Abstract
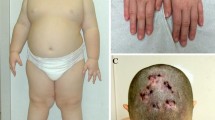
NAD(P) steroid dehydrogenase-like (NSDHL) is an X-linked gene that encodes a 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway. Loss-of-function mutations in NSDHL cause Congenital Hemidysplasia with Ichthyosiform erythroderma and Limb Defects (CHILD) and CK syndromes. CHILD syndrome is a male lethal X-linked dominant disorder characterized by asymmetric skin and limb anomalies in affected females. CK syndrome is an intellectual disability disorder characterized by disproportionate short stature, brain malformations, and dysmorphic features in affected males. To understand better the relationship of the expression of mRNA and protein encoded by human NSDHL to the peripheral malformations of these disorders, we characterized the peripheral expression of the mRNA and protein by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry. We also profiled the mRNA expression of mouse Nsdhl by in situ hybridization. Expression of the mRNA and protein encoded by human NSDHL parallels that of mouse Nsdhl mRNA for most but not all tissues. Furthermore, human NSDHL protein and mouse Nsdhl mRNA were expressed in tissues synthesizing cholesterol and steroids and in all peripheral tissues affected by CHILD or CK syndromes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avgerinou GP, Asvesti AP, Katsambas AD, Nikolaou VA, Christofidou EC, Grzeschik KH, Happle R (2010) CHILD syndrome: the NSDHL gene and its role in CHILD syndrome, a rare hereditary disorder. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 24(6):733–736
Bloch K, Borek E, Rittenberg D (1946) Synthesis of cholesterol in surviving liver. J Biol Chem 162:441–449
Bornholdt D, Konig A, Happle R, Leveleki L, Bittar M, Danarti R, Vahlquist A, Tilgen W, Reinhold U, Poiares Baptista A, Grosshans E, Vabres P, Niiyama S, Sasaoka K, Tanaka T, Meiss AL, Treadwell PA, Lambert D, Camacho F, Grzeschik KH (2005) Mutational spectrum of NSDHL in CHILD syndrome. J Med Genet 42(2):e17
Caldas H, Herman GE (2003) NSDHL, an enzyme involved in cholesterol biosynthesis, traffics through the golgi and accumulates on ER membranes and on the surface of lipid droplets. Hum Mol Genet 12(22):2981–2991
Caldas H, Cunningham D, Wang X, Jiang F, Humphries L, Kelley RI, Herman GE (2005) Placental defects are associated with male lethality in bare patches and striated embryos deficient in the NAD(P)H steroid dehydrogenase-like (NSDHL) enzyme. Mol Genet Metab 84(1):48–60
Chander R, Varghese B, Jabeen M, Garg T, Jain M (2010) CHILD syndrome with thrombocytosis and congenital dislocation of hip: a case report from India. Dermatol Online J 16(8):6
Cunningham D, Spychala K, McLarren KW, Garza LA, Boerkoel CF, Herman GE (2009) Developmental expression pattern of the cholesterogenic enzyme NSDHL and negative selection of NSDHL-deficient cells in the heterozygous Bpa(1H)/+mouse. Mol Genet Metab 98(4):356–366
Danarti R, Grzeschik KH, Radiono S, Konig A, Happle R (2010) Left-sided CHILD syndrome caused by a nonsense mutation in exon 7 of the NSDHL gene. Eur J Dermatol 20(5):634–635
Dietschy JM, Siperstein MD (1965) Cholesterol synthesis by the gastrointestinal tract: localization and mechanisms of control. J Clin Invest 44(8):1311–1327
Dirksen TR (1969) The in vitro incorporation of acetate-14C into the lipids of new born rat calvaria. Arch Biochem Biophys 134(2):603–609
du Souich C, Chou A, Yin J, Oh T, Nelson TN, Hurlburt J, Arbour L, Friedlander R, McGillivray BC, Tyshchenko N, Rump A, Poskitt KJ, Demos MK, Van Allen MI, Boerkoel CF (2009) Characterization of a new X-linked mental retardation syndrome with microcephaly, cortical malformation, and thin habitus. Am J Med Genet A 149A(11):2469–2478
du Souich C, Raymond FL, Grzeschik KH, Konig A, Boerkoel CF (2011) (Updated [February 1, 2011]). NSDHL-related disorders. In: GeneReviews at GeneTests: medical genetics information resource (database online). Copyright, University of Washington, Seattle, 1997–2011. Available at http://www.genetests.org. Accessed 15 Aug 2010
Gawantka V, Pollet N, Delius H, Vingron M, Pfister R, Nitsch R, Blumenstock C, Niehrs C (1998) Gene expression screening in Xenopus identifies molecular pathways, predicts gene function and provides a global view of embryonic patterning. Mech Dev 77(2):95–141
Happle R (2010) The group of epidermal nevus syndromes Part I. Well defined phenotypes. J Am Acad Dermatol 63(1):1–22 quiz 23–24
Happle R, Koch H, Lenz W (1980) The CHILD syndrome. Congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosiform erythroderma and limb defects. Eur J Pediatr 134(1):27–33
Hummel M, Cunningham D, Mullett CJ, Kelley RI, Herman GE (2003) Left-sided CHILD syndrome caused by a nonsense mutation in the NSDHL gene. Am J Med Genet A 122A(3):246–251
Kim CA, Konig A, Bertola DR, Albano LM, Gattas GJ, Bornholdt D, Leveleki L, Happle R, Grzeschik KH (2005) CHILD syndrome caused by a deletion of exons 6–8 of the NSDHL gene. Dermatology 211(2):155–158
Konig A, Happle R, Bornholdt D, Engel H, Grzeschik KH (2000) Mutations in the NSDHL gene, encoding a 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, cause CHILD syndrome. Am J Med Genet 90(4):339–346
Konig A, Happle R, Fink-Puches R, Soyer HP, Bornholdt D, Engel H, Grzeschik KH (2002) A novel missense mutation of NSDHL in an unusual case of CHILD syndrome showing bilateral, almost symmetric involvement. J Am Acad Dermatol 46(4):594–596
Konig A, Skrzypek J, Loffler H, Oeffner F, Grzeschik KH, Happle R (2010) Donor dominance cures CHILD nevus. Dermatology 220(4):340–345
Laubner D, Breitling R, Adamski J (2003) Embryonic expression of cholesterogenic genes is restricted to distinct domains and colocalizes with apoptotic regions in mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 115(1):87–92
Liu XY, Dangel AW, Kelley RI, Zhao W, Denny P, Botcherby M, Cattanach B, Peters J, Hunsicker PR, Mallon AM, Strivens MA, Bate R, Miller W, Rhodes M, Brown SD, Herman GE (1999) The gene mutated in bare patches and striated mice encodes a novel 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Nat Genet 22(2):182–187
Lucas ME, Ma Q, Cunningham D, Peters J, Cattanach B, Bard M, Elmore BK, Herman GE (2003) Identification of two novel mutations in the murine Nsdhl sterol dehydrogenase gene and development of a functional complementation assay in yeast. Mol Genet Metab 80(1–2):227–233
McLarren KW, Severson TM, du Souich C, Stockton DW, Kratz LE, Cunningham D, Hendson G, Morin RD, Wu D, Paul JE, An J, Nelson TN, Chou A, Debarber AE, Merkens LS, Michaud JL, Waters PJ, Yin J, McGillivray B, Demos M, Rouleau GA, Grzeschik KH, Smith R, Tarpey PS, Shears D, Schwartz CE, Gecz J, Stratton MR, Arbour L, Hurlburt J, Van Allen MI, Herman GE, Zhao Y, Moore R, Kelley RI, Jones SJ, Steiner RD, Raymond FL, Marra MA, Boerkoel CF (2010) Hypomorphic temperature-sensitive alleles of NSDHL cause CK syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 87(6):905–914
Porter FD, Herman GE (2011) Malformation syndromes caused by disorders of cholesterol synthesis. J Lipid Res 52(1):6–34
Sakakura Y, Shimano H, Sone H, Takahashi A, Inoue N, Toyoshima H, Suzuki S, Yamada N (2001) Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins induce an entire pathway of cholesterol synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286(1):176–183
Srere PA, Chaikoff IL, Treitman SS, Burstein LS (1950) The extrahepatic synthesis of cholesterol. J Biol Chem 182(2):629–634
Tang TT, McCreadie SR (1974) Q–congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosis. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 10(5):257–261
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Drs. Gail Herman and David Cunningham for critical review of this manuscript. This work was supported in part by a British Columbia Children’s Hospital Foundation Telethon Award (C.D.S.), a Scottish Rite Foundation Award (C.D.S.) and a Child & Family Research Institute Establishment Award (C.F.B.). C.F.B. is a scholar of the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morimoto, M., du Souich, C., Trinh, J. et al. Expression profile of NSDHL in human peripheral tissues. J Mol Hist 43, 95–106 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9375-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9375-x