Abstract
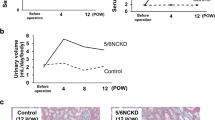
Sulfatide is a major component of glycosphingolipids in lipoproteins. Recently, we reported that a low serum level of sulfatide in hemodialysis patients might be related to the high incidence of cardiovascular diseases. However, the serum kinetics of sulfatide in kidney disease patients and the function of endogenous serum sulfatide are still unclear. To obtain novel knowledge concerning these issues, we investigated the serum kinetics of sulfatide in 5 adult kidney transplant recipients. We also analyzed the correlated factors influencing the serum sulfatide level, using multiple regression analysis. Kidney transplantation caused a dramatic increase of serum sulfatide without an alteration of its composition in all recipients in a time-dependent manner; however, the recovery speed was slower than that of the improvement of kidney function and the serum sulfatide reached a nearly normal level after 1 year. Multiple regression analysis showed that the significant correlated factor influencing the serum sulfatide level was log duration (time parameter) throughout the observation period, and the correlated factors detected in the stable phase were the decrease of serum concentration of malondialdehyde (an oxidative stress marker) as well as the elevation of platelet count. The current study results demonstrated the gradual but reliable recovery of the serum sulfatide level in kidney transplant recipients for the first time, suggesting a close correlation between serum sulfatide and kidney function. The recovery of serum sulfatide might derive from the attenuation of systemic oxidative stress. The normal level of serum sulfatide in kidney transplant recipients might affect platelet function, and contribute to the reduction of cardiovascular disease incidence.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKI:
-
Acute kidney injury
- CST:
-
Cerebroside sulfotransferase
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- GP:
-
Glycoproteins
- HD:
-
Hemodialysis therapy
- LS:
-
Lysosulfatide
- d18:2:
-
Sphingadienine
- d18:1:
-
(4E)-sphingenine
- d18:0:
-
Sphinganine
- t18:0:
-
Phytosphingosine
- d20:1:
-
(4E)-icosasphingenine
- d20:0:
-
Icosasphinganine
- t20:0:
-
4D-hydroxyicosasphinganine
- MALDI-TOF MS:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- PD:
-
Peritoneal dialysis therapy
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- vWF:
-
Von Willebrand factor
References
Ishizuka, I.: Chemistry and functional distribution of sulfoglycolipids. Prog Lipid Res 36, 245–319 (1997)
Honke, K., Zhang, Y., Cheng, X., Kotani, N., Taniguchi, N.: Biological roles of sulfoglycolipids and pathophysiology of their deficiency. Glycoconj J 21, 59–62 (2004)
Nagai, K., Tadano-Aritomi, K., Niimura, Y., Ishizuka, I.: Higher expression of renal sulfoglycolipids in marine mammals. Glycoconj J 25, 723–726 (2008)
Hara, A., Taketomi, T.: Occurrence of sulfatide as a major glycosphingolipid in WHHL rabbit serum lipoproteins. J Biochem 102, 83–92 (1987)
Zhu, X.H., Hara, A., Taketomi, T.: The existence of galactosylceramide I3-sulfate in serums of various mammals and its anticoagulant activity. J Biochem 110, 241–245 (1991)
Kyogashima, M.: The role of sulfatide in thrombogenesis and haemostasis. Arch Biochem Biophys 426, 157–162 (2004)
Hara, A., Taketomi, T.: Characterization and changes of glycosphingolipids in the aorta of the Watanabe hereditable hyperlipidemic rabbit. J Biochem 109, 904–908 (1991)
Hara, A., Uemura, K., Taketomi, T.: Sulfatide prolongs blood-coagulation time and bleeding time by forming a complex with fibrinogen. Glycoconj J 13, 187–194 (1996)
Hu, R., Li, G., Kamijo, Y., Aoyama, T., Nakajima, T., Inoue, T., Node, K., Kannagi, R., Kyogashima, M., Hara, A.: Serum sulfatides as a novel biomarker for cardiovascular disease in patients with end-stage renal failure. Glycoconj J 24, 565–571 (2007)
Zhang, X., Nakajima, T., Kamijo, Y., Li, G., Hu, R., Kannagi, R., Kyogashima, M., Aoyama, T., Hara, A.: Acute kidney injury induced by protein-overload nephropathy down-regulates gene expression of hepatic cerebroside sulfotransferase in mice, resulting in reduction of liver and serum sulfatides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390, 1382–1388 (2009)
Matsuo, S., Imai, E., Horio, M., Yasuda, Y., Tomita, K., Nitta, K., Yamagata, K., Tomino, Y., Yokoyama, H., Hishida, A.: Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR: revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis 53, 982–992 (2009)
Hara, A., Radin, N.S.: Lipid extraction of tissues with a low-toxicity solvent. Anal Biochem 90, 420–426 (1978)
Li, G., Hu, R., Kamijo, Y., Nakajima, T., Aoyama, T., Inoue, T., Node, K., Kannagi, R., Kyogashima, M., Hara, A.: Establishment of a quantitative, qualitative, and high-throughput analysis of sulfatides from small amounts of sera by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 362, 1–7 (2007)
Sugiyama, E., Hara, A., Uemura, K.: A quantitative analysis of serum sulfatide by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry with delayed ion extraction. Anal Biochem 274, 90–97 (1999)
Aoyama, T., Peters, J.M., Iritani, N., Nakajima, T., Furihata, K., Hashimoto, T., Gonzalez, F.J.: Altered constitutive expression of fatty acid-metabolizing enzymes in mice lacking the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha). J Biol Chem 273, 5678–5684 (1998)
Aoyama, T., Uchida, Y., Kelley, R.I., Marble, M., Hofman, K., Tonsgard, J.H., Rhead, W.J., Hashimoto, T.: A novel disease with deficiency of mitochondrial very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 191, 1369–1372 (1993)
Aoyama, T., Yamano, S., Waxman, D.J., Lapenson, D.P., Meyer, U.A., Fischer, V., Tyndale, R., Inaba, T., Kalow, W., Gelboin, H.V., Gonzalez, F.J.: Cytochrome P-450 hPCN3, a novel cytochrome P-450 IIIA gene product that is differentially expressed in adult human liver. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence and distinct specificities of cDNA-expressed hPCN1 and hPCN3 for the metabolism of steroid hormones and cyclosporine. J Biol Chem 264, 10388–10395 (1989)
Roberts, D.D., Rao, C.N., Magnani, J.L., Spitalnik, S.L., Liotta, L.A., Ginsburg, V.: Laminin binds specifically to sulfated glycolipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82, 1306–1310 (1985)
Roberts, D.D., Haverstick, D.M., Dixit, V.M., Frazier, W.A., Santoro, S.A., Ginsburg, V.: The platelet glycoprotein thrombospondin binds specifically to sulfated glycolipids. J Biol Chem 260, 9405–9411 (1985)
Roberts, D.D., Williams, S.B., Gralnick, H.R., Ginsburg, V.: Von Willebrand factor binds specifically to sulfated glycolipids. J Biol Chem 261, 3306–3309 (1986)
Merten, M., Thiagarajan, P.: Role for sulfatides in platelet aggregation. Circulation 104, 2955–2960 (2001)
Jones, J.C., Dehart, G.W., Gonzales, M., Goldfinger, L.E.: Laminins: an overview. Microsc Res Tech 51, 211–213 (2000)
Hawiger, J.: Mechanisms involved in platelet vessel wall interaction. Thromb Haemost 74, 369–372 (1995)
Borthakur, G., Cruz, M.A., Dong, J.F., McIntire, L., Li, F., López, J.A., Thiagarajan, P.: Sulfatides inhibit platelet adhesion to von Willebrand factor in flowing blood. J Thromb Haemost 1, 1288–1295 (2003)
Sarnak, M.J., Levey, A.S., Schoolwerth, A.C., Coresh, J., Culleton, B., Hamm, L.L., McCullough, P.A., Kasiske, B.L., Kelepouris, E., Klag, M.J., Parfrey, P., Pfeffer, M., Raij, L., Spinosa, D.J., Wilson, P.W., American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention: Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation 108, 2154–2169 (2003)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by GL Sciences (Tokyo, Japan) and Shinshu Public Utility Foundation for the Promotion of Medical Sciences (Matsumoto, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lixuan Wang and Yuji Kamijo contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Kamijo, Y., Matsumoto, A. et al. Kidney transplantation recovers the reduction level of serum sulfatide in ESRD patients via processes correlated to oxidative stress and platelet count. Glycoconj J 28, 125–135 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-011-9329-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-011-9329-2