Abstract
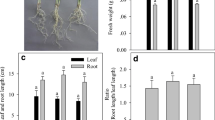
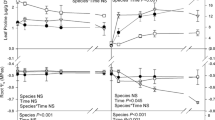
The present study investigated the developmental tolerance of Atriplex halimus to osmotic and/or ionic stress. A. halimus was exposed to NaCl (0, 100, 250 and 400 mM), KCl (0, 100, 250 and 400 mM) and sorbitol (0, 200, 500 and 800 mM) at the level of germination, seedling emergence and vegetative stages. The response of A. halimus to different salts was stage dependent especially to NaCl that had a remarkable effect on A. halimus growth at each stage. At the germination stage, the growth reduction could be attributed to osmotic effect and HRD may have a role in that osmotic sensitivity. At this stage, the accumulation of Na+ into vacuole could be a strategy for alleviating the osmotic effect. At the seedling emergence stage, the inhibition of growth could be mainly attributed to the ionic effect that may have resulted from excessive accumulation of Na+ along with inconsistent regulations of Na+ manipulating genes. A. halimus at the vegetative stage was an obligate halophyte with regulated mechanisms of tolerance to both ionic and osmotic components of salt stress. A. halimus exhibits glycophytic features at the early growth stages but it is an obligate halophyte at the vegetative stage.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abogadallah GM, Nada RM, Malinowski R, Quick P (2011) Overexpression of HARDY, an AP2/ERF gene from Arabidopsis, improves drought and salt tolerance by reducing transpiration and sodium uptake in transgenic Trifolium alexandrinum L. Planta 233:1265–1276
Albregts EE, Howard CM (1973) Influence of temperature and moisture stress from sodium chloride salinization on okra emergence. Agron J 65:836–837
Almansouri M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (2001) Effect of salt and osmotic stresses on germination in durum wheat (Triticum durum desf.). Plant Soil 231:243–254
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Ashby WC, Beadle NCW (1957) Salinity factors in the growth of Australian saltbushes. Ecology 38:344–352
Bajji M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (1998) Salt stress effects on roots and leaves of Atriplex halimus L. and their corresponding callus cultures. Plant Sci 137:131–142
Bajji M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (2002) Osmotic and ionic effects of NaCl on germination, early seedling growth, and ion content of Atriplex halimus (Chenopodiaceae). Can J Bot 80:297–304
Ben Hassine A, Ghanem ME, Bouzid S, Lutts S (2008) An inland and a coastal population of the Mediterranean xero-halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. differ in their ability to accumulate proline and glycinebetaine in response to salinity and water stress. J Exp Bot 59:1315–1326
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1456:140–151
Boorman LA (1968) Some aspects of the reproductive biology of Limonium ulgare Mill. and Limonium humile Mill. Ann Bot 32:803–824
Egan TP, Ungar IA, Meekins JF (1997) The effect of different salts of sodium and potassium on the germination of Atriplex prostrate (Chenopodiaceae). J Plant Nutr 20:1723–1730
Eshel A (1985) Responses of Suaeda aegyptiaca to NaCl, KCl and Na2SO4 treatments. Physiol Plant 64:308–315
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2008) Salinity tolerance in halophytes. New Phytol 179:945–963
Flowers TJ, Troke PF, Yeo AR (1977) The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 28:89–121
Flowers TJ, Hajibagheri MA, Clipson NJW (1986) Halophytes. Q Rev Biol 61:313–337
Glenn E, Miyamoto M, Moore D, Brown JJ, Thompson TL, Brown P (1997) Water requirements for cultivating Salicornia bigelovii Torr. With seawater on sand in a coastal desert environment. J Arid Environ 36:711–730
Glenn EP, Brown JJ, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance and crop potential of halophytes. Cri Rev Plant Sci 18:227–255
Gorham J, Wyn Jones RG (1983) Solute distribution in Suaeda maritima. Planta 157:344–349
Grieve CM, Grattan SR (1983) Rapid assay for determination of water soluble quaternary ammonium compounds. Plant Soil 70:303–307
Hansen EH, Munns DN (1988) Effect of caso4 and nacl on mineral content of Leucaena leucocephala. Plant Soil 7:101–105
Hariadi Y, Marandon K, Tian Y, Jacobsen SE, Shabala S (2011) Ionic and osmotic relations in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) plants grown at various salinity levels. J Exp Bot 62:185–193
Hayashi H, Murata N (1998) Genetically engineered enhancement of salt tolerance in higher plants. In: Satoh K, Murata N (eds) Stress responses of photosynthetic organisms. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 133–148
Hewitt EJ (1966) Sand and water culture methods used in the study of plant nutrition. Technical communication 22. Commonwealth Bureau of horticulture plantation crops, GB
Jain D, Chattopadhyay D (2013) Role of DREB-like proteins in improving stress tolerance of transgenic crops. In: Tteja N, Gill SS (eds) Plant acclimation to environmental stress. Springer, New York, pp 147–161
Karaba A, Dixit S, Greco R, Aharoni A, Trijatmiko KR, Marsch-Martinez N, Krishnan A, Nataraja KN, Udayakumar M, Pereira A (2007) Improvement of water use efficiency in rice by expression of HARDY, an Arabidopsis drought and salt tolerance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5270–15275
Katembe WJ, Ungar IA, Mitchell JP (1998) Effect of salinity on germination and seedling growth of two Atriplex species (Chenopodiaceae). Ann Bot 82:167–175
Keiffer CH, Ungar IA (1997) The effects of extended exposure to hypersaline conditions on the germination of five inland halophytes species. Am J Bot 54:104–111
Khan MA, Ungar IA (1984) The effect of salinity and temperature on germination of polymorphic seeds and growth of Atriplex triangularis. Am J Bot 71:481–489
Khan MA, Ungar IA (1997) Effects of thermoperiod on recovery of seed germination of halophytes from saline conditions. Am J Bot 84:279–283
Khedr AA, Serag MS, Nemat-Alla MM, Abo-Elnaga AZ, Nada RM, Quick WP, Abogadallah GM (2011) A DREB gene from the xero-halophyte Atriplex halimus is induced by osmotic but not ionic stress and shows distinct differences from glycophytic homologues. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 106:191–206
Knight H, Knight MR (2001) Abiotic stress signalling pathways: specificity and cross-talk. Trends Plant Sci 6:262–267
Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, Abe H, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1998) Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and lowtemperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1391–1406
Macke AJ, Ungar IA (1971) The effect of salinity on germination and early growth of Puccinella nuttalliana. Can J Bot 49:515–520
Martınez JP, Ledent JF, Bajji M, Kinet JM, Lutts S (2003) Effect of water stress on growth, Na+ and K+ accumulation and water use efficiency in relation to osmotic adjustment in two populations of Atriplex halimus L. Plant Growth Regul 41:63–73
Martınez JP, Kinet JM, Bajji M, Lutts S (2005) NaCl alleviates polyethylene glycol-induced water stress in the halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. J Exp Bot 56:2421–2431
Meyer AM, Poljakoff-Mayber A (1963) The germination of seeds. Macmillan Company, New York, p 236
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140:411–432
Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozak K (2006) Regulons involved in osmotic stress-responsive and cold stress-responsive gene expression in plants. Physiol Plant 126:62–71
Niu X, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (1995) Ion homeostasis in NaCl stress environments. Plant Physiol 109:735–742
Orsini F, Accorsi M, Gianquinto G, Dinelli G, Antognoni FB, Carrascoc MartinezEA, Alnayef M, Marotti I, Bosi S, Biondi S (2011) Beyond the ionic and osmotic response to salinity in Chenopodium quinoa: functional elements of successful halophytism. Funct Plant Biol 38:818–831
Parida AK, Das AB (2005) Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 60:324–349
Parida AK, Das AB, Mohanty P (2004) Defense potentials to NaCl in a mangrove Brugieara parviflora: differential changes of isoforms of some antioxidant enzymes. J Plant Physiol 161:531–542
Petruzzelli L, Melillo MT, Zacheo TB, Taranto G (1992) Physiological and ultrastructural changes in isolated wheat embryos during salt and osmotic shock. Ann Bot 69:25–31
Poljakoff-Mayber A, Somers GF, Werker E, Gallagher JL (1994) Seeds of Kosteletzkya virginica (Malvacae): their structure, germination and salt tolerance. II. Germination and salt tolerance. Am J Bot 81:54–59
Rao KVM, Raghavendra AS, Reddy KJ (2006) Physiology and molecular biology of stress tolerance in plants. Springer, Netherlands, pp 191–200
Rhodes D, Hanson AD (1993) Quaternary ammonium and tertiary sulfonium compounds in higher plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 44:357–384
Sekmen AH, Turkan I, Tanyolac ZO, Ozfidan C, Dinc A (2012) Different antioxidant defense responses to salt stress during germination and vegetative stages of endemic halophyte Gypsophila oblanceolata Bark. Environ Exp Bot 77:63–76
Shabala S (2013) Learning from halophytes: physiological basis and strategies to improve abiotic stress tolerance in crops. Ann Bot 112:1209–1221
Short DC, Colmer TD (1999) Salt tolerance in the halophyte Haloscaria pergranulata subsp. Pergranulata. Ann Bot 83:207–213
Song J, Feng G, Tian C, Zhang F (2005) Strategies for adaptation of Suaeda physophora, Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum to a saline environment during seed-germination stage. Ann Bot 96:399–405
Turkan I, Demiral T (2009) Recent developments in understanding salinity tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 67:2–9
Undurraga SF, Santos MP, Paez-Valencia J, Yang H, Hepler PT, Facanha AR, Hirschi KD, Gaxiola RA (2012) Arabidopsis sodium dependent and independent phenotypes triggered by H +-PPase up-regulation are SOS1 dependent. Plant Sci 183:96–105
Ungar IA (1982) Germination ecology of halophytes. In: Sen DN, Rajpurohit KS (eds) Contributions to the ecology of halophytes. Dr. W. Junk Publishers, The Hague, pp 143–154
Ungar IA (1995) Seed germination and seed-bank ecology of halophytes. In: Kigel J, Galili G (eds) Seed development and germination. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 599–627
Ungar IA (1996) Effect of salinity on seed germination, growth, and ion accumulation of Atriplex patula (Chenopodiaceae). Am J Bot 83:604–607
Volkmar KM, Hu Y, Steppuhn H (1998) Physiological responses of plants to salinity: a review. Can J Plant Sci 78:19–27
Waisel Y, Ovadia S (1972) Biological flora of Israel. Suaeda monica Forsk. Ex J. F. Gmel. Israel J Bot 21:42–52
Winicov L, Bastola DR (1997) Salt tolerance in crop plants: new approaches through tissue culture and gene regulation. Acta Physiol Plant 19:435–449
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1994) A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell 6:251–264
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular response and the tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Ann Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Yeo AR (1981) Salt tolerance in the halophyte Suaeda maritima (L.) Dum.: intracellular compartmentation of ions. J Exp Bot 32:487–497
Yeo A, Flowers T (1986) Ion transport in Suaeda maritima: its relation to growth and implications for the pathway of radial transport of ions across the root. J Exp Bot 37:143–159
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Ann Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Zimmermann P, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Hennig L, Gruissem W (2004) Genevestigator: arabidopsis microarray database and analysis toolbox. Plant Physiol 136:2621–2632
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to Prof W. Paul Quick, Department of Animal and Plant Sciences, University of Sheffield, UK, for hosting this work. Thanks are also due to the Department of Missions, Egypt, for sponsoring and funding the researcher’s visit to UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nada, R.M., Abogadallah, G.M. Developmental acquisition of salt tolerance in the halophyte Atriplex halimus L. is related to differential regulation of salt inducible genes. Plant Growth Regul 75, 165–178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9941-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9941-9