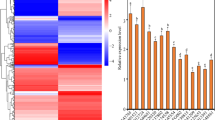
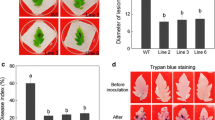
Abstract
WRKY proteins are a superfamily of plant transcriptional factors with potential regulatory roles pertaining to a variety of biotic and abiotic stress responses. In this study, we investigated the expression profiles of OsWRKY23 under different developmental stages, pathogen infection, continuous-dark and hormone treatments. Under normal growth conditions, OsWRKY23 expressed exclusively in roots and senescing leaves. Under biotic and abiotic stresses treatments, OsWRKY23 was markedly induced by continuous-dark-induced leaf senescence and infection by rice pathogen Pyricularia oryzae Cav as well as salicylic acid (SA). Further analysis of 35S:OsWRK23 Arabidopsis plants showed that over-expression of OsWRKY23 resulted in enhanced expression of the pathogenesis-related (PR) genes and increased resistance to the bacterial pathogen Pseudomanas syringae. Furthermore, over-expression of OsWRKY23 accelerated leaf senescence in darkness. The senescence-associated marker genes SAG12 and SEN1 were altered in darkness in 35S:WRKY23 Arabidopsis plants. In conclusion, these results suggest that OsWRKY23 is a novel modulator of pathogen responses as well as dark-induced leaf senescence.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ACC:
-
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
- ET:
-
Ethylene
- HR:
-
Hypersensitive response
- JA:
-
Jasmonate
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MeJA:
-
Methyl jasmonic acid
- PAMPs:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- PCD:
-
Programmed cell death
- PR:
-
Pathogenesis related
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- SAR:
-
Systemic acquired resistance
References
Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J (2002) MAP kinase signaling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415:977–983. doi:10.1038/415977a
Babu MM, Iyer LM, Balaji S, Aravind L (2006) The natural history of the WRKY-GCM1 zinc fingers and the relationship between transcription factors and transposons. Nucleic Acids Res 34:6505–6520. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl888
Bouche N, Bouchez D (2001) Arabidopsis gene knockout: phenotypes wanted. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:111–117. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00145-X
Buchanan-Wollaston V, Page T, Harrison E, Breeze E, Lim PO, Nam HG, Lin JF, Wu SH, Swidzinski J, Ishizaki K, Leaver CJ (2005) Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals significant differences in gene expression and signalling pathways between developmental and dark/starvation-induced senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J 42:567–585. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02399.x
Catalino N, Somssich I, Roby D, Kroj T (2006) The transcription factors WRKY11 and WRKY17 act as negative regulators of basal resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 18:3289–3302. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.044149
Chen C, Chen Z (2002) Potentiation of developmentally regulated plant defense response by AtWRKY18, a pathogen-induced Arabidopsis transcription factor. Plant Physiol 129:706–716. doi:10.1104/pp.001057
Dai X, Xu Y, Ma Q, Xu W, Wang T, Xue Y, Chong K (2007) Overexpression of a R1R2R3 MYB Gene, OsMYB3R–2, increases tolerance to freezing, drought, and salt stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1739–1751. doi:10.1104/pp.106.094532
Devaiah BN, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG (2007) WRKY75 transcription factor is a modulator of phosphate acquisition and root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1789–1801. doi:10.1104/pp.106.093971
Dong X (1998) SA, JA, ethylene, and disease resistance in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:316–323. doi:10.1016/1369-5266(88)80053-0
Dong J, Chen C, Chen Z (2003) Expression profiles of the Arabidopsis WRKY gene superfamily during plant defense response. Plant Mol Biol 51:21–37. doi:10.1023/A:1020780022549
Du L, Chen Z (2000) Identification of genes encoding receptor-like protein kinases as possible targets of pathogen- and salicylic acid-induced WRKY DNA-binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant J 24:837–847. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00923.x
Dubouzet J, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Dubouzet E, Miura S, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J 33:751–763. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01661.x
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2000) The WRKY superfamily of plant transcriptional factors. Trends Plant Sci 5:199–206. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(00)01600-9
Glazebrook J (2005) Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:205–227. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.040204.135923
Guo FQ, Crawford NM (2005) Arabidopsis nitric oxide synthase1 is targeted to mitochondria and protects against oxidative damage and dark-induced senescence. Plant Cell 17:3436–3450. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.037770
Guo Y, Cai Z, Gan S (2004) Transcriptome of Arabidopsis leaf senescence. Plant Cell Environ 27:521–549. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2003.01158.x
Hanaoka H, Noda T, Shirano Y, Kato T, Hayashi H, Shibata D, Tabata S, Ohsumi Y (2002) Leaf senescence and starvation-Induced chlorosis are accelerated by the disruption of an Arabidopsis autophagy gene. Plant Physiol 129:1181–1193. doi:10.1104/pp.011024
Hinderhofer K, Zentgraf U (2001) Identification of a transcription factor specifically expressed at the onset of leaf senescence. Planta 213:469–473. doi:10.1007/s004250000512
Koch E, Slusarenko A (1990) Arabidopsis is susceptible to infection by a downy mildew fungus. Plant Cell 2:437–445
Li J, Brader G, Palva T (2004) The WRKY70 transcription factor: a node of convergence for Jasmonate-mediated and salicylate-mediated signals in plant defense. Plant Cell 16:319–331. doi:10.1105/tpc.016980
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Lin JF, Wu SH (2004) Molecular events in senescing Arabidopsis leaves. Plant J 39:612–628. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02160.x
Lohman K, Gan S, John M, Amasino RM (1994) Molecular analysis of natural leaf senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 92:322–328. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1994.tb05343.x
Maleck K, Levine A, Eulgem T, Morgan A, Schmid J, Lawton K, Dangl J, Dietrich R (2000) The transcriptome of Arabidopsis thaliana during systemic acquired resistance. Nat Genet 26:403–410. doi:10.1038/82521
Mangelsen E, Kilian J, Berendzen K, Kolukisaoglu Ü, Harter K, Jansson C, Wanke D (2008) Phylogenetic and comparative gene expression analysis of barley (Hordeum vulgare) WRKY transcription factor family reveals putatively retained functions between monocots and dicots. BMC Genomics 9:194. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-194
Miao Y, Zentgraf U (2007) The antagonist function of Arabidopsis WRKY53 and ESR/ESP in leaf senescence is modulated by the Jasmonic and salicylic acid equilibrium. Plant Cell 19:819–830. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.042705
Miao Y, Laun T, Zimmermann P, Zentgraf U (2004) Targets of the WRKY53 transcription factor and its role during leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 55:853–867
Miao Y, Laun TM, Smykowski A (2007) Arabidopsis MEKK1 can take a short cut: it can directly interact with senescence related WRKY53 transcription factor on the protein level and can bind to its promoter. Plant Mol Biol 65:63–76. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9198-z
Oh SA, Lee SY, Chung IK, Lee CH, Nam HG (1996) A senescence associated gene of Arabidopsis thaliana is distinctively regulated during natural and artificially induced leaf senescence. Plant Mol Biol 30:739–754. doi:10.1007/BF00019008
Qiu Y, Yu D (2009) Over-expression of the stress-induced OsWRKY45 enhances disease resistance and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Environ Exp Bot 65:35–47. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.07.002
Qiu Y, Jing S, Fu J, Li L, Yu D (2004) Cloning and analysis of expression profile of 13 WRKY genes in rice. Chin Sci Bull 49:2159–2168. doi:10.1360/982004-183
Qiu D, Xiao J, Ding X, Xiong M, Cai M, Cao Y, Li X, Xu C, Wang S (2007) OsWRKY13 mediates rice disease resistance by regulating defense-related genes in salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent signaling. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:492–499. doi:10.1094/MPMI-20-5-0492
Ramamoorthy R, Jiang SY, Kumar N, Prasanna NV, Ramachandran S (2008) A comprehensive transcriptional profiling of the WRKY gene family in rice under various abiotic and phytohormone treatments. Plant Cell Physiol 49:865–879. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcn061
Robatzek S, Somssich I (2001) A new nember of the Arabidopsis WRKY transcription factor family, AtWRKY6, is associated with both senescence and defense-related processes. Plant J 28:123–133. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01131.x
Robatzek S, Somssich I (2002) Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense. Genes Dev 16:139–149. doi:10.1101/gad.222702
Ross CA, Liu Y, Shen QX (2007) The WRKY gene family in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 49:827–842. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00504.x
Shen QH, Saijo Y, Mauch S, Biskup C, Bieri S, Keller B, Seki H, Ulker B, Somssich E, Schulze-Lefert P (2007) Nuclear activity of MLA immune receptors links isolate-specific and basal disease-resistance responses. Science 315:1089–1103. doi:10.1126/science.1136372
Shimono M, Sugano S, Nakayama A, Jiang C, Ono K, Toki S (2007) Rice WRKY45 plays a crucial role in benzothiadiazole-inducible blast resistance. Plant Cell 10:1105–1118
Weaver LM, Gan S, Quirino B, Amasino RM (1998) A comparison of the expression patterns of several senescence-associated genes in response to stress and hormone treatment. Plant Mol Biol 37:455–469. doi:10.1023/A:1005934428906
Wu KL, Guo ZJ, Wang HH, Li J (2005) The WRKY family of transcription factors in rice and Arabidopsis and their origins. DNA Res 12:9–26. doi:10.1093/dnares/12.1.9
Xie Z, Zhang ZL, Zou X, Huang J, Ruas P, Thompson D, Shen QJ (2005) Annotations and functional analyses of the rice WRKY gene superfamily reveal positive and negative regulators of abscisic acid signaling in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol 137:176–189. doi:10.1104/pp.104.054312
Xu X, Chen C, Fan B, Chen Z (2006) Physical and functional interactions between pathogen-induced Arabidopsis WRKY18, WRKY40, and WRKY60 transcription factors. Plant Cell 18:1310–1326. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.037523
Yoshida S (2003) Molecular regulation of leaf senescence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:79–84. doi:10.1016/S1369526602000092
Yu D, Chen C, Chen Z (2001) Evidence for an important role of WRKY DNA binding protein in the regulation of NPR1 gene expression. Plant Cell 13:1527–1539
Zhang YJ, Wang LJ (2005) The WRKY transcription factor superfamily: its origin in eukaryotes and expansion in plants. BMC Evol Biol 5:1. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-5-1
Zhang ZL, Xie Z, Zou X, Casaretto J, Ho TH, Shen QJ (2004) A rice WRKY gene encodes a transcriptional repressor of the gibberellin signaling pathway in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol 134:1500–1513. doi:10.1104/pp.103.034967
Zheng Z, Qamar S, Chen Z, Mengiste T (2006) Arabidopsis WRKY33 transcription factor is required for resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant J 48:592–605. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02901.x
Zhou B, Peng K, Zhao C, Wang S, Zhang Q (2002) The defense-responsive genes showing enhanced and repressed expression after pathogen infection in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci China C Life Sci 45:449–467. doi:10.1360/02yc9050
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Zhixiang Chen (Department of Botany and Plant Pathology, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA) and Mr. Eric McDowell (Department of Plant Sciences, University of Arizona) for critically reading the manuscript. We would like to thank National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences of Japan for rice cDNA clones.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10725_2009_9366_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 1 Normal responses of 35S:WRKY23 plants to Botrytis cinerea. (a) Disease responses of drop-inoculated plants at 7 days. (b) Expression of PDF1.2 during Botrytis cinerea infection (TIFF 19237 kb)
10725_2009_9366_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 2 Normal responses of 35S:WRKY23 plants to ACC treatment. (a) Images taken at 4 and 10 days after ACC spraying. (b) Expression of SAG12 and SEN1 during ACC-induced senescence (TIFF 10313 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, S., Zhou, X., Song, Y. et al. Heterologous expression of OsWRKY23 gene enhances pathogen defense and dark-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis . Plant Growth Regul 58, 181–190 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-009-9366-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-009-9366-z