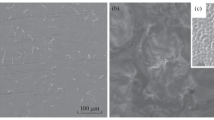
When surfactants are present in polishing compositions severe damage is done to the initial crystal structure of a very thin (tenths and hundredths of a micron thick) surface layer of the material (silicon) being processed and the deformation-strength properties of the material change as a result of the Rebinder effect. The use of active additives in polishing compositions, including unconventional ones, makes it possible to decrease the thickness of the damaged layer by a factor of 1.5 – 2, significantly increasing the polishing efficiency in the process.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. A. Rebinder, Reports at the 6th Conference of Russian Physicists [in Russian], OGIZ, Moscow (1928).
A. A. Kanaev, V. N. L’vov, S. Ya. Veiler, and P. A. Rebinder, “Discovery of adsorption plasticizing of a surface layer of metal under the influence of an active lubricant during boundary flow,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 187(2), 314 – 317 (1969).
A. A. Kanaev and A. E. Gorodetskii, “Formation of the crystal structure of the surface of ruby under the influence of surface-active media in diamond polishing,” Steklo Keram., No. 2, 31 – 32 (2007); A. A. Kanaev and A. E. Gorodetskii, “Formation of the crystal structure of the surface of ruby under the effect of surface-active media in diamond polishing,” Glass Ceram., 64(1 – 2), 66 – 67 (2007).
A. A. Kanaev and A. E. Gorodetskii, “Effect of active components in polishing compositions on the dispersion of the surface layer of ruby during fine abrasive machining,” Steklo Keram., No. 10, 41 – 42 (2013); A. A. Kanaev and A. E. Gorodetskii, “Effect of the active components of polishing compositions on the dispersion of the surface layer of ruby during fine abrasive machining,” Glass Ceram., 70(9 – 10), 382 – 384 (2013).
A. A. Stekolnikov, G. Furthmuller, and F. Bechstedt, “Absolut surface energies of group-IV semiconductors: dependence on orientation and reconstruction,” Phys. Rev. B, 65, 115318 (2002).
R. F. Kokhan, N. P. Sokolova, A. A. Kanaev, et al., “Investigation of mechano-chemical phenomena in boundary friction processes,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 201(3), 643 – 646 (1971).
I. A. Gazina, A. A. Kanaev, N. P. Sokolova and O. A. Khlebnikova, “Mechanism of the interaction of quartz glasses with lubricating-cooling liquid in the polishing process,” Steklo Keram., No. 10, 8 – 10 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 5, pp. 29 – 32, May, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanaev, A.A., Gorodetskii, A.E. Formation of the Crystalline Structure of a Silicon Surface in Active Media During Polishing. Glass Ceram 71, 169–171 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-014-9644-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-014-9644-8