Abstract
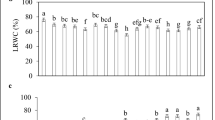
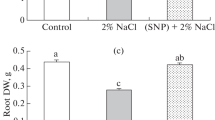
Nitric oxide and calcium are two kinds of signaling molecules that are the key secondary messenger. An experiment was conducted in saline culture solution to examine the cross-talk interactions of nitric oxide and calcium in common wheat under NaCl stress. Addition of 100 mM NaCl reduced plant growth, decreased the chlorophyll content and root activity, increased the reactive oxygen species (such as \( {\text{O}}_{2}^{ \cdot - } \) and H2O2) level, lipid peroxidation and electrolyte leakage, and suppressed the activities of antioxidant enzymes in wheat seedlings. Moreover, high Na+ resulted in the deficiency of mineral nutrients. While addition of 0.10 mM sodium nitroprusside (a NO donor) and/or 17.50 mM Ca(NO3)2 (Na/Ca = 5) alleviated a decline in chlorophyll content, root activity and soluble sugar content, stimulated the activities of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and catalase and decreased the electrolyte leakage, lipid peroxidation, H2O2 content, \( {\text{O}}_{2}^{ \cdot - } \) generation rate. Furthermore, the concentrations of potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), zinc (Zn), iron (Fe) and copper (Cu) concentrations in the leaves and roots of wheat were increased, indicating that application of Ca(NO3)2 facilitated the maintenance of ion homeostasis, while the exogenous NO improved the uptake of Ca. The results suggest that the nitric oxide and calcium are effective in alleviating the adverse effects of salt stress: the nitric oxide is more actively involved in antioxidant system while the calcium is more beneficial to ion homeostasis. When applied in combination, Ca(NO3)2 could counteract the toxicity of exogenous NO to the root, while the exogenous NO may promote the selectivity of uptake and transport of Ca2+.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [Ca2+]cyt :
-
Cytosolic free calcium
- cADPR:
-
Cyclic ADP-ribose
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- cGMP:
-
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- \( {\text{O}}_{2}^{ \cdot - } \) :
-
Superoxide anion radical
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SNP:
-
Sodium nitroprusside
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Bernstein L, Francois LE, Clark RA (1974) Interactive effects of salinity and fertility on yields of grains and vegetables. Agron J 66:412–421
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Briskin DP, Leonard RT, Hodges TK (1987) Isolation of the plasma membrane: markers and general principles. Methods Enzymol 148:542–558
Buet A, Moriconi JI, Santa-María GE, Simontacchi M (2014) An exogenous source of nitric oxide modulates zinc nutritional status in wheat plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 83:337–345
Clark D, Durner J, Navarre DA (2000) Nitric oxide inhibition of tobacco catalase and ascorbate peroxidase. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:1380
Deinlein U, Stephan AB, Horie T, Luo W, Xu G, Schroeder JI (2014) Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci 19(6):371–379
Delledonne M (2005) NO news is good news for plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:390–396
Duncan DR, Widholm JM (2004) Osmotic induced stimulation of the reduction of the viability dye 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride by maize roots and callus cultures. J Plant Physiol 161:397–403
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70:616–620
Giannakoula A, Moustakas M, Mylona P, Ioannis P, Traianos Y (2008) Aluminium tolerance in maize is correlated with increased levels of mineral nutrients, carbohydrates and proline and decreased levels of lipid peroxidation and Al accumulation. J Plant Physiol 165:385–396
Gould KS, Lamotte O, Klinguer A, Pugin A, Wendehenne D (2003) Nitric oxide production in tobacco leaf cells: a generalized stress response? Plant Cell Environ 26:1851–1862
Hammerschmidt R, Nuckles EM, Kuc J (1982) Association of enhanced peroxidase activity with induced systemic resistance of cucumber to colletotrchum lagenarium. Physiol Plant Pathol 20:73–82
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Huang B, Duncan RR, Carrow RN (1997) Drought-resistance mechanisms of seven warm-season tur grasses under surface soil drying. Crop Sci 37:1863–1869
Kaya C, Ak BE, Higgs D, Murillo-Amador B (2002) Influence of foliar applied calcium nitrate on strawberry plants grown under salt stress conditions. Aust J Exp Agric 42:631–636
Khan MN, Siddiqui MH, Mohammad F, Khan MMA, Naeem M (2007) Salinity induced changes in growth, enzyme activities, photosynthesis, proline accumulation and yield in linseed genotypes. World J Agric Sci 3:685–695
Khan MN, Siddiqui MH, Mohammad F, Naeem M (2012) Interactive role of nitric oxide and calcium chloride in enhancing tolerance to salt stress. Nitric Oxide 27:210–218
Lamotte O, Courtois C, Dobrowolska G, Besson A, Pugin A, Waendehenne D (2006) Mechanism of nitric-oxide-induced increase of free cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia cells. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1369–1376
Läuchli A (1990) Calcium, salinity and the plasma membrane. In: Leonard RT, Hepler PK (eds) Calcium in plant growth and development. American Society of Plant Physiology, Rockville, pp 26–35
Läuchli A, Epstein E (1990) Plant responses to saline and sodic conditions. In: Tanji KK (ed) Agricultural salinity assessment and management. Manuals rep. on eng. practice no. 71. ASCE, New York, pp 113–137
Leitner M, Vandelle E, Gaupels F, Bellin D, Delledonne M (2009) NO signals in the haze—nitric oxide signalling in plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:451–458
Liang Y, Si J, Nikolic M, Peng Y, Chen W, Jiang Y (2005) Organic manure stimulates biological activity and barley growth in soil subject to secondary salinization. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1185–1195
Lichtenthaler H (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382
Liu S, Dong Y, Xu L, Kong J (2014) Effects of foliar applications of nitric oxide and salicylic acid on salt-induced changes in photosynthesis and antioxidative metabolism of cotton seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 73:67–68
Magdalena A, Jolanta FW (2007) Nitric oxide as a bioactive signalling molecule in plant stress responses. Plant Sci 172:876–887
Marschner P (2012) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing
Misra AN, Vladkova R, Singh R, Misra M, Dobrikova AG, Apostolova EL (2014) Action and target sites of nitric oxide in chloroplasts. Nitric Oxide 39:35–45
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Muhammed S, Akbar M, Neue HU (1987) Effect of Na/Ca and Na/K ratios in saline culture solution on growth and mineral nutrition of rice. Plant Soil 104:57–62
Murillo-Amador B, Jones HG, Kaya C et al (2006) Effects of foliar application of calcium nitrate on growth and physiological attributes of cowpea grown under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 58:188–196
Nakazawa H, Genka C, Fujishima M (1996) Pathological aspects of active oxygens/free radicals. J Physiol 46:15–32
Ohinishi T, Gall RS, Mayer ML (1975) An improved assay of inorganic phosphate in the presence of extralabile phosphate compounds: application to the ATP-ase assay in the presence of phosphocreatine. Anal Biochem 69:261–267
Patel NT, Vaghela PM, Patel AD, Pandey AN (2011) Implications of calcium nutrition on the response of Caesalpinia crista (Fabaceae) to soil salinity. Acta Ecol Sin 31:24–30
Peiter E (2011) The plant vacuole: emitter and receiver of calcium signals. Cell Calcium 50:120–128
Qi W, Liu H, Liu P et al (2012) Morphological and physiological characteristics of corn roots from cultivars with different yield potentials. Eur J Agron 38:54–63
Rengel Z (1992) The role of calcium in salt toxicity. Plant Cell Environ 15:625–632
Sairam RK, Srivastava GC (2002) Changes in antioxidant activity in sub-cellular fractions of tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes in response to long term salt stress. Plant Sci 162:897–904
Scrase-Field S, Knight MR (2003) Calcium: just a chemical switch? Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:500–506
Serrano R, Rodriguez-Navarro A (2001) Ion homeostasis during salt stress in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:399–404
Shi Q, Ding F, Wang X, Wei M (2007) Exogenous nitric oxide protect cucumber roots against oxidative stress induced by salt stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:542–550
Simaei M, Khavarinejada RA, Saadatmanda S, Bernardb F, Fahimia H (2011) Interactive effects of salicylic acid and nitric oxide on soybean plants under NaCl salinity. Russ J Plant Physiol 58:783–790
Tariq A, Masroor M, Khan A, Jaime A, da Teixeira S, Mohd I, Naeem M (2011) Role of salicylic acid in promoting salt stress tolerance and enhanced artemisinin production in Artemisia annua L. J Plant Growth Regul 30:425–435
Trewavas AJ, Malhó R (1998) Ca2+ signaling in plant cells: the big network! Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:428–433
Tuna AL, Kaya C, Ashraf M, Altunlu H, Yokas I, Yagmur B (2007) The effects of calcium sulphate on growth, membrane stability and nutrient uptake of tomato plants grown under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 59:173–178
Wang Q, Liang X, Dong Y, Xu L, Zhang X, Hou J, Zhen Y (2013) Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on cadmium toxicity, element contents and antioxidative system in perennial ryegrass. Plant Growth Regul 69:11–20
Wendehenne D, Durner J, Klessig DF (2004) Nitric oxide: a new player in plant signalling and defence responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:449–455
Zheng C, Dong J, Liu F (2009) Effects of salt and waterlogging stresses and their combination on leaf photosynthesis, chloroplast ATP synthesis, and antioxidant capacity in wheat. Plant Sci 176:575–582
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Chinese National Basic Research Program (2015CB150404), indigenous innovation project of Shandong province (2014 ZZCX07401) and a Project of Shandong Agricultural University saline and alkaline land (75030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, X., He, M., Wang, Z. et al. Application of nitric oxide and calcium nitrate enhances tolerance of wheat seedlings to salt stress. Plant Growth Regul 77, 343–356 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0069-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0069-3