Abstract
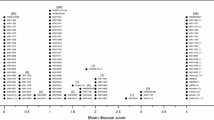
Unlocking resistance genes in genbank collections are of prime importance for securing sustainable crop production. In this regard, the Serbian GenBank barley collection, comprising 93 local landraces and 36 commercial cultivars and elite barley breeding lines, was screened for novel resistances to powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei) using a set of 28 isolates with a wide spectrum of virulences/avirulences. No line was resistant to all the isolates, but one and three accessions showed resistance to 27 and 26 isolates, respectively. Twenty landraces (21.51 %) and ten cultivars (27.78 %) exhibited resistance to 50 % of the isolates. Infection type 2 was most frequent among resistant accessions. Nine B. graminis isolates were sufficient for gene postulation in 73 barley lines. In total, thirty-five different resistance spectra were recorded and the following known resistance genes were postulated namely, Mlra, Mlh, Mla12, Mla7(Mlu), Mlg, MlLa, Mla6, Mla7, Mlt, Mla22, Mlat, Mla1, Mlk. The majority of resistance profiles was constituted by only one line. Unidentified genes alone or in combination were proposed for twenty landraces and six cultivars. This report demonstrated that the barley collection held at the Serbian GenBank could be exploited as a new source for powdery mildew resistance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (1991) Specific recommendation B designations of barley powdery mildew resistance and virulence in Europe. In: Jørgensen JH (ed) Integrated control of cereal mildews: virulence patterns and their change. Risø National Laboratory, Roskilde, pp 12–14
Backes G, Hatz B, Jahoor A, Fischbeck G (2003) RFLP diversity within and between major groups of barley in Europe. Plant Breed 122:291–299
Balkema-Boomstra AG, Mastebroek HD (1995) Effect of powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei) on photosynthesis and grain yield of partially resistant genotypes of spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Breed 114:126–130
Beschreibende Sortenliste (2013) Getreide, Mais, Öl- und Faserpflanzen, Leguminosen, Rüben, Zwischenfrüchte. Bundessortenamt, Hannover, BSA, pp 296
Biffen RK (1907) Studies on the inheritance of disease resistance. J Agric Sci 2:109–128
Brown JKM, Jørgensen JH (1991) A catalogue of mildew resistance genes in European barley varieties. In: Jørgensen JH (ed) Integrated control of cereal mildews: virulence patterns and their change. Risø National Laboratory, Roskilde, pp 263–286
Ceccarelli S, Grando S, van Leur JAG (1995) Barley landraces of the fertile crescent offer new breeding options for stress environments. Diversity 11:112–113
Ceccarelli S, Grando S, Tutwiler R, Baha J, Martini AM, Salahieh H, Goodchild A, Michael M (2000) A methodological study on participatory barley breeding I. Selection phase. Euphytica 111:91–104
Cox TS, Murphy JP, Rodgers DM (1986) Changes in genetic diversity in the red winter wheat regions of the United States. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:5583–5586
Czembor JH (1996) Presence and expression of resistance genes to powdery mildew of barley in selections from Tunisian barley landraces. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Plant Pathology, Montana State University, Bozeman, USA
Czembor JH (1999) Resistance to powdery mildew in barley landraces from Tunisia. Plant Breed Seed Sci 43:49–65
Czembor JH (2000) Resistance to powdery mildew in barley landraces from Morocco. J Plant Pathol 82:187–200
Czembor JH (2001) Resistance to powdery mildew in selections from barley landraces collected in Greece. Agric Food Sci Finl 10:133–142
Czembor JH, Czembor HJ (1999) Resistance to powdery mildew in barley landraces collected from Jordan. Plant Breed Seed Sci 43:67–83
Czembor JH, Czembor HJ (2000) Powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei) resistance in Moroccan barley landraces. Bulg J Agric Sci 6:271–284
Czembor HJ, Czembor JH (2001) Resistance to powdery mildew in barley cultivars and breeding lines included in 1998–2000 Polish registration trials. Plant Breed Seed Sci 45:21–41
Czembor JH, Frese L (2003) Powdery mildew resistance in selections from barley landraces collected from Turkey. Die Bodenkultur 54:35–40
Czembor HJ, Gacek ES (1990) Selected problems of the disease resistance breeding of cereals. Biuletyn IHAR 173–174:53–62
Czembor HJ, Gacek ES (1995) Systems for increasing durability of disease resistance in cereals. In: Arseniuk E, Góral T, Czembor PC (eds) Proceedings of second symposium on Plant Resistance to Diseases, Pests and Unfavourable Environmental symposium on Conditions, IHAR Radzików, Poland, pp 39–48
Dreiseitl A (2007) Powdery mildew resistance in winter barley cultivars. Plant Breed 126:268–273
Dreiseitl A (2011) Resistance of ‘Laverda’ to powdery mildew and its presence in some winter barley cultivars. Cereal Res Commun 39:569–576
Dreiseitl A (2012) Identity of barley powdery mildew resistances Bw and Ru2. Czech J Gen Plant Breed 48:185–188
Dreiseitl A (2013a) Genes for resistance to powdery mildew in European winter barley cultivars registered in the Czech Republic and Slovakia to 2010. Plant Breed 132:558–562
Dreiseitl A (2013b) Postulation of genes for resistance to powdery mildew in spring barley cultivars registered in the Czech Republic from 1996 to 2010. Euphytica 191:183–489
Dreiseitl A, Rashal I (2004) Powdery mildew resistance genes in Latvian barley varieties. Euphytica 135:325–332
Dreiseitl A, Yang J (2007) Powdery mildew resistance in a collection of Chinese barley varieties. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:259–266
Dunn JO (1964) Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 6:241–252
FAO (2012) FAOSTAT. http://faostat.fao.org/site/370/default.aspx. Accessed 10 Apr 2014
Feuillet C, Langridge P, Waugh R (2007) Cereal breeding takes a walk on the wild side. Trends Genet 24:24–32
Fischbeck G, Jahoor A (1991) The transfer of genes for mildew resistance from Hordeum spontaneum. In: Jørgensen JH (ed) Integrated control of cereal mildews: virulence patterns and their change. Risø National Laboratory, Roskilde, pp 247–255
Flor HH (1971) Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Ann Rev Phytopathol 9:275–296
Freialdenhoven A, Scherag B, Hollricher K, Collinge DB, Thordal-Christensen H, Schulze-Lefert P (1994) Nar-1 and Nar-2, two loci required for Mla12-specified racespecific resistance to powdery mildew in barley. Plant Cell 6:983–994
Friedt W, Ordon F (2007) Molecular markers for gene pyramiding and disease resistance breeding in barley. In: Varshney RV, Tuberosa R (eds) Genomics-assisted crop improvement, vol 2. Genomics application in crops. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 81–101
Gilmour J (1973) Octal notation for designating physiologic races of plant pathogens. Nature 242:620
Gururani MA, Venkatesh J, Upadhyaya CP, Nookaraju A, Pandey SK, Park SW (2012) Plant disease resistance genes: current status and future directions. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 78:51–65
Hamblin MT, Close TJ, Bhat PR, Chao S, Kling JG et al (2010) Population structure and linkage disequilibrium in U.S. barley germplasm: implications for association mapping. Crop Sci 50:556–566
Heitefuss R, Ebrahim-Nesbat F, Ordonez MT, Schorn-Kasten K (1997) Investigations on adult plant resistance of barley against Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei. J Phytopathol 145:177–184
Herrmann A, Löwer CF, Schachtel GA (1999) A new tool for entry and analysis of virulence data for plant pathogens. Plant Pathol 48:154–158
Honecker L (1938) Über die physiologische Spezialisierung des Gerstenmeltaues als Grundlage für die Immunitätszüchtung. Züchter 10:169–181
Honecker L (1942) Erbanalytische Untersuchungen über das Verhalten der Gerste gegenüber verschiedenen physiologischen Rassen des Mehltaues (Erysiphe graminis hordei Marchal). Zeitschrift für Pflanzenzüzchtung 24:429–506
Hovmoller MS, Caffier V, Jalli M, Andersen O, Besenhofer G et al (2000) The European barley powdery mildew virulence survey and disease nursery 1993–1999. Agronomie 20:729–743
Huckelhoven R, Fodor J, Trujillo M, Kogel KH (2000) Barley Mla and Rar mutants compromised in the hypersensitive cell death response against Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei are modified in their ability to accumulate reactive oxygen intermediates at sites of fungal invasion. Planta 212:16–24
Jahoor A (1986) Mehltauresistenz israelischer Wildgersten-Resistenzspektrum, Vererbung und Lokalisierung. Dissertation, Technische Universität München, Freising-Weihenstephan
Jahoor A, Fischbeck G (1987) Genetical studies of resistance of powdery mildew in barley lines derived from Hordeum spontaneum collected from Israel. Plant Breed 99:265–273
Jahoor A, Fischbeck G (1993) Identification of new genes for mildew resistance of barley at the Mla locus in lines derived from Hordeum spontaneum. Plant Breed 110:116–122
Jakob SS, Rödder D, Engler JO, Shaaf S, Özkan H, Blattner FR, Kilian B (2014) Evolutionary history of wild barley (Hordeum vulgare subsp. spontaneum) analyzed using multilocus sequence data and paleodistribution modeling. Genome Biol Evol 6:685–702
Jensen HP (1995) Presence of barley powdery mildew resistance gene Mla8 in some ‘Pallas’ near-isogenic barley lines. Barley Genet Newsl 24:71–74
JMP Genomics 5.1. SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, USA
Jørgensen JH (1994) Genetics of powdery mildew resistance in barley. Crit Rev Plant Sci 13:97–119
Jørgensen JH, Jensen HP (1997) Powdery mildew resistance in barley landrace material I. Screening for resistance. Euphytica 97:227–233
Knüpffer H, Maggioni L, Jalli M, Kolodinska A, Brantestam D, Fasoula E and Lipman T (2011) Report of a working group on barley–seventh meeting 10–12th May 2011, Nicosia, Cyprus, Bioversity International, Rome. http://www.bioversityinternational.org/nc/publications/publication/issue/report_of_a_working_group_on_barley.html
Kølster P, Munk L, Stølen O, Løhde J (1986) Near-isogenic barley lines with genes for resistance to powdery mildew. Crop Sci 26:903–907
König J, Steffenson B, Kopahnke D, Przulj N, Romeis T, Ordon F, Perović D (2012) Genetic mapping of novel leaf rust (Puccinia hordei Otth) resistance in barley landrace MBR1012. Mol Breed 30:1253–1264
Kruger WM, Carver TLW, Zeyen RJ (2002) Phenolic inhibition of penetration resistance to Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei in barley near isogenic lines containing seven independent resistance genes or alleles. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 61:41–51
Kruger WM, Szabo L, Zeyen RJ (2003) Transcription of the defense response genes chitinase IIb, PAL and peroxidase is induced by the barley powdery mildew fungus and is only indirectly modulated by R genes. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 63:167–178
Lopez PB (1994) A new plant disease: uniformity. CERES 26:41–47
Morrell PL, Clegg MT (2007) Genetic evidence for a second domestication of barley (Hordeum vulgare) east of the Fertile Crescent. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3289–3294
Panstruga R, Molina-Cano JL, Reinstadler A, Müller J (2005) Molecular characterization of mlo mutants in North American two and six-rowed malting barley cultivars. Mol Plant Pathol 6:315–320
Perović D, Przulj N, Milovanovic M, Prodanovic S, Perović J, Kopahnke D, Ordon F, Graner A (2001) Characterisation of spring barley genetic resources in Yugoslavia. In: Proceedings of a symposium dedicated to the 100th birthday of Rudolf Mansfeld, Schriften zu Genetischen Ressourcen, Band 22:301–306
Pourkheirandish M, Komatsuda T (2007) The importance of barley genetics and domestication in a global perspective. Ann Bot 100:999–1008
Repkova J, Dreiseitl A (2010) Candidate markers for powdery mildew resistance genes from wild barley PI284752. Euphytica 175:283–292
SAS Institute (1988) SAS/STATTM user’s guide, release 6.03. Edition. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc., p 1028
Schönfeld M, Ragni A, Fischbeck G, Jahoor A (1996) RFLP mapping of three new loci for resistance genes to powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei) in barley. Theor Appl Genet 93:48–56
Silvar C, Flath K, Kopahnke D, Gracia MP, Lasa JM, Casas AM, Igartua E, Ordon F (2011) Analysis of powdery mildew resistance in the Spanish barley core collection. Plant Breed 130:195–2003
Silvar C, Perović D, Nussbaumer T, Spannagl M, Usadel B, Casas A, Igartua E, Ordon F (2013) Towards positional isolation of three quantitative trait loci conferring resistance to powdery mildew in two Spanish barley landraces. PLoS One 8:e67336
Singh RP, Hodson DP, Jin Y, Huerta-Espino J, Kinyua MG, Wanyera R, Njau P, Ward RW (2006) Current status, likely migration and strategies to mitigate the threat to wheat production from race Ug99 (TTKS) of stem rust pathogen. CAB Rev Perspect Agric Vet Sci Nutr Nat Resour 1:1–13
Surlan-Momirovic G, Krämer I, Bratkovic K, Zoric M, Momirovic U, Brankovic G, Calic I, Kandic V, Przulj N, Ordon F, Perović D (2013) Molecular characterization of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) accessions of the Serbian Genebank by SSR fingerprinting. Genetika 45:167–180
Valz PD, Thompson ME (1994) Exact Inference for Kendall’s S and Spearman’s Rho with extensions to fisher’s exact test in contingency tables. J Comput Graph Stat 3:459–472
Ward JH (1963) Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J Am Stat Assoc 58:236–244
Wolfe MS, McDermott JM (1994) Population genetics of plant pathogen interactions: the example of the Erysiphe graminis-Hordeum vulgare pathosystem. Ann Rev Phytopathol 32:89–113
Yahyaoui AH, Reinhold M, Scharen AL (1997) Virulence spectrum in populations of barley powdery mildew pathogen, Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei in Tunisia and Morocco in 1992. Plant Pathol 46:139–146
Zhang Z, Henderson C, Perfect E, Carver TLW, Thomas BJ, Skamnioti P, Gurr SJ (2005) Of genes and genomes, needles and haystacks: Blumeria graminis and functionality. Mol Plant Pathol 6:561–575
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) and was conducted at the Julius Kühn-Institut (JKI), Federal Research Centre for Cultivated Plants, Institute for Plant Protection in Field Crops and Grassland, Kleinmachnow, Germany. This work was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Serbia (Grant No. TR31092).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10722_2015_246_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Hierachical clustering of the infection types for the mildew isolates in a set of 30 differential barley lines. (TIFF 7297 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šurlan-Momirović, G., Flath, K., Silvar, C. et al. Exploring the Serbian GenBank barley (Hordeum vulgare L. subsp. vulgare) collection for powdery mildew resistance. Genet Resour Crop Evol 63, 275–287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-015-0246-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-015-0246-2