Abstract
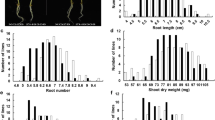
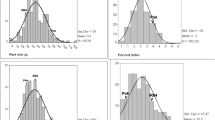
Potassium (K) is one of the essential macronutrients of rice growth and eventually affects yields. To investigate the genetics of low K tolerance and related ions concentrations at the seedling stage in rice, quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were detected using a doubled haploid population derived from a cross between a japonica cultivar CJ06 and an indica accession TN1. A total of 96 QTLs were identified with phenotypic variation 5–29 %, including 30 QTLs found to be associated with shoot height, root length, shoot dry weight, root dry weight and total dry weight under the control (40 mg L−1 K+) and low K stress conditions (4 mg L−1 K+), 14 putative QTLs associated with the K tolerance coefficient of all examined traits and synthetic appraisal index, and 52 QTLs controlling four ions (Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+) concentrations of root and shoot under two treatments. The results indicated that low K tolerance and related ions concentrations were quantitatively inherited, and the detected major QTLs may be useful for marker-assistant selection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DH:
-
Doubled haploid
- QTLs:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- K:
-
Potassium
- RDW:
-
Root dry weight
- SDW:
-
Shoot dry weight
- TDW:
-
Total dry weight
- SH:
-
Shoot height
- RL:
-
Root length
- RNC:
-
Root Na+ concentration
- RCC:
-
Root Ca2+ concentration
- RKC:
-
Root K+ concentration
- RMC:
-
Root Mg2+ concentration
- SNC:
-
Shoot Na+ concentration
- SCC:
-
Shoot Ca2+ concentration
- SKC:
-
Shoot K+ concentration
- SMC:
-
Shoot Mg2+ concentration
- KTC:
-
K tolerance coefficient
- SAI:
-
Synthetic appraisal index
References
Ahmadi N, Negrão S, Katsantonis D, Frouin J, Ploux J, Letourmy P, Droc G, Babo P, Trindade H, Bruschi G, Greco R, Oliveira M, Piffanelli P, Courtois B (2011) Targeted association analysis identified japonica rice varieties achieving Na+/K+ homeostasis without the allelic make-up of the salt tolerant indica variety Nona Bokra. Theor Appl Genet 123:881–895
Armengaud P, Breitling R, Amtmann A (2004) The potassium-dependent transcriptome of Arabidopsis reveals a prominent role of jasmonic acid in nutrient signaling. Plant Physiol 136(1):2556–2576
Cheng L, Wang Y, Meng L, Hu X, Cui Y, Sun Y, Zhu L, Ali J, Xu J, Li Z (2012) Identification of salt tolerant QTLs with strong genetic background effect using two sets of reciprocal introgression lines in rice. Genome 55:45–55
Cho YI, Jiang WZ, Chin JH, Piao Z, Cho YG, McCouch S, Koh HJ (2007) Identification of QTLs associated with physiological nitrogen use efficiency in rice. Mol Cells 23(1):72–79
Dobermann A, Cassman KG, Mamaril CP, Sheehy JE (1998) Management of phosphorus, potassium and sulfur in intensive, irrigated lowland rice. Field Crops Res 56:113–138
Heffer P, Prud’homme M (2010) Fertilizer outlook 2010–2014. In: 78th IFA Annual Conference, Paris
Hu B, Wu P, Liao C, Zhang W, Ni J (2001) QTLs and epistasis underlying activity of acid phosphatase under phosphorus sufficient and deficient condition in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 230:99–105
Koyama ML, Levesley A, Koebner RM, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for component physiological traits determining salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol 125(1):406–422
Laegreid M, Bockman OC, Kaarstad O (1999) Agriculture, fertilizers and the environment. CABI, Oxon
Lian XM, Xing YZ, Yan H, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2005) QTLs for low nitrogen tolerance at seedling stage identified using a recombinant inbred line population derived from an elite rice hybrid. Theor Appl Genet 112:85–96
Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano MJ, Gao P, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu XH, Ren ZH, Chao DY (2004) QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 108:253–260
Liu GD, Liu GL (2002) Screening indica rice for K-efficient genotypes. Acta Agron Sin 28(2):161–166
Liu J, Yang X, Yang Y, Wu L (2003) Some agronomic and nutritional characteristics for potassium efficient rice genotypes under low potassium stress. Plant Nutr Fert Sci 9(2):190–195
McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11–13
Miyamotoa T, Ochiaia K, Takeshitaa S, Matoha T (2012) Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with shoot sodium accumulation under low potassium conditions in rice plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 58:728–736
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S, Lin HX (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet 37:1141–1146
Sogava K, Qian Q, Zeng DL, Hu J, Zeng LJ (2005) Differential expression of whitebacked planthopper resistance in the japonica/indica doubled haploid rice population under field evaluation and seedbox screening test. Rice Sci 12:63–67
Tai D, Zhang X, Su Z, Wang Y, Luo Y, Xia J (2004) Screening for low-kalium tolerance varieties at seedling stage from the core germplasm of integrated international rice molecular breeding program. J Plant Genet Resour 5(4):356–359
Wang Z, Chen Z, Cheng J, Lai Y, Wang J, Bao Y, Huang J, Zhang H (2012) QTL analysis of Na+ and K+ concentrations in roots and shoots under different levels of NaCl stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS One 7(12):e51202
Wang G, Lu W, Chen H, Zhang X, Xue D (2015) Seedling screening of rice germplasm resources with low potassium tolerance. J Hangzhou Normal Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 14(1):46–50
Watanabe T, Broadley MR, Jansen S, White PJ, Takada J, Satake K, Takamatsu T, Tuah SJ, Osaki M (2007) Evolutionary control of leaf element composition in plants. New Phytol 174:516–523
White PJ, Karley AJ (2010) Potassium. In: Hell R, Mendel R (eds) Cell biology of metals and nutrients in plants. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 119–224
Wissuwa M, Yano M, Ae N (1998) Mapping of QTLs for phosphorus-deficiency tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 97:777–783
Wu P, Ni J, Luo A, Jin G, Tao Q (1997) Investigation of QTLs underlying rice tolerance for potassium deficiency via molecular markers. Plant Nutr Fert Sci 3(3):209–217
Wu P, Ni JJ, Luo AC (1998) QTLs underlying rice tolerance to low-potassium stress in rice seedlings. Crop Sci 38:1458–1462
Yang X, Liu J, Wang W, Ye Z, Luo A (2004) Potassium internal use efficiency relative to growth vigor, potassium distribution, and carbohydrate allocation in rice genotypes. J Plant Nutr 27:837–852
Yang J, Hu CC, Hu H, Yu RD, Xia Z, Ye XZ, Zhu J (2008) QTLNetwork: mapping and visualizing genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 24:721–723
Yoshida S, Forna DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (1976) Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice. Intemational Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, pp 62–63
Zeng DL, Hu J, Dong GJ, Liu J, Qian Q (2009) Quantitative trait loci mapping of flag–leaf ligule length in rice and alignment with gene. J Integr Plant Biol 51(4):360–366
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Science and Technology Bureau (2012C22039); National Natural Science Foundation of China (31171535; 31101135); Hangzhou Scientific and Technological Program (20130432B04). The authors are grateful to the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yunxia Fang, Weiming Wu and Xiaoqin Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Y., Wu, W., Zhang, X. et al. Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with tolerance to low potassium and related ions concentrations at seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Growth Regul 77, 157–166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0047-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0047-9