that NF-κB mediated down-regulation of miRNA-29 and lower expression of miRNA-29 promoted the deposition of collagens in fibrotic liver. Our previous research demonstrated that the increased Hedgehog (Hh) signaling, a key regulator for hepatic fibrogenesis, induced the severe hepatic fibrosis in the livers with impaired NF-κB signaling. These findings led us to investigate the effect of Hh and miRNA-29 on the hepatic fibrosis under dysregulated NF-κB signaling. In this study, we used IKKβF/F and IKKβ-deficient IKKβΔHEP mouse model with a defective NF-κB signaling pathway, and assessed the expression of the miRNA-29 family (miRNA-29a, miRNA-29b, and miRNA-29c), Hh, and proliferation of MF-HSCs in liver from IKKβF/F mice and IKKβΔHEP mice both before and after MCDE treatment. The activation of NF-κB was significantly increased in MCDE diet-fed IKKβF/F mice compared to IKKβΔHEP mice. Expression of miRNA-29 family was greater in MCDE diet-fed IKKβΔHEP mice than IKKβF/F mice, demonstrating that the impaired NF-κB pathway was unable to suppress the expression of miRNA-29s after injury. However, expression of the Hh signaling pathway was greatly enhanced, and activation of Hh promoted the accumulation of MF-HSCs with impaired NF-κB, eventually increasing fibrogenesis in the damaged liver of IKKβΔHEP mice. Therefore, these results demonstrated that Hh signaling regulates the proliferation of MF-HSCs irrespective of the action of miRNA-29, eventually contributing hepatic fibrosis, when the NF-κB pathway is disrupted.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Alb:
-
Albumin
- α-SMA:
-
Alpha smooth muscle actin
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- Gli:
-
Glioblastoma
- Hh:
-
Hedgehog
- HIP:
-
Hedgehog-interacting protein
- HSC:
-
Hepatic stellate cell
- IκB:
-
Inhibitor of kappa B
- IKK:
-
IκB kinase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MCDE:
-
Methionine/choline-deficient diet supplemented with 0.15 % ethionine
- MF-HSC:
-
Myofibroblastic hepatic stellate cell
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- Q-HSC:
-
Quiescent hepatic stellate cell
References
Bär KJ, Schurigt U, Scholze A, von Banchet GS, Stopfel N, Bräuer R, Halbhuber KJ, Schaible HG (2004) The expression and localization of somatostatin receptors in dorsal root ganglion neurons of normal and monoarthritic rats. Neuroscience 127(1):197–206
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115(2):209–218
Choi SS, Diehl AM (2009) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions in the liver. Hepatology 50(6):2007–2013
Choi SS, Omenetti A, Witek RP, Moylan CA, Syn WK, Jung Y, Yang L, Sudan DL, Sicklick JK, Michelotti GA (2009) Hedgehog pathway activation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions during myofibroblastic transformation of rat hepatic cells in culture and cirrhosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297(6):G1093–G1106
Choi S, Park S, Kim S, Lim C, Kim J, Cha DR, Oh J (2012) Recombinant fusion protein of albumin-retinol binding protein inactivates stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 418(1):191–197
De Minicis S, Seki E, Uchinami H, Kluwe J, Zhang Y, Brenner DA, Schwabe RF (2007) Gene expression profiles during hepatic stellate cell activation in culture and in vivo. Gastroenterology 132(5):1937–1946
Elsharkawy A, Oakley F, Mann D (2005) The role and regulation of hepatic stellate cell apoptosis in reversal of liver fibrosis. Apoptosis 10(5):927–939
Gilmore TD (2006) Introduction to NF-κB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 25(51):6680–6684
Grimm S, Bauer M, Baeuerle PA, Schulze-Osthoff K (1996) Bcl-2 down-regulates the activity of transcription factor NF-kappaB induced upon apoptosis. J Cell Biol 134(1):13–23
Guo CJ, Pan Q, Cheng T, Jiang B, Chen GY, Li DG (2009) Changes in microRNAs associated with hepatic stellate cell activation status identify signaling pathways. FEBS J 276(18):5163–5176
Hooper JE, Scott MP (2005) Communicating with hedgehogs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(4):306–317
Jung Y, Witek RP, Syn WK, Choi SS, Omenetti A, Premont R, Guy CD, Diehl AM (2010) Signals from dying hepatocytes trigger growth of liver progenitors. Gut 59(5):655–665
Kim N, Yoo W, Lee J, Kim H, Lee H, Kim Y-S, Kim D-U, Oh J (2009) Formation of vitamin A lipid droplets in pancreatic stellate cells requires albumin. Gut 58(10):1382–1390
Kwiecinski M, Elfimova N, Noetel A, Schievenbusch S, Strack I, Toex U, Drebber U, Steffen H, Dienes H, Odenthal M (2010) Mir-29, inhibiting synthesis of profibrogenic mediators, is released into the blood stream after chronic hepatitis C infection, indicating progression of fibrosis. Hepatology 52(4 Suppl):446A–447A
Lewis BP, Shih I, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115(7):787–798
Luna C, Li G, Qiu J, Epstein DL, Gonzalez P (2009) Role of miR-29b on the regulation of the extracellular matrix in human trabecular meshwork cells under chronic oxidative stress. Mol Vis 15:2488
Maeda S, Kamata H, Luo JL, Leffert H, Karin M (2005) IKKβ couples hepatocyte death to cytokine-driven compensatory proliferation that promotes chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell 121(7):977–990
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Poulaki V, Schlossman R, Akiyama M, Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Treon SP, Munshi NC, Richardson PG (2002) Activation of NF-kB and upregulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins via the IGF-1/Akt signaling in human multiple myeloma cells: therapeutic implications. Oncogene 21(37):5673–5683
Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (2007) Mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis. Oncogene 26(42):6133–6140
Mott JL, Kurita S, Cazanave SC, Bronk SF, Werneburg NW, Fernandez-Zapico ME (2010) Transcriptional suppression of mir-29b-1/mir-29a promoter by c-Myc, hedgehog, and NF-kappaB. J Cell Biochem 110(5):1155–1164
Muriel P (2009) NF-κB in liver diseases: a target for drug therapy. J Appl Toxicol 29(2):91–100
Ogawa T, Iizuka M, Sekiya Y, Yoshizato K, Ikeda K, Kawada N (2010) Suppression of type I collagen production by microRNA-29b in cultured human stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(1):316–321
Olsen AL, Bloomer SA, Chan EP, Gaça MDA, Georges PC, Sackey B, Uemura M, Janmey PA, Wells RG (2011) Hepatic stellate cells require a stiff environment for myofibroblastic differentiation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301(1):G110–G118
Omenetti A, Choi S, Michelotti G, Diehl AM (2011) Hedgehog signaling in the liver. J Hepatol 54(2):366–373
Perkins ND (2007) Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-κB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(1):49–62
Rangwala F, Guy CD, Lu J, Suzuki A, Burchette JL, Abdelmalek MF, Chen W, Diehl AM (2011) Increased production of sonic hedgehog by ballooned hepatocytes. J Pathol 224(3):401–410
Reeves HL, Friedman SL (2002) Activation of hepatic stellate cells-a key issue in liver fibrosis. Front Biosci 7(4):808–826
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, Vucur M, Zimmermann H, Schmidt S, Janssen J, Koppe C, Knolle P, Castoldi M (2011) Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 53(1):209–218
Ryan KM, Ernst MK, Rice NR, Vousden KH (2000) Role of NF-kB in p53-mediated programmed cell death. Nature 404(6780):892–896
Santanam U, Zanesi N, Efanov A, Costinean S, Palamarchuk A, Hagan JP, Volinia S, Alder H, Rassenti L, Kipps T (2010) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia modeled in mouse by targeted miR-29 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(27):12210
Seki E, De Minicis S, Österreicher CH, Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA, Schwabe RF (2007) TLR4 enhances TGF-β signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med 13(11):1324–1332
Sicklick JK, Li YX, Choi SS, Qi Y, Chen W, Bustamante M, Huang J, Zdanowicz M, Camp T, Torbenson MS (2005) Role for hedgehog signaling in hepatic stellate cell activation and viability. Lab Invest 85(11):1368–1380
Stehlik C, de Martin R, Binder BR, Lipp J (1998) Cytokine induced expression of porcine inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family member is regulated by NF-B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 243(3):827–832
Ura S, Honda M, Yamashita T, Ueda T, Takatori H, Nishino R, Sunakozaka H, Sakai Y, Horimoto K, Kaneko S (2009) Differential microRNA expression between hepatitis B and hepatitis C leading disease progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 49(4):1098–1112
Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F, Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP, Odenthal M (2008) MicroRNA gene expression profile of hepatitis C virus–associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47(4):1223–1232
Wang JY, Guo JS, Li H, Liu SL, Zern MA (1998) Inhibitory effect of glycyrrhizin on NF-κB binding activity in CC14-plus ethanol-induced liver cirrhosis in rats. Liver Int 18(3):180–185
Xiong Y, Fang JH, Yun JP, Yang J, Zhang Y, Jia WH, Zhuang SM (2010) Effects of MicroRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 51(3):836–845
Yang L, Wang Y, Mao H, Fleig S, Omenetti A, Brown KD, Sicklick JK, Li YX, Diehl AM (2008) Sonic hedgehog is an autocrine viability factor for myofibroblastic hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 48(1):98–106
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Bio-Scientific Research Grant funded by the Pusan National University (PNU, Bio-Scientific Research Grant) (PNU-2010-101-250).
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyun, J., Choi, S.S., Diehl, A.M. et al. Potential role of Hedgehog signaling and microRNA-29 in liver fibrosis of IKKβ-deficient mouse. J Mol Hist 45, 103–112 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9532-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9532-5