Abstract
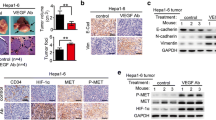
Simultaneous silencing of multiple up-regulated genes is an attractive and viable strategy to treat many incurable diseases including cancer. Herein we used dual gene targeted siRNA (DGT siRNA) conjugate composed of NET-1 and VEGF siRNA sequences in the same backbone could inhibit growth and angiogenesis HCC. DGT siRNA showed a further down regulation on VEGF mRNA and protein levels compared with NET-1 siRNA or VEGF siRNA, but not on NET-1 expression. It also exhibited greater suppression on proliferation and trigger of apoptosis in HepG2 cells than NET-1 siRNA or VEGF siRNA; this could be explained by the significant down regulation of cyclin D1 and Bcl-2. A lower level of ANG2 mRNA and protein was detected in HUVEC cultured with supernatant of HepG2 cells treated with DGT siRNA than that of VEGF siRNA or NET-1 siRNA, resulting in much more inhibited angiogenesis of HUVEC. Tumor growth was inhibited and microvessel density dropped in the xenograft tumor models compared to the untreated controls. NET-1 and VEGF silencing play a key role in inhibiting hepatocellular cell proliferation, promoting apoptosis, and reducing angiogenesis. Simultaneous silencing of NET-1 and VEGF using DGT siRNA construct may provide an advantageous alternative in development of therapeutics for Hepatocellular carcinoma.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carroll VA, Ashcroft M (2006) Role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha versus HIF-2alpha in the regulation of HIF target genes in response to hypoxia, insulin-like growth factor-I, or loss of von Hippel-Lindau function: implications for targeting the HIF pathway. Cancer Res 66:6264–6270
Chen L, Wang Z, Zhan X, Li DC, Zhu YY, Zhu J (2007) Association of NET-1 gene expression with human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Surg Pathol 15:346–353
Chen L, Li X, Wang GL, Wang Y, Zhu YY, Zhu J (2008) Clinicopathological significance of overexpression of TSPAN1, Ki67 and CD34 in gastric carcinoma. Tumori 94:531–538
Chen L, Zhu YY, Zhang XJ, Wang GL, Li XY, He S, Zhang JB, Zhu JW (2009) TSPAN1 protein expression: a significant prognostic indicator for patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 15:2270–2276
Chen L, Yuan D, Wang GL, Wang Y, Wu YY, Zhu J (2010a) Clinicopathological significance of expression of Tspan-1, Jab1 and p27 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Korean Med Sci 25:1438–1442
Chen L, Yuan D, Zhao R, Li H, Zhu J (2010b) Suppression of TSPAN1 by RNA interference inhibits proliferation and invasion of colon cancer cells in vitro. Tumori 96:744–750
Chen L, Zhu Y, Li H, Wang GL, Wu YY, Lu YX, Qin J, Tuo J, Wang JL, Zhu J (2010c) Knockdown of TSPAN1 by RNA silencing and antisense technique inhibits proliferation and infiltration of human skin squamous carcinoma cells. Tumori 96:289–295
Cheng K, Mahato RI (2007) Gene modulation for treating liver fibrosis. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 24:93–146
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116:205–219
Deane NG, Parker MA, Aramandla R, Diehl L, Lee WJ, Washington MK, Nanney LB, Shyr Y, Beauchamp RD (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma results from chronic cyclin D1 overexpression in transgenic mice. Cancer Res 61:5389–5395
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:1899–1911
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Hashizume H, Falcon B, Kuroda T, Baluk P, Coxon A, Yu D, Bready J, Oliner J, McDonald D (2010) Complementary actions of inhibitors of angiopoietin-2 and VEGF on tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Res 70:2213–2223
Hongo T, Kajikawa M, Ishida S, Ozawa S, Ohno Y, Sawada J, Ishikawa Y, Honda H (2006) Gene expression property of high-density three-dimensional tissue of HepG2 cells formed in radial-flow bioreactor. J Biosci Bioeng 101:243–250
Koblizek TI, Weiss C, Yancopoulos GD, Deutsch U, Risau W (1998) Angiopoietin-1 induces sprouting angiogenesis in vitro. Curr Biol 8:529–532
Lee SH, Mok H, Jo S, Hong CA, Park TG (2011) Dual gene targeted multimeric siRNA for combinatorial gene silencing. Biomaterials 32:2359–2368
Liu Y, Poon R, Li Q, Kok T, Lau C, Fan S (2005) Both antiangiogenesis- and angiogenesis-independent effects are responsible for hepatocellular carcinoma growth arrest by tyrosine kinase inhibitor PTK787/ZK222584. Cancer Res 65:3691–3699
Maecker HT, Todd SC, Levy S (1997) The tetraspanin superfamily: molecular facilitators. FASEB J 11:428–442
Mahato RI, Cheng K, Guntaka RV (2005) Modulation of gene expression by antisense and antigene oligodeoxynucleotides and small interfering RNA. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2:3–28
Meyer M, Clauss M, Lepple-Wienhues A, Waltenberger J, Augustin HG, Ziche M, Lanz C, Büttner M, Rziha HJ, Dehio C (1999) A novel vascular endothelial growth factor encoded by Orf virus, VEGF-E, mediates angiogenesis via signalling through VEGFR-2 (KDR) but not VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J 18:363–374
Ng IO, Poon RT, Lee JM, Fan ST, Ng M, Tso WK (2001) Microvessel density, vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1/KDR in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 116:838–845
Oda Y, Yamamoto H, Tamiya S, Matsuda S, Tanaka K, Yokoyama R, Iwamoto Y, Tsuneyoshi M (2006) CXCR4 and VEGF expression in the primary site and the metastatic site of human osteosarcoma: analysis within a group of patients, all of whom developed lung metastasis. Mod Pathol 19:738–745
Oh H, Takagi H, Suzuma K, Otani A, Matsumura M, Honda Y (1999) Hypoxia and vascular endothelial growth factor selectively up-regulate angiopoietin-2 in bovine microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 274:15732–15739
Pang R, Poon RT (2006) Angiogenesis and antiangiogenic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 242:151–167
Qiu MB, Zhang JX, Liu LM, Gong BD, Wu BL, Zhu SS, Wen Y (2004) Inhibitory effects of antisense oligodeoxynucleotide on expression of vascular endothelia growth factor by human hepatocarcinoma cells. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 3:552–557
Raskopf E, Vogt A, Sauerbruch T, Schmitz V (2008) siRNA targeting VEGF inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and tumor angiogenesis in vivo. J Hepatol 49:977–984
Reed JC (1999) Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer. J Clin Oncol 17:2941–2953
Scholz CJ, Kurzeder C, Koretz K, Windisch J, Kreienberg R, Sauer G, Deissler H (2009) Tspan-1 is a tetraspanin preferentially expressed by mucinous and endometrioid subtypes of human ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Lett 275:198–203
Serru V, Dessen P, Boucheix C, Rubinstein E (2000) Sequence and expression of seven new tetraspans. Biochim Biophys Acta 1478:159–163
Sherr CJ (1993) Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell 73:1059–1065
Siegel AB, Cohen EI, Ocean A, Lehrer D, Goldenberg A, Knox JJ, Chen H, Clark-Garvey S, Weinberg A, Mandeli J, Christos P, Mazumdar M, Popa E, Brown RS, Rafii S, Schwartz JD (2008) Phase II trial evaluating the clinical and biologic effects of bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:2992–2998
Thomas MB, Morris JS, Chadha R, Iwasaki M, Kaur H, Lin E, Kaseb A, Glover K, Davila M, Abbruzzese J (2009) Phase II trial of the combination of bevacizumab and erlotinib in patients who have advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27:843–850
Wollscheid V, Kühne-Heid R, Stein I, Jansen L, Köllner S, Schneider A, Dürst M (2002) Identification of a new proliferation-associated protein NET-1/C4.8 characteristic for a subset of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical carcinomas. Int J Cancer 99:771–775
Yauch RL, Hemler ME (2000) Specific interactions among transmembrane 4 superfamily (TM4SF) proteins and phosphoinositide 4-kinase. Biochem J 351(Pt 3):629–637
Yoo JY, Kim JH, Kwon YG, Kim EC, Kim NK, Choi HJ, Yun CO (2007) VEGF-specific short hairpin RNA-expressing oncolytic adenovirus elicits potent inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Mol Ther 15:295–302
Zeng H, Sanyal S, Mukhopadhyay D (2001) Tyrosine residues 951 and 1059 of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (KDR) are essential for vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelium migration and proliferation, respectively. J Biol Chem 276:32714–32719
Zhu AX, Blaszkowsky LS, Ryan DP, Clark JW, Muzikansky A, Horgan K, Sheehan S, Hale KE, Enzinger PC, Bhargava P, Stuart K (2006) Phase II study of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin in combination with bevacizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24:1898–1903
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by fundings: from the Advanced Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, Foundation of the Ministry of Health, Jangsu provience, China (No.H201052), the Science Foundation of Nantong City, Jiangsu province, China (No.K2009060), and Foundation of medical school, Nantong university, Jangsu province, China (No.YXY-200908), respectively. We thank Biomics Biotechnologies Co., Ltd. (Nantong, Jiangsu, China) for kindly providing synthesis of siRNAs and shRNAs.
Conflict of interest
All the authors declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Li Chen: Joint first author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, YY., Chen, L., Wang, GL. et al. Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma growth and angiogenesis by dual silencing of NET-1 and VEGF. J Mol Hist 44, 433–445 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9480-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9480-5