Abstract
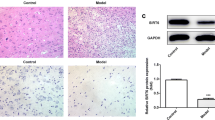
Studies indicated that many tissues could express FSH. New functions of FSH have been recognized beyond reproduction regulation. However, no report has been made about the expression and function of FSH in rat spinal cord. Double-labeled immunofluorescence stain and in situ hybridization were used to study the co-localization of FSH with its receptor and co-localization of FSH with GnRH receptor in rat spinal cord. Spinal cord ischemia injury models were built, TUNEL stain and Fas immunostaining were made to observe the anti-apoptotic effects of FSH to neurons induced by spinal cord ischemia injury. The results found that some neurons and glias of rat spinal cord showed both FSH immunoreactivity and FSH mRNA positive signals; not only FSH and its receptor but also FSH and GnRH receptor co-located in cells of both gray matter and white matter; treatment with certain concentration of FSH before ischemia–reperfusion injury, less TUNEL positive cells and Fas positive cells were found in motor neurons of ventral gray matter in FSH experiment group than that in control group. These suggested that rat spinal cord could express FSH, it is also a target organ of FSH; FSH might exert functions through its receptor by paracrine or autocrine effects; GnRH in spinal cord might regulate FSH positive neurons through GnRH receptor; FSH might inhibit ischemia induced neuron apoptosis by down-regulating Fas expression in spinal cord.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Timimi A, Fox H (1986) Immunohistochemical localization of follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, growth hormone, adrenocorticotrophic hormone and prolactin in the human placenta. Placenta 7:163–172
Baccetti B, Collodel G, Costantino-Ceccarini E, Eshkol A, Gambera L, Moretti E, Strazza M, Piomboni P (1998) Localization of human follicle-stimulating hormone in the testis. FASEB J 12:1045–1054
Coss D, Jacobs SB, Bender CE, Mellon PL (2004) A novel AP-1 site is critical for maximal induction of the follicle-stimulating hormone beta gene by gonadotropin-releasing hormone. J Biol Chem 279:152–162
Cuzzocrea S, Genovese T, Mazzon E, Esposito E, Di Paola R, Muià C, Crisafulli C, Peli A, Bramanti P, Chaudry IH (2008) Effect of 17beta-estradiol on signal transduction pathways and secondary damage in experimental spinal cord trauma. Shock 29:362–371
Dolan S, Evans NP, Richter TA, Nolan AM (2003) Expression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor in sheep spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 346:120–122
Dumont RJ, Okonkwo DO, Verma S, Hurlbert RJ, Boulos PT, Ellegala DB, Dumont AS (2001) Acute spinal cord injury, part I: pathophysiologic mechanisms. Clin Neuropharmacol 24:254–264
Evrard HC (2006) Estrogen synthesis in the spinal dorsal horn: a new central mechanism for the hormonal regulation of pain. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291:291–299
Findlay JK, Drummond AE (1999) Regulation of the FSH Receptor in the ovary. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10:183–188
Fujii S, Sato S, Fukui A, Kimura H, Kasai G, Saito Y (2001) Continuous administration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist during the luteal phase in IVF. Hum Reprod 16:1671–1675
Garde SV, Sheth AR, Joseph R (1993) Occurrence and de novo biosynthesis of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) in benign and malignant conditions of human breast. Cancer Lett 75:1–9
Gromoll J, Pekel E, Nieschlag E (1996) The structure and organization of the human follicle-stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR) gene. Genomics 35:308–311
Jia J, Guan D, Zhu W, Alkayed NJ, Wang MM, Hua Z, Xu Y (2009) Estrogen inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis in experimental stroke. Exp Neurol 215:48–52
Jover T, Tanaka H, Calderone A, Oguro K, Bennett MV, Etgen AM, Zukin RS (2002) Estrogen against global ischemia-induced neuronal death and prevents activation of apoptotic signaling cascades in the hippocampal CA1. J Neurosci 22:2115–2124
Kaplan DR, Miller FD (2000) Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10:381–391
Liu R, Wen Y, Perez E, Wang X, Day AL, Simpkins JW, Yang SH (2005) 17beta-Estradiol attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in female rats. Brain Res 1060:55–61
Mandrekar PS, Sheth AR, Doctor VM, Zaveri JP, Sheth NA (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of follicle stimulating hormone in normal human stomach. Anat Rec 227:334–339
Miller NR, Jover T, Cohen HW, Zukin RS, Etgen AM (2005) Estrogen can act via estrogen receptor alpha and beta to protect hippocampal neurons against global ischemia-induced cell death. Endocrinology 146:3070–3079
Mizrachi D, Shemesh M (1999) Follicle-stimulating hormone receptor and its messenger ribonucleic acid are present in the bovine cervix and can regulate cervical prostanoid synthesis. Biol Reprod 61:776–784
Platania P, Laureanti F, Bellomo M, Giuffrida R, Giuffrida Stella AM, Catania MV, Sortino MA (2003) Differential expression of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in the spinal cord during postnatal development: localization in glial cells. Neuroendocrinology 77:334–340
Rao SC, Li X, ChV Rao, Magnuson DS (2003) Human chorionic gonadotropin/luteinizing hormone receptor expression in the adult rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 336:135–138
Sakurai M, Hayashi T, Abe K, Sadahiro M, Tabayashi K (1998) Delayed and selective motor neuron death after transient spinal cord ischemia: a role of apoptosis? Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 115:1310–1315
Shah MG, Hurkadli KS, Garde SV, Sheth AR (1991) Prostate—a novel target for evaluation of FSH modulating peptides. Indian J Exp Biol 29:101–104
Sribnick EA, Matzelle DD, Ray SK, Banik NL (2006) Estrogen treatment of spinal cord injury attenuates calpain activation and apoptosis. J Neurosci Res 84:1064–1075
Tanaka H, Grooms SY, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2000) The AMPAR subunit GluR2: still front and center-stage. Brain Res 886:190–207
Usul H, Arslan E, Cansever T, Cobanoglu U, Baykal S (2008) Effects of clotrimazole on experimental spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Spine 33:2863–2867
Vanderhorst VG, Gustafsson JA, Ulfhake B (2005) Estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta immunoreactive neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord of male and female mice: relationships to monoaminergic, cholinergic, and spinal projection systems. J Comp Neurol 488:152–179
Zheng W, Magid MS, Kramer EE, Chen YT (1996) Follicle-stimulating hormone receptor is expressed in human ovarian surface epithelium and fallopian tube. Am J Pathol 148:47–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, C., Xu, B. & Huang, W. Studies on expression of FSH and its anti-apoptotic effects on ischemia injury in rat spinal cord. J Mol Hist 41, 165–176 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-010-9273-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-010-9273-7