Abstract
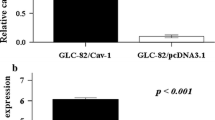
GD1a was previously shown responsible for regulating cell motility, cellular adhesiveness to vitronectin, phosphorylation of c-Met and metastatic ability of mouse FBJ osteosarcoma cells. To determine the particular molecules regulated by GD1a, FBJ cells were assessed for tumor-related gene expression by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. Caveolin-1 and stromal interaction molecule 1 (Stim1) expression in FBJ-S1 cells, rich in GD1a, were found to be 6 and 4 times as much, respectively, than in FBJ-LL cells devoid of GD1a. Enhanced production of caveolin-1 in protein was confirmed by Western blotting. A low-metastatic FBJ-LL cell variant, having high GD1a expression through β1-4GalNAcT-1 (GM2/GD2 synthase) cDNA transfection (Hyuga S, et al, Int J Cancer 83: 685-91, 1999), showed enhanced production of caveolin-1 and Stim1 in mRNA and protein, compared to mock-transfectant M5. Incubation of FBJ-M5 cells with exogenous GD1a augmented the expression of caveolin-1 in mRNA and protein and Stim1 in mRNA as well. Treatment of FBJ-S1 with fumonisin B1, an inhibitor of N-acylsphinganine synthesis, for 15 days caused the complete depletion of gangliosides and suppressed the expression of caveolin-1 and Stim1. St3gal5 siRNA transfected cells showed decreased expression of caveolin-1 and Stim1 mRNA, as well as St3gal5 mRNA. These findings clearly indicate ganglioside GD1a to be involved in the regulation of the transformation suppressor genes, caveolin-1 and Stim1. Moreover, treatment with GD1a of mouse melanoma B16 cells and human hepatoma HepG2 cells brought about elevated expression of caveolin-1 and Stim1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GD1a:
-
Neu5Acα3Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu5Acα3)Galβ4GlcCer
- GD3:
-
Neu5Acα8Neu5Acα3Galβ4GlcCer
- Gg3:
-
GalNAcβ4Galβ4 Glc
- GM1:
-
Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu5Acα3)Galβ4GlcCer
- GM1b:
-
Neu5Acα3Galβ3GalNAcβ4Galβ4GlcCer
- GM3:
-
Neu5Acα3Galβ4GlcCer
- GT1b:
-
Neu5Acα3Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu-5Acα8Neu5Acα3)Galβ4GlcCer
- GM2/GD2 synthase:
-
UDP-N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamine: (N-acetylneuraminyl)-galactosylglucosylceramide-β-1,4-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
- HPTLC:
-
high performance thin layer chromatography
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- D-PDMP:
-
D-threo-1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol
- St3gal5:
-
CMP-NeuAc:lactosylceramide alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase
References
Hyuga, S., Yamagata, S., Tai, T., Yamagata, T.: Inhibition of highly metastatic FBJ-LL cell migration by ganglioside GD1a highly expressed in poorly metastatic FBJ-S1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 231, 340–43 (1997)
Hyuga, S., Kawasaki, N., Ohta, M., Shibayama, R., Kawanishi, T., Yamagata, S., Yamagata, T., Hayakawa, T.: Ganglioside GD1a inhibits HGF-induced motility and scattering of cancer cells through suppression of tyrosine-phosphorylation of c-Met. Int. J. Cancer 94, 328–34 (2001)
Hyuga, S., Yamagata, S., Takatsu, Y., Hyua, M., Nakanishi, H., Furukawa, K., Yamagata, T.: Suppression of FBJ-LL cell adhesion to vitronectin by ganglioside GD1a and loss of metastatic capacity. Int. J. Cancer 83, 685–91 (1999)
Glenney, J.R.: Tyrosine phosphorylation of a 22,kD protein is correlated with transformation with Rous sarcoma virus. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 20163–166 (1989)
Glenney, J.R., Zokas, L.: Novel tyrosine kinase substrates from Rous sarcoma virus transformed cells are present in the membrane cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 108, 2401–08 (1989)
Glenney, J.R.: The sequence of human caveolin reveals identity with VIP 21, a component of transport vesicles. FEBS Lett. 314, 45–48 (1992)
Glenney, J.R., Soppet, D.: Sequence and expression of caveolin, a protein component of caveolae plasma membrane domains phosphorylated on tyrosine in RSV-transformed fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89, 10517–21 (1992)
Rothberg, K.G., Heuser, J.E., Donzell, W.C., Ying, Y., Glenney, J.R., Anderson, R.G.W.: Caveolin, a protein component of caveolae membrane coats. Cell 68, 673–82 (1992)
Scherer, P.E., Lewis, R.Y., Volonte, D., Engelman, J.A., Galbiati, F., Couet, J., Kohtz, D.S., van Donselaar, E., Peters, P., Lisanti, M.P.: Cell-type and tissue-specific expression of caveolin-2. Caveolins 1 and 2 co-localize and form a stable hetero-oligomeric complex in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 29337–346 (1997)
Scherer, P.E., Okamoto, T., Chun, M., Nishimoto, I., Lodish, H.F., Lisanti, M.P.: Identification, sequence, and expression of caveolin-2 defines a caveolin gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93, 131–35 (1996)
Gargalovic, P., Dory, L.: Caveolin-1 and Caveolin-2 expression in mouse macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 26164–170 (2001)
Tang, Z.P., Scherer, P.E., Okamoto, T., Song, K., Chu, C., Kohtz, D.S., Nishimoto, I., Lodish, H.F., Lisanti, M.P.: Molecular cloning of caveolin-3, a novel member of the caveolin gene family expressed predominantly in muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 2255–61 (1996)
Parton, R.G., Way, M., Zorzi, N., Stang, E.: Caveolin-3 associates with developing T-tubules during muscle differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 136, 137–54 (1997)
Parton, R.G.: Caveolae and caveolins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8, 542–48 (1996)
Harder, T., Simons, K.: Caveolae, DIGs, and the dynamics of sphingolipid-cholesterol microdomains. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 534–42 (1997)
Hooper, N.M.: Detergent-insoluble glycosphingolipid/cholesterol-rich membrane domains, lipid rafts and caveolae. Mol. Membr. Biol. 16, 145–56 (1999)
van Deurs, B., Roepstorff, K., Hommelgaard, A.M., Svig, K.: Caveolae: anchored, multifunctional platforms in the lipid ocean. Trends Cell Biol. 13, 92–100 (2003)
Okamoto, T., Schlegel, A., Scherer, P.E., Lisanti, M.P.: Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for organizing “preassembled signaling complexes” at the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5419–22 (1998)
Smart, E.J., Graf, G.A., McNiven, M.A., Sessa, W.C., Engelman, J.A., Scherer, P.E., Okamoto, T., Lisanti, M.P.: Caveolins, liquid-ordered domains, and signal transduction. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 7289–7304 (1999)
Krajewska, W.M., Masowska, I.: Caveolins: structure and function in signal transduction. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 9, 195–220 (2004)
Berven, L.A., Willard, F.S., Crouch, M.F.: Role of the P70S6K pathway in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration. Exp. Cell Res. 296, 183–95 (2004)
Navarro, A., Anad-Apte, B., Parat, M.O.: A role for caveolae in cell migration. FASEB J. 18, 1801–11 (2004)
Koleske, A.J., Baltimore, D., Lisanti, M.P.: Reduction of caveolin and caveolae in oncogenically transformed cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 92, 1381–85 (1995)
Razani, B., Engelman, J.A., Wang, X.B., Schubert, W., Zhang, X.Z., Marks, C.B., Macaluso, F., Russell, R.G., Li, M., Pestell, R.G., Di Vizio, D., Hou, H,Jr., Kneitz, B., Lagaud, G., George, J., Christ, G., Edelmann, W., Lisanti, M.P.: Caveolin-1 Null Mice Are Viable but Show Evidence of Hyperproliferative and Vascular Abnormalities. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 38121–138 (2001)
Engelman, J.A., Wykoff, C.C., Yasuhara, S., Song, K.S., Okamoto, T., Lisanti, M.P.: Recombinant expression of caveolin-1 in oncogenically transformed cells abrogates anchorage-independent growth. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16374–381 (1997)
Lee, S.W., Reimer, C.L., Oh, P., Campbell, D.B., Schnitzer, J.E.: Tumor cell growth inhibition by caveolin re-expression in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 16, 1391–97 (1998)
Williams, T.M., Medina, F., Badano, I., Hazan, R.B., Hutchinson, J., Muller, W.J., Chopra, N.G., Scherer, P.E., Pestell, R.G., Lisanti, M.P.: Caveolin-1 Gene Disruption Promotes Mammary Tumorigenesis and Dramatically Enhances Lung Metastasis in Vivo: Role of cav-1 in cell invasiveness and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-2/9) secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 51630–646 (2004)
Parker, N.J., Begley, C.G., Smith, P.J., Fox, R.M.: Molecular cloning of a novel human gene (D11S4896E) at chromosomal region11p15.5. Genomic 37, 253–56 (1996)
Williams, R.T., Senior, P.V., Van Stekelenburg, L., Layton, J.E., Smith, P.J., Dziadek, M.A.: Stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1), a transmembrane protein with growth suppressor activity, contains an extracellular SAM domain modified by N-linked glycosylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1596, 131–37 (2002)
Manji, S.S., Parker, N.J., Williams, R.T., van Stekelenburg, L., Pearson, R.B., Dziadek, M., Smith. P.J.: STIM1: a novel phosphoprotein located at the cell surface. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1481, 147–55 (2000)
Overall, M.L., Parker, N.J., Scarcella, D.L., Smith, P.J., Dziadek, M.: Murine Stim1 maps to distal chromosome 7 and is not imprinted. Mamm. Genome. 9, 657–59 (1998)
Sabbioni, S., Barbanti-Brodano, G., Croce, C.M., Negrini, M.: GOK: a gene at 11p15 involved in rhabdomyosarcoma and rhabdoid tumor development. Cancer Res. 57, 4493–97 (1997)
Suyama, E., Wadhwa, R., Kaur, K., Miyagishi, M., Kaul, S.C., Kawasaki, H., Taira, K.: Identification of Metastasis-related Genes in a Mouse Model Using a Library of Randomized Ribozymes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 38083–086 (2004)
Liou, J., Kim, M.L., Heo, W.D., Jones, J.T., Myers, J.W., Ferrell, J.E.,Jr, Meyer, T.: STIM is a Ca2+ sensor essential for Ca2+-store-depletion-triggeed Ca2+ influx. Current Biology 15, 1235–41 (2005)
Roos, J., DiGregorio, P.J., Yeromin, A.V., Ohlsen, K., Lioudyno, A., Zhang, S., Safrina, O., Kozak, J.A., Wagner, S.L., Cahalan, M.D., Velicelebi, G., Stauderman, K.A.: STIM1, an essential and conserved component of store-operated Ca2+ channel function. J. Cell Biol. 169, 435–45 (2005)
Yamagata, S., Miwa, M., Tanaka, K., Yamagata, T.: FBJ virus-induced osteosarcoma has type V collagen consisting of A, B and C-like chains in addition to type I collagen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 105, 1208–14 (1982)
Yamagata, S., Tanaka, R., Ito, Y., Shimizu, S.: Gelatinases of murine metastatic tumor cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 158, 228–34 (1989)
Kasuya, M.C.Z., Wang, L.X., Lee, Y.C., Mitsuki, M., Nakajima, H., Miura, Y., Sato, T., Hatanaka, K., Yamagata, S., Yamagata, T.: Azido glycoside primer: A versatile building block for the biocombinatorial synthesis of glycosphingolipid analogues. Carbohydr. Res. 329, 755–63 (2000)
Galbiati, F., Volont, D., Engelman, J.A., Watanabe, G., Burk, R., Pestell, R.G., Lisanti, M.P.: Targeted downregulation of caveolin-1 is sufficient to drive cell transformation and hyperactivate the p42/44 MAP kinase cascade. EMBO J. 17, 6633–48 (1998)
Pito, M., Brunner, J., Ferraretto, A., Ravasi, D., Palestini, P., Masserini, M.: Use of photoactivable GM1 ganglioside analogue to assess lipid distribution in caveolae bilayer. Glycoconj. J. 17, 215–22 (2000)
Mutoh, T., Tokuda, A., Inokuchi, J., Kuriyama, M.: Glucosylceramide Synthase Inhibitor Inhibits the Action of Nerve Growth Factor in PC12 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 26001–007 (1998)
Meivar-Levy, Futerman, A.H.: Up-regulation of Neutral Glycosphingolipid Synthesis upon Long Term Inhibition of Ceramide Synthesis by Fumonisin B1. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 4607–12 (1999)
Prinetti, A., Prioni, S., Chigorno, V., Karagogeos, D., Tettamanti, G., Sonnino, S.: Immunoseparation of sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains enriched in Src family protein tyrosine kinases and in the neuronal adhesion molecule TAG-1 by anti-GD3 ganglioside monoclonal antibody. J. Neurochem. 78, 1162–67 (2001)
Kasahara, K., Watanabe, K., Takeuchi, K., Kaneko, H., Oohira, A., Yamamoto, T., Sanai, Y.: Involvement of Gangliosides in Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored Neuronal Cell Adhesion Molecule TAG-1 Signaling in Lipid Rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 34701–709 (2000)
Fra, A.M., Masserini, M., Palestini, P., Sonnino, S., Simons, K.: A photo-reactive derivative of ganglioside GM1 specifically cross-links VIP21-caveolin on the cell surface. FEBS Lett. 375, 11–14 (1995)
Chigorno, V., Palestini, P., Sciannamblo, M., Dolo, V., Pavan, A., Tettamanti, G., Sonnino, S.: Evidence that ganglioside enriched domains are distinct from caveolae in MDCK II and human fibroblast cells in culture. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 4187–97 (2000)
Iwabuchi, K., Handa, L., Hakomori, S.: Separation of “Glycosphingolipid Signaling Domain” from Caveolin-containing Membrane Fraction in Mouse Melanoma B16 Cells and Its Role in Cell Adhesion Coupled with Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33766–776 (1998)
Ito, M., Yamagata, T.: Purification and characterization of glycosphingolipid-specific endoglycosidases (endoglycoceramidases) from a mutant strain of Rhodococcus sp. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 9510–19 (1989)
Wang, X.Q., Sun, P., Paller, A.S.: Ganglioside induces caveolin-1 redistribution and interaction with the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 47028–034 (2002)
Li, R., Liu,Y., Ladisch, S.: Enhancement of epidermal growth factor Signaling and activation of Src kinase by gangliosides. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 42782–792 (2001)
Li, R., Liu,Y., Ladisch, S.: Exogenous ganglioside GD1a enhances epidermal growth factor receptor binding and dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 36481–489 (2004)
Lin, M., DiVito, M.M., Merajver, S.D., Boyanapall, I.M., van Golen, K.L.: Regulation of pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion by RhoC GTPase and caveolin-1. Mol. Cancer 4, 21 doi:101186/1476-4598-4-21 (2005)
Higashi, H., Yamagata, T.: Mechanism for ganglioside-mediated modulation of a calmodulin-dependent enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 9839–43 (1992)
Higashi, H., Yoshida, S., Sato, K., Yamagata, T.: Interaction of ganglioside with specific peptide sequences as a mechanism for the modulation of calmodulin-dependent enzymes. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 120, 66–73 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Li Wang and Shizuka Takaku are equal contributors to the present work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Takaku, S., Wang, P. et al. Ganglioside GD1a regulation of caveolin-1 and Stim1 expression in mouse FBJ cells:Augmented expression of caveolin-1 and Stim1 in cells with increased GD1a content. Glycoconj J 23, 303–315 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-006-5742-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-006-5742-3