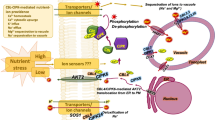
Abstract
Plants are sessile organisms and have multiple tolerance mechanisms which allow them to adapt to the environmental stresses to which they may be exposed. Key to a plant’s tolerance of abiotic stresses is the ability to rapidly detect stress and activate the appropriate stress response mechanism. The calcineurin B-like (CBL) and CBL-interacting protein kinase (CIPK) signalling pathway is a flexible Ca2+ signalling network which allows a plant to fine tune its response to stress, via both pre- and post-translational mechanisms. Genes encoding CBLs and CIPKs have now been identified in a variety of plant species. Plants have been found to have large gene families of CBLs and CIPKs, each encoding proteins with specific upstream and downstream targets, thus providing the flexibility required to allow a plant to adapt to a variety of stresses. Characterisation of CBL and CIPK mutants have shown them to be important for a plant to survive cold, drought, heat, salinity and low nutrient stresses. Many CBLs and CIPKs have been shown to be involved in the transport of ions through a plant, either limiting the supply of toxic ions to certain tissues or maximising the uptake of beneficial nutrients from the soil. This review will provide an update into the current knowledge of CBL and CIPK interactions and their role in ion transport during abiotic stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht V, Ritz O, Linder S, Harter K, Kudla J (2001) The NAF domain defines a novel protein–protein interaction module conserved in Ca2+-regulated kinases. EMBO J 20:1051–1063
Albrecht V, Weinl S, Blazevic D, D’Angelo C, Batistic O, Kolukisaoglu Ü, Bock R, Schulz B, Harter K, Kudla J (2003) The calcium sensor CBL1 integrates plant responses to abiotic stresses. Plant J 36:457–470
Alemán F, Nieves-Cordones M, Martínez V, Rubio F (2011) Root K+ acquisition in plants: the Arabidopsis thaliana model. Plant Cell Physiol 52:1603–1612
Alexieva V, Sergiev I, Mapelli S, Karanov E (2001) The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ 24:1337–1344
Batistič O, Kudla J (2004) Integration and channeling of calcium signaling through the CBL calcium sensor/CIPK protein kinase network. Planta 219:915–924
Batistič O, Kudla J (2012) Analysis of calcium signaling pathways in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:1283–1293
Batistič O, Sorek N, Schültke S, Yalovsky S, Kudla J (2008) Dual fatty acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:1346–1362
Batistič O, Waadt R, Steinhorst L, Held K, Kudla J (2010) CBL-mediated targeting of CIPKs facilitates the decoding of calcium signals emanating from distinct cellular stores. Plant J 61:211–222
Bose J, Pottosin II, Shabala SS, Palmgren MG, Shabala S (2011) Calcium efflux systems in stress signaling and adaptation in plants. Front Plant Sci 2:1–17
Chakraborty K, Sairam RK, Bhattacharya RC (2012) Differential expression of salt overly sensitive pathway genes determines salinity stress tolerance in Brassica genotypes. Plant Physiol Biochem 51:90–101
Chen J-H, Sun Y, Sun F, Xia X-L, Yin W-L (2011a) Tobacco plants ectopically expressing the Ammopiptanthus mongolicus AmCBL1 gene display enhanced tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses. Plant Growth Regul 63:259–269
Chen X, Gu Z, Liu F, Ma B, Zhang H (2011b) Molecular analysis of rice CIPKs involved in both biotic and abiotic stress responses. Rice Sci 18:1–9
Chen L, Ren F, Zhou L, Wang Q-Q, Zhong H, Li X-B (2012) The Brassica napus calcineurin B-Like 1/CBL-interacting protein kinase 6 (CBL1/CIPK6) component is involved in the plant response to abiotic stress and ABA signalling. J Exp Bot 63:6211–6222
Chen L, Wang Q-Q, Zhou L, Ren F, Li D-D, Li X-B (2013) Arabidopsis CBL-interacting protein kinase (CIPK6) is involved in plant response to salt/osmotic stress and ABA. Mol Biol Rep 40:4759–4767
Chen X, Huang Q, Zhang F, Wang B, Wang J, Zheng J (2014) ZmCIPK21, a maize CBL-interacting kinase, enhances salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci 15:14819–14834
Cheong Y, Kim K, Pandey G, Gupta R, Grant J, Luan S (2003) CBL1, a calcium sensor that differentially regulates salt, drought, and cold responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:1833–1845
Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Grant JJ, Batistic O, Li L, Kim B-G, Lee S-C, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) Two calcineurin B-like calcium sensors, interacting with protein kinase CIPK23, regulate leaf transpiration and root potassium uptake in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52:223–239
Cheong YH, Sung SJ, Kim B-G, Pandey GK, Cho J-S, Kim K-N, Luan S (2010) Constitutive overexpression of the calcium sensor CBL5 confers osmotic or drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol Cells 29:159–165
Chérel I, Michard E, Platet N, Mouline K, Alcon C, Sentenac H, Thibaud JB (2002) Physical and functional interaction of the Arabidopsis K+ channel AKT2 and phosphatase AtPP2CA. Plant Cell 14:1133–1146
Choi W-G, Toyota M, Kim S-H, Hilleary R, Gilroy S (2014) Salt stress-induced Ca2+ waves are associated with rapid, long-distance root-to-shoot signaling in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:6497–6502
Cuéllar T, Pascaud F, Verdeil J-L, Torregrosa L, Adam-Blondon A-F, Thibaud J-B, Sentenac H, Gaillard I (2010) A grapevine Shaker inward K+ channel activated by the calcineurin B-like calcium sensor 1-protein kinase CIPK23 network is expressed in grape berries under drought stress conditions. Plant J 61:58–69
Cuéllar T, Azeem F, Andrianteranagna M, Pascaud F, Verdeil J-L, Sentenac H, Zimmermann S, Gaillard I (2013) Potassium transport in developing fleshy fruits: the grapevine inward K+ channel VvK1.2 is activated by CIPK–CBL complexes and induced in ripening berry flesh cells. Plant J 73:1006–1018
D’Angelo C, Weinl S, Batistič O, Pandey GK, Cheong YH, Schültke S, Albrecht V, Ehlert B, Schulz B, Harter K, Luan S, Bock R, Kudla J (2006) Alternative complex formation of the Ca2+-regulated protein kinase CIPK1 controls abscisic acid-dependent and independent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 48:857–872
De la Torre F, Gutiérrez-Beltrán E, Pareja-Jaime Y, Chakravarthy S, Martin GB, del Pozo O (2013) The tomato calcium sensor CBL10 and its interacting protein kinase CIPK6 define a signaling pathway in plant immunity. Plant Cell 25:2748–2764
Deeken R, Geiger D, Fromm J, Koroleva O, Ache P, Langenfeld-Heyser R, Sauer N, May ST, Hedrich R (2002) Loss of the AKT2/3 potassium channel affects sugar loading into the phloem of Arabidopsis. Planta 216:334–344
Deng X, Hu W, Wei S, Zhou S, Zhang F, Han J, Chen L, Li Y, Feng J, Fang B, Luo Q, Li S, Liu Y, Yang G, He G (2013a) TaCIPK29, a CBL-interacting protein kinase gene from wheat, confers salt stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. PLoS One 8:e69881
Deng X, Zhou S, Hu W, Feng J, Zhang F, Chen L, Huang C, Luo Q, He Y, Yang G, He G (2013b) Ectopic expression of wheat TaCIPK14, encoding a calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase, confers salinity and cold tolerance in tobacco. Physiol Plant 149:367–377
Dennison KL, Robertson WR, Lewis BD, Hirsch RE, Sussman MR, Spalding EP (2001) Functions of AKT1 and AKT2 potassium channels determined by studies of single and double mutants of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 127:1012–1019
Dodd AN, Kudla J, Sanders D (2010) The language of calcium signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:593–620
Drerup MM, Schlücking K, Hashimoto K, Manishankar P, Steinhorst L, Kuchitsu K, Kudla J (2013) The calcineurin B-like calcium sensors CBL1 and CBL9 together with their interacting protein kinase CIPK26 regulate the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase RBOHF. Mol Plant 6:559–569
Eckert C, Offenborn JN, Heinz T, Armarego-Marriott T, Schültke S, Zhang C, Hillmer S, Heilmann M, Schumacher K, Bock R, Heilmann I, Kudla J (2014) The vacuolar calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 affect seed size and embryonic development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 78:146–156
Elphick CH, Sanders D, Maathuis FJM (2001) Critical role of divalent cations and Na+ efflux in Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 24:733–740
Forde BG (2002) Local and long-range signaling pathways regulating plant responses to nitrate. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:203–224
Gajdanowicz P, Michard E, Sandmann M, Rocha M, Corrêa LGG, Ramírez-Aguilar SJ, Gomez-Porras JL, González W, Thibaud J-B, van Dongen JT, Dreyer I (2011) Potassium (K+) gradients serve as a mobile energy source in plant vascular tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:864–869
Gao S, Yuan L, Zhai H, Liu C, He S, Liu Q (2012) Overexpression of SOS genes enhanced salt tolerance in sweetpotato. J Integr Agric 11:378–386
Gill PK, Sharma AD, Singh P, Bhullar SS (2003) Changes in germination, growth and soluble sugar contents of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench seeds under various abiotic stresses. Plant Growth Regul 40:157–162
Gu Z, Ma B, Jiang Y, Chen Z, Su X, Zhang H (2008) Expression analysis of the calcineurin B-like gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under environmental stresses. Gene 415:1–12
Guo Y, Xiong L, Song C-P, Gong D, Halfter U, Zhu J-K (2002) A calcium sensor and its interacting protein kinase are global regulators of abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 3:233–244
Guo Y, Qiu Q-S, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Ohta M, Zhang C, Schumaker KS, Zhu J-K (2004) Transgenic evaluation of activated mutant alleles of SOS2 reveals a critical requirement for its kinase activity and C-terminal regulatory domain for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16:435–449
Halfter U, Ishitani M, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3735–3740
He L, Yang X, Wang L, Zhu L, Zhou T, Deng J, Zhang X (2013) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel cotton CBL-interacting protein kinase gene (GhCIPK6) reveals its involvement in multiple abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435:209–215
Held K, Pascaud F, Eckert C, Gajdanowicz P, Hashimoto K, Corratgé-Faillie C, Offenborn JN, Lacombe B, Dreyer I, Thibaud J-B, Kudla J (2011) Calcium-dependent modulation and plasma membrane targeting of the AKT2 potassium channel by the CBL4/CIPK6 calcium sensor/protein kinase complex. Cell Res 21:1116–1130
Ho C-H, Lin S-H, Hu H-C, Tsay Y-F (2009) CHL1 functions as a nitrate sensor in plants. Cell 138:1184–1194
Hu H-C, Wang Y-Y, Tsay Y-F (2009) AtCIPK8, a CBL-interacting protein kinase, regulates the low-affinity phase of the primary nitrate response. Plant J 57:264–278
Hu D-G, Li M, Luo H, Dong Q-L, Yao Y-X, You C-X, Hao Y-J (2012) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of MdSOS2 reveals its involvement in salt tolerance in apple callus and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 31:713–722
Huang N, Chiang C, Crawford NM, Tsay Y-F (1996) CHL1 encodes a component of the low-affinity nitrate uptake system in Arabidopsis and shows cell type-specific expression in roots. Plant Cell 8:2183–2191
Huertas R, Olías R, Eljakaoui Z, Gálvez FJ, Li J, De Morales PA, Belver A, Rodríguez-Rosales MP (2012) Overexpression of SlSOS2 (SlCIPK24) confers salt tolerance to transgenic tomato. Plant Cell Environ 35:1467–1482
Jacobs B, Pearson C (1999) Growth, development and yield of rice in response to cold temperature. J Agron Crop Sci 182:79–88
Jannesar M, Razavi K, Saboora A (2014) Effects of salinity on expression of the salt overly sensitive genes in Aeluropus lagopoides. Aust J Crop Sci 8:1–8
Kim B-G, Waadt R, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Dominguez-Solis JR, Schültke S, Lee SC, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52:473–484
Kleist TJ, Spencley AL, Luan S (2014) Comparative phylogenomics of the CBL–CIPK calcium-decoding network in the moss Physcomitrella, Arabidopsis, and other green lineages. Front Plant Sci 5:1–17
Kolukisaoglu Ü, Weinl S, Blazevic D, Batistic O, Kudla J (2004) Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL–CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol 134:43–58
Krouk G, Crawford NM, Coruzzi GM, Tsay Y-F (2010) Nitrate signaling: adaptation to fluctuating environments. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:266–273
Kushwaha HR, Kumar G, Verma PK, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2011) Analysis of a salinity induced BjSOS3 protein from Brassica indicate it to be structurally and functionally related to its ortholog from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:996–1004
Lacombe B, Pilot G, Michard E, Gaymard F, Sentenac H, Thibaud JB (2000) A shaker-like K+ channel with weak rectification is expressed in both source and sink phloem tissues of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:837–851
Lagarde D, Basset M, Lepetit M, Conejero G, Gaymard F, Astruc S, Grignon C (1996) Tissue-specific expression of Arabidopsis AKT1 gene is consistent with a role in K+ nutrition. Plant J 9:195–203
Lee SC, Lan W-Z, Kim B-G, Li L, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Lu G, Buchanan BB, Luan S (2007) A protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation network regulates a plant potassium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15959–15964
Li L, Kim B-G, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Luan S (2006) A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulates a K+ channel for low-K response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12625–12630
Li D, Song S, Xia X, Yin W (2012a) Two CBL genes from Populus euphratica confer multiple stress tolerance in transgenic triploid white poplar. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 109:477–489
Li R, Zhang J, Wu G, Wang H, Chen Y, Wei J (2012b) HbCIPK2, a novel CBL-interacting protein kinase from halophyte Hordeum brevisubulatum, confers salt and osmotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 35:1582–1600
Li Z-Y, Xu Z-S, He G-Y, Yang G-X, Chen M, Li L-C, Ma Y-Z (2012c) Overexpression of soybean GmCBL1 enhances abiotic stress tolerance and promotes hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 427:731–736
Li D-D, Xia X-L, Yin W-L, Zhang H-C (2013) Two poplar calcineurin B-like proteins confer enhanced tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Biol Plant 57:70–78
Li J, Long Y, Qi GN, Xu ZJ, Wu WH, Wang Y (2014a) The Os-AKT1 channel is critical for K+ uptake in rice roots and is modulated by the rice CBL1–CIPK23 complex. Plant Cell 26:3387–3402
Li Q, Fan L, Luo Q, He H, Zhang J, Zeng Q, Li Y, Zhou W, Huang Z, Deng H, Qi Y (2014b) Co-overexpression of AtCBL9, AtCIPK23 and AtAKT1 enhances K+ uptake of sugarcane under low-K+ stress. Plant Omics 7:188–194
Liu J, Zhu J (1997) An Arabidopsis mutant that requires increased calcium for potassium nutrition and salt tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14960–14964
Liu K, Huang C, Tsay Y (1999) CHL1 is a dual-affinity nitrate transporter of Arabidopsis involved in multiple phases of nitrate uptake. Plant Cell 11:865–874
Liu L-L, Ren H-M, Chen L-Q, Wang Y, Wu W-H (2013) A protein kinase, calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein Kinase9, interacts with calcium sensor calcineurin B-like Protein3 and regulates potassium homeostasis under low-potassium stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 161:266–277
Luan S, Kudla J, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Yalovsky S, Gruissem W (2002) Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins: calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell 14:S389–S400
Lv F, Zhang H, Xia X, Yin W (2014) Expression profiling and functional characterization of a CBL-interacting protein kinase gene from Populus euphratica. Plant Cell Rep 33:807–818
Lyzenga WJ, Liu H, Schofield A, Muise-Hennessey A, Stone SL (2013) Arabidopsis CIPK26 interacts with KEG, components of the ABA signalling network and is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. J Exp Bot 64:2779–2791
Ma D-M, Xu W-R, Li H-W, Jin F-X, Guo L-N, Wang J, Dai H-J, Xu X (2014) Co-expression of the Arabidopsis SOS genes enhances salt tolerance in transgenic tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.). Protoplasma 251:219–231
Maierhofer T, Diekmann M, Offenborn JN, Lind C, Bauer H, Hashimoto K, Al-Rasheid KAS, Luan S, Kudla J, Geiger D, Hedrich R (2014) Site-and kinase-specific phosphorylation-mediated activation of SLAC1, a guard cell anion channel stimulated by abscisic acid. Sci Signal 7:1–12
Martínez-Atienza J, Jiang X, Garciadeblas B, Mendoza I, Zhu J-K, Pardo JM, Quintero FJ (2007) Conservation of the salt overly sensitive pathway in rice. Plant Physiol 143:1001–1012
Munns R, Schachtman D, Condon A (1995) The significance of a two-phase growth response to salinity in wheat and barley. Funct Plant Biol 22:561–569
Nieves-Cordones M, Caballero F, Martínez V, Rubio F (2012) Disruption of the Arabidopsis thaliana inward-rectifier K+ channel AKT1 improves plant responses to water stress. Plant Cell Physiol 53:423–432
Ohta M, Guo Y, Halfter U, Zhu J-K (2003) A novel domain in the protein kinase SOS2 mediates interaction with the protein phosphatase 2C ABI2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11771–11776
Olías R, Eljakaoui Z, Li J, De Morales PA, Marín-Manzano MC, Pardo JM, Belver A (2009) The plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 is essential for salt tolerance in tomato and affects the partitioning of Na+ between plant organs. Plant Cell Environ 32:904–916
Pandey GK, Cheong H, Kim K, Grant JJ, Li L, Hung W, Angelo CD, Weinl S, Kudla J, Luan S (2004) The calcium sensor calcineurin B-like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:1912–1924
Pandey GK, Cheong YH, Kim B-G, Grant JJ, Li L, Luan S (2007) CIPK9: a calcium sensor-interacting protein kinase required for low-potassium tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 17:411–421
Pandey GK, Grant JJ, Cheong YH, Kim B-G, Li LG, Luan S (2008) Calcineurin B-like protein CBL9 interacts with target kinase CIPK3 in the regulation of ABA response in seed germination. Mol Plant 1:238–248
Pilot G, Gaymard F, Mouline K, Chérel I, Sentenac H (2003) Regulated expression of Arabidopsis shaker K+ channel genes involved in K+ uptake and distribution in the plant. Plant Mol Biol 51:773–787
Qiu Q-S, Guo Y, Dietrich MA, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8436–8441
Qiu Q-S, Guo Y, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Schumaker KS, Zhu J-K (2004) Regulation of vacuolar Na+/H+ exchange in Arabidopsis thaliana by the salt-overly-sensitive (SOS) pathway. J Biol Chem 279:207–215
Quan R, Lin H, Mendoza I, Zhang Y, Cao W, Yang Y, Shang M, Chen S, Pardo JM, Guo Y (2007) SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 19:1415–1431
Quintero FJ, Ohta M, Shi H, Zhu J-K, Pardo JM (2002) Reconstitution in yeast of the Arabidopsis SOS signaling pathway for Na+ homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9061–9066
Rao X-L, Zhang X-H, Li R-J, Shi H-T, Lu Y-T (2011) A calcium sensor-interacting protein kinase negatively regulates salt stress tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa). Funct Plant Biol 38:441–450
Reddy AR, Chaitanya KV, Vivekanandan M (2004) Drought-induced responses of photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism in higher plants. J Plant Physiol 161:1189–1202
Ren X-L, Qi G-N, Feng H-Q, Zhao S, Zhao S-S, Wang Y, Wu W-H (2013) Calcineurin B-like protein CBL10 directly interacts with AKT1 and modulates K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 74:258–266
Rivandi J, Miyazaki J, Hrmova M, Pallotta M, Tester M, Collins NC (2011) A SOS3 homologue maps to HvNax4, a barley locus controlling an environmentally sensitive Na+ exclusion trait. J Exp Bot 62:1201–1216
Roy SJ, Huang W, Wang XJ, Evrard A, Schmöckel SM, Zafar ZU, Tester M (2013) A novel protein kinase involved in Na+ exclusion revealed from positional cloning. Plant Cell Environ 36:553–568
Rudd J, Franklin-Tong V (2001) Unravelling response-specificity in Ca2+ signalling pathways in plant cells. New Phytol 151:7–33
Saadia M, Jamil A, Ashraf M, Akram NA (2013) Comparative study of SOS2 and a novel PMP3-1 gene expression in two sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) lines differing in salt tolerance. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:980–987
Sairam R, Rao K, Srivastava G (2002) Differential response of wheat genotypes to long term salinity stress in relation to oxidative stress, antioxidant activity and osmolyte concentration. Plant Sci 163:1037–1046
Sanders D, Brownlee C, Harper J (1999) Communicating with calcium. Plant Cell 11:691–706
Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C, Harper JH (2002) Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell 14:401–418
Sandmann M, Skłodowski K, Gajdanowicz P, Michard E, Rocha M, Gomez-Porras JL, González W, Corrêa LGG, Ramírez-Aguilar SJ, Cuin TA, van Dongen JT, Thibaud J-B, Dreyer I (2011) The K+ battery-regulating Arabidopsis K+ channel AKT2 is under the control of multiple post-translational steps. Plant Signal Behav 6:558–562
Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Gassmann W (1994) Perspectives on the physiology and structure of inward-rectifying K+ channels in higher plants: biophysical implications for K+ uptake. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23:441–471
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6896–6901
Shi H, Lee B, Wu S, Zhu J (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21:81–87
Sun Z, Qi X, Li P, Wu C, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Wang Z (2008) Overexpression of a Thellungiella halophila CBL9 homolog, ThCBL9, confers salt and osmotic tolerances in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Biol 51:25–34
Szyroki A, Ivashikina N, Dietrich P, Roelfsema M, Ache P, Reintanz B, Deeken R, Godde M, Felle H, Steinmeyer R, Palme K, Hedrich R (2001) KAT1 is not essential for stomatal opening. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2917–2921
Tang R-J, Liu H, Bao Y, Lv Q-D, Yang L, Zhang H-X (2010) The woody plant poplar has a functionally conserved salt overly sensitive pathway in response to salinity stress. Plant Mol Biol 74:367–380
Tang R-J, Liu H, Yang Y, Yang L, Gao X-S, Garcia VJ, Luan S, Zhang H-X (2012) Tonoplast calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 control plant growth and ion homeostasis through regulating V-ATPase activity in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 22:1650–1665
Tang R-J, Yang Y, Yang L, Liu H, Wang C-T, Yu M-M, Gao X-S, Zhang H-X (2014) Poplar calcineurin B-like proteins PtCBL10A and PtCBL10B regulate shoot salt tolerance through interaction with PtSOS2 in the vacuolar membrane. Plant Cell Environ 37:573–588
Tripathi V, Parasuraman B, Laxmi A, Chattopadhyay D (2009) CIPK6: a CBL-interacting protein kinase is required for development and salt tolerance in plants. Plant J 58:778–790
Wang M, Gu D, Liu T, Wang Z, Guo X, Hou W, Bai Y, Chen X, Wang G (2007) Overexpression of a putative maize calcineurin B-like protein in Arabidopsis confers salt tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 65:733–746
Wang X, Li J, Zou X, Lu L, Li L, Ni S, Liu F (2010) Ectopic expression of AtCIPK23 enhances tolerance against low-K+ stress in transgenic potato. Am J Potato Res 88:153–159
Wang R-K, Li L-L, Cao Z-H, Zhao Q, Li M, Zhang L-Y, Hao Y-J (2012) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel apple MdCIPK6L gene reveals its involvement in multiple abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 79:123–135
Weinl S, Kudla J (2009) The CBL–CIPK Ca2+-decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytol 184:517–528
Wu SJ, Ding L, Zhu JK (1996) SOS1: a genetic locus essential for salt tolerance and potassium acquisition. Plant Cell 8:617–627
Wu Y, Ding N, Zhao X, Zhao M, Chang Z, Liu J, Zhang L (2007) Molecular characterization of PeSOS1: the putative Na+/H+ antiporter of Populus euphratica. Plant Mol Biol 65:1–11
Xiang Y, Huang Y, Xiong L (2007) Characterization of stress-responsive CIPK genes in rice for stress tolerance improvement. Plant Physiol 144:1416–1428
Xiao B-Z, Chen X, Xiang C-B, Tang N, Zhang Q-F, Xiong L-Z (2009) Evaluation of seven function-known candidate genes for their effects on improving drought resistance of transgenic rice under field conditions. Mol Plant 2:73–83
Xu J, Li H-D, Chen L-Q, Wang Y, Liu L-L, He L, Wu W-H (2006) A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin B-like proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 125:1347–1360
Yang Q, Chen Z-Z, Zhou X-F, Yin H-B, Li X, Xin X-F, Hong X-H, Zhu J-K, Gong Z (2009) Overexpression of SOS (Salt Overly Sensitive) genes increases salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2:22–31
Ye C-Y, Xia X, Yin W (2013a) Evolutionary analysis of CBL-interacting protein kinase gene family in plants. Plant Growth Regul 71:49–56
Ye J, Zhang W, Guo Y (2013b) Arabidopsis SOS3 plays an important role in salt tolerance by mediating calcium-dependent microfilament reorganization. Plant Cell Rep 32:139–148
Zeng L, Shannon M (2000) Salinity effects on seedling growth and yield components of rice. Crop Sci 40:996–1003
Zhang H, Yin W, Xia X (2008) Calcineurin B-Like family in Populus: comparative genome analysis and expression pattern under cold, drought and salt stress treatment. Plant Growth Regul 56:129–140
Zhang H, Lv F, Han X, Xia X, Yin W (2013) The calcium sensor PeCBL1, interacting with PeCIPK24/25 and PeCIPK26, regulates Na+/K+ homeostasis in Populus euphratica. Plant Cell Rep 32:611–621
Zhang H, Yang B, Liu W-Z, Li H, Wang L, Wang B, Deng M, Liang W, Deyholos MK, Jiang Y-Q (2014) Identification and characterization of CBL and CIPK gene families in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol 14:8
Zhao D, Oosterhuis D, Bednarz C (2001) Influence of potassium deficiency on photosynthesis, chlorophyll content and chloroplast ultrastructure of cotton plants. Photosynthetica 39:103–109
Zhao J, Sun Z, Zheng J, Guo X, Dong Z, Huai J, Gou M, He J, Jin Y, Wang J, Wang G (2009) Cloning and characterization of a novel CBL-interacting protein kinase from maize. Plant Mol Biol 69:661–674
Zhou J, Wang J, Bi Y, Wang L, Tang L, Yu X, Ohtani M, Demura T, Zhuge Q (2014) Overexpression of PtSOS2 enhances salt tolerance in transgenic poplars. Plant Mol Biol Report 32:185–197
Zhu JK, Liu J, Xiong L (1998) Genetic analysis of salt tolerance in Arabidopsis: evidence for a critical role of potassium nutrition. Plant Cell 10:1181–1191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thoday-Kennedy, E.L., Jacobs, A.K. & Roy, S.J. The role of the CBL–CIPK calcium signalling network in regulating ion transport in response to abiotic stress. Plant Growth Regul 76, 3–12 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0034-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0034-1