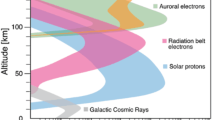
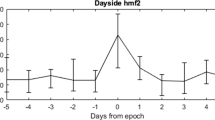
Abstract
Current knowledge concerning the lower ionosphere (D- and E-region) is reviewed with an emphasis on new aspects of empirical results. Starting with an overview of experimental techniques and corresponding data bases, both regarding charged as well as the most relevant neutral constituents of this altitude range, the ionospheric variability is discussed both concerning regular (e.g. diurnal and seasonal) as well as irregular variations (e.g. driven by the variability of nitric oxide). We then turn to ‘new players’ in the lower ionosphere, i.e. charged aerosol particles such as mesospheric ice particles in noctilucent clouds or polar mesospheric summer echoes and meteor smoke particles originating from ablated meteoric matter. These species have received considerable attention in recent years, in part because it is speculated that observations of their properties might be useful for the detection of climate change signals. The available experimental data base regarding these species is reviewed and we show that there is now compelling evidence for the ubiquitous presence of these very heavy charge carriers throughout the lower ionosphere. While many fundamental details regarding these charged species are not yet completely understood, this emphasizes that charged aerosol particles may not be neglected in a comprehensive treatment of the lower ionospheric charge balance and related phenomena. Finally, we close with suggestions for future research.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikin AC, Goldberg RA, Jones W, Kane JA (1977) Observations of the mid-latitude lower ionosphere in winter. J Geophys Res 82(13):1869–1875
Amyx K, Sternovsky Z, Knappmiller S, Robertson S, Horányi M, Gumbel J (2008) In situ measurement of smoke particles in the wintertime polar mesosphere between 80 and 85 km altitude. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 70(1):61–70. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2007.09.013
Arnold F, Krankowsky D (1977) Rate constants of NO+ N2 formation at low temperatures. J Atmos Terr Phys 39:625–629
Balsiger F, Kopp E, Friedrich M, Torkar KM, Wälchli U, Witt G (1996) Positive ion depletion in a Noctilucent cloud. Geophys Res Lett 23(1):93–96
Bardeen CG, Toon OB, Jensen EJ, Marsh DR, Harvey VL (2008) Numerical simulation of the three-dimensional distribution of meteoric dust in the mesosphere and upper stratosphere. J Geophys Res 113:D17202. doi:10.1029/2008JD009515
Barth CA, Mankoff KD, Bailey SM, Solomon SC (2003) Global observations of nitric oxide in the thermosphere. J Geophys Res 108(A1):1027. doi:10.1029/2002JA009458
Baumgarten G, Fiedler J, Lübken F-J, von Cossart G (2008) Particle properties and water content of Noctilucent clouds and their interannual variation. J Geophys Res 113:D06203. doi:10.1029/2007JD008884
Beig G, Keckhut P, Lowe RP, Roble RG, Mlynczak MG, Scheer J, Fomichev VI, Offermann D, French WJR, Shepherd MG, Semenov AI, Remsberg EE, She CY, Lübken F-J, Bremer J, Clemesha BR, Stegman J, Sigernes F, Fadnavis S (2003) Review of mesospheric temperature trends. Rev Geophys 41(4):672. doi:10.1029/2002RG000121
Belova E, Chilson PB, Kirkwood S, Rietveld MT (2003) The response time of ionospheric heating to PMSE. J Geophys Res 108(D8):8446. doi:10.1029/2002JD002385
Belova E, Kirkwood S, Ekeberg J, Osepian A, Häggström I, Nilsson H, Rietveld M (2005) Polar mesosphere winter echoes observed simultaneously by EISCAT VHF and ESRAD MST radars. Ann Geophys 23:1239–1247
Belova E, Smirnova M, Rietveld MT, Isham B, Kirkwood S, Sergienko T (2008) First observation of the overshoot effect for polar mesosphere winter echoes during radiowave electron temperature modulation. Geophys Res Lett 35:L03110. doi:10.1029/2007GL032457
Bilitza D (1990) International reference ionosphere, Rep. NSSDC/WDC-A-R&S 90-22. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt
Blix TA (1999) The importance of charged aerosols in the polar mesosphere in connection with Noctilucent clouds and polar mesosphere summer echoes. Adv Space Res 24(12):1645–1654
Blix TA, Rapp M, Lübken F-J (2003) Relations between small scale electron number density fluctuations, radar backscatter and charged aerosol particles. J Geophys Res 108(D8):8450. doi:10.1029/2002JD002430
Brasseur G, Solomon S (1986) Aeronomy of the middle atmosphere, 2nd edn. D. Reidel Publ. Co, Dordrecht
Brattli A, Lie-Svendsen Ø, Svenes K, Hoppe U-P, Rapp M, Latteck R, Friedrich M (2009) The ECOMA 2007 rocket campaign: observations and numerical modelling of aerosol particle charging and plasma depletion in a PMSE/NLC layer. Ann Geophys 27(2):781–796
Chau JL, Woodman RF (2005) D and E region incoherent scatter radar density measurements over Jicamarca. J Geophys Res 110:A12314. doi:10.1029/2005JA011438
Chen C-F, Ward BD, Reinisch BW, Buonsanto MJ, Gamache RR (1991) Ionosonde observations of the E-F valley and comparison with incoherent scatter radar profiles. Adv Space Res 11(19):89–92
Chilson PB, Belova E, Rietveld M, Kirkwood S, Hoppe U-P (2000) First artificially induced modulation of PMSE using the EISCAT heating facility. Geophys Res Lett 27:3801–3804
Cho JYN, Sulzer MP, Kelley MC (1998) Meteoric dust effects on D-region incoherent scatter radar spectra. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 60:349–357
Croskey C, Mitchell J, Friedrich M, Torkar K, Hoppe U-P, Goldberg R (2001) Electrical structure of PMSE and NLC regions during the DROPPS program. Geophys Res Lett 28:1427–1430
Croskey CL, Mitchell JD, Goldberg RA, Blix TA, Rapp M, Latteck R, Friedrich M, Smiley B (2004) Coordinated investigation of plasma and neutral density fluctuations and particles during the MaCWAVE/MIDAS summer 2002 program. Geophys Res Lett 31:L24S08. doi:10.1029/2004GL929169
Czechowsky P, Rüster R, Schmidt G (1979) Variations of mesospheric structures in different seasons. Geophys Res Lett 6:459–462
Danilov AD, Kalgin YA, Pokhunkov AA (1979) Variation of the turbopause level in equatorial regions. Space Res 20:23–46
Danilov AD, Kalgin YA, Pokhunkov AA (1980) Variations in the turbopause level in the polar region. Geomagnetizm i Aeronomiya 20(6):474–476
Dickinson PHG, Bennett FDG (1978) Diurnal variation in the D-region during a storm after-effect. J Atmos Terr Phys 40(5):549–551
Ecklund WL, Balsley BB (1981) Long-term observations of the arctic mesosphere with the MST radar at Poker Flat, Alaska. J Geophys Res 86:7775–7780
Enell CF, Kero A, Turunen E, Ulich T, Verronen PT, Seppälä A, Marple S, Honary F, Senior A (2005) Effects of D-region rf heating studied with the Sodankylä ion chemistry model. Ann Geophys 23:1575–1583
Eremenko MN, Petelina SV, Zasetsky AY, Karlsson B, Rinsland CP, Llewellyn EJ, Sloan JJ (2005) Shape and composition of PMC particles derived from satellite remote sensing measurements. Geophys Res Lett 32:L16S06. doi:10.1029/2005GL023013
Friedrich M (2000) Electron densities and Auroral zone radio-wave absorption. In: Egeland A, Thrane EV, Søraas F, Brekke A, Hansen A-H, Magnussen SN (eds) Historien om Andøya Rakettskytefelt gjenom 40 år. E. Pettersen & Co. AS, Oslo, pp 120–127
Friedrich M, Plane JMC (2008) Electron scavenging in the night-time mesosphere—a collection of empirical data, Poster SA41A-1550. Presented at AGU Fall meeting, San Francisco
Friedrich M, Torkar KM (2001) FIRI: a semiempirical model of the lower ionosphere. J Geophys Res 106(A10):21409–21418
Friedrich M, Siskind DE, Torkar KM (1998) HALOE nitric oxide measurements in view of ionospheric data. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 60:1445–1457
Friedrich M, Gumbel J, Pilgram R (1999) Atomic oxygen in the mesosphere and its relevance for the ionosphere: a summary of empirical evidence. ESA SP-437:287–290
Friedrich M, Harrich M, Steiner RJ, Torkar KM, Lübken F-J (2004) The quiet auroral ionosphere and its neutral background. Adv Space Res 33(6):943–948
Friedrich M, Torkar KM, Lehmacher GA, Croskey CL, Mitchell JD, Kudeki E, Milla M (2006) Rocket and incoherent scatter radar common-volume electron measurements of the equatorial ionosphere. Geophys Res Lett 33(8):L08807. doi:10.1029/2005GL024622
Friedrich M, Torkar KM, Singer W, Strelnikova I, Rapp M, Robertson S (2009) Signatures of mesospheric particles in ionospheric data. Ann Geophys 27(2):823–829
Ganguly S, Zinn J (1998) Time-variation of the D region electron densities and comparison with model computations. Stud Geoph et geod 42:500–510
García RR, Lieberman R, Russell JM III, Mlynczak MG (2005) Large-scale waves in the mesosphere and thermosphere observed by SABER. J Atmos Sci 62:4384–4399
Gelinas LJ, Lynch KA, Kelley MC, Collins S, Baker S, Zhou Q, Friedman JS (1998) First observation of meteoritic charged dust in the tropical mesosphere. Geophys Res Lett 25:4047–4050
Gelinas LJ, Lynch KA, Kelley MC, Collins RL, Widholm M, MacDonald E, Ulwick J, Mace P (2005) Mesospheric charged dust layer: implications for neutral chemistry. J Geophys Res 110:A01310. doi:10.1029/2004JA01050
Gerding M, Höffner J, Lautenbach J, Rauthe M, Lübken F-J (2008) Seasonal variation of nocturnal temperatures between 1 and 105 km altitude at 54°N observed by lidar. Atmos Chem Phys 8:7465–7482
Giebeler J, Lübken F-J, Nägele M (1993) CONE—a new sensor for in situ observations of neutral and plasma density fluctuations. ESA SP-355:311–318
Goldberg R, Kopp E, Witt G, Swartz W (1993) An overview of NLC-91: a rocket/radar study of the polar summer mesosphere. Geophys Res Lett 20:2443–2446
Goldberg RA, Lehmacher GA, Schmidlin FJ, Fritts DC, Mitchell JD, Croskey CL, Friedrich M, Swartz WE (1997) Equatorial dynamics observed by rocket, radar, and satellite during the CADRE/MALTED campaign 1. Programmatics and small-scale fluctuations. J Geophys Res 102(D22):26179–26190
Goldberg R, Pfaff R, Holzworth R, Schmidlin F, Voss H, Tuzzolino A, Croskey C, Mitchell J, Friedrich M, Murtagh D, Gumbel J, von Zahn U, Singer W, Hoppe U-P (2001) DROPPS: a study of the polar summer mesosphere with rocket, radar and lidar. Geophys Res Lett 28:1407–1410
Gumbel J (1997) Rocket-Borne optical measurements of minor constituents in the middle atmosphere. PhD Thesis, Stockholm University
Hargreaves JK, Friedrich M (2003) The estimation of D-region electron densities from riometer data. Ann Geophys 21:603–613
Harrich M (2001) Empirical modelling of electron densities in the high latitude mesosphere. PhD Thesis, Graz University of Technology
Havnes O (2004) Polar mesospheric summer echoes PMSE overshoot effect due to cycling of electron heating. J Geophys Res 109:A02309. doi:10.1029/2003JA010159
Havnes O, Næsheim LI (2007) On the secondary charging effects and structure of mesospheric dust particles impacting on rocket probes. Ann Geophys 25:623–637
Havnes O, de Angelis U, Bingham R, Goertz CK, Morfill GE, Tsytovich V (1990) On the role of dust in the summer mesopause. J Atmos Terr Phys 52:637–643
Havnes O, Trøim J, Blix T, Mortensen W, Næsheim LI, Thrane E, Tønnesen T (1996) First detection of charged dust particles in the earth’s mesosphere. J Geophys Res 101:10839–10847
Havnes O, Brattli A, Aslaksen T, Singer W, Latteck R, Blix T, Thrane E, Trøim J (2001) First common volume observations of layered plasma structures and polar mesospheric summer echoes by rocket and radar. Geophys Res Lett 28:1419–1422
Havnes O, La Hoz C, Næsheim L, Rietveld M (2003) First observation of the PMSE overshoot effect and its use for investigating the conditions in the summer mesosphere. Geophys Res Lett 30(23):2229. doi:10.1029/2003GL018429
Hedin J, Gumbel J, Rapp M (2007) On the efficiency of rocket-borne particle detection in the mesosphere. Atmos Chem Phys 7:3701–3711
Hervig M, Thompson R, McHugh M, Gordley L, Russell J III, Summers M (2001) First confirmation that water ice is the primary component of polar mesospheric clouds. Geophys Res Lett 28:971–974
Holzworth RH, Goldberg RA (2004) Electric field measurements in Noctilucent clouds. J Geophys Res 109:D16203. doi:10.1029/2003JD004468
Holzworth R, Pfaff R, Goldberg R, Bounds S, Schmidlin F, Voss H, Tuzzolino A, Croskey C, Mitchell J, von Cossart G, Singer W, Hoppe U-P, Murtagh D, Witt G, Gumbel J, Friedrich M (2001) Large electric potential perturbations in PMSE during DROPPS. Geophys Res Lett 28:1435–1438
Hoppe UP, Eriksen T, Thrane EV, Blix TA, Fiedler J, Lübken F-J (1999) Observations in the polar middle atmosphere by rocket-borne Rayleigh lidar: first results. Earth Planet Space 51:815–824
Horányi M, Gumbel J, Witt G, Robertson S (1999) Simulation of Rocket-borne particle measurements in the mesosphere. Geophys Res Lett 26(11):1537–1540
Horányi M, Robertson S, Smiley B, Gumbel J, Witt G, Walch B (2000) Rocket-borne mesospheric measurement of heavy charge carriers. Geophys Res Lett 27(23):3825–3828
Huang FT, Mayr HG, Reber CA, Russell J, Mlynczak M, Mengel J (2006) Zonal-mean temperature variations inferred from SABER measurements on TIMED compared with UARS observations. J Geophys Res 111:A10S07. doi:10.1029/2005JA011427
Hunten DM, Turco RP, Toon OB (1980) Smoke and dust particles of meteoric origin in the mesosphere and stratosphere. J Atmos Sci 37:1342–1357
Inhester B, Ulwick J, Cho J, Kelley M, Schmidt G (1990) Consistency of rocket and radar electron density observations: implications about the anisotropy of turbulence. J Atmos Terr Phys 52:855–873
Jacobsen TA, Friedrich M (1979) Electron density measurements in the lower D-region. J Atmos Terr Phys 41(12):1195–1200
Janches D, Fritts DC, Nicolls MJ, Heinselman CJ (2009) Observations of the D-region structure and atmospheric tides with PFISR during active aurora. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 71(6–7):688–696. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.08.015
Jesse O (1885) Auffallende Erscheinungen am Abendhimmel. Met Zeit 2:311–312
Kassa M, Havnes O, Belova E (2005) The effect of electron bite-outs on artificial electron heating and the PMSE overshoot. Ann Geophys 23:3633–3643
Kavanagh AJ, Honary F, Rietveld MT, Senior A (2006) First observations of the artificial modulation of polar mesosphere winter echoes. Geophys Res Lett 33:L19801. doi:10.1029/2006GL02756
Kazil J, Kopp E, Chabrillat S, Bishop J (2003) The University of Bern atmospheric ion model: time-dependent modelling of the ions in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. J Geophys Res 108(D14):4432. doi:10.1029/2002JD003024
Kero A, Enell C-F, Kavanagh AJ, Vierinen J, Virtanen I, Turunen E (2008) Could negative ion production explain the polar mesosphere winter echo (PMWE) modulation in active HF heating experiments? Geophys Res Lett 35:L23102. doi:10.1029/2008GL035798
Kerzenmacher T et al (2008) Validation of NO2 and NO from the Atmospheric Chemistry Experiment (ACE). Atmos Chem Phys 8:5801–5841
Kirkwood S, Collis PN (1991) The high latitude lower ionosphere observed by EISCAT. Adv Space Res 11(10):109–112
Kirkwood S, Barabash V, Belova E, Nilsson H, Rao TN, Stebel K, Osepian A, Chilson PB (2002) Polar mesosphere winter echoes during solar proton events. Adv Polar Upper Atmos Res 16:111–125
Kirkwood S, Chilson P, Belova E, Dalin P, Häggström I, Rietveld M, Singer W (2006) Infrasound—the cause of polar mesosphere winter echoes? Ann Geophys 24:75–491
Kudeki E, Milla M, Friedrich M, Lehmacher G, Sponseller D (2006) ALTAIR incoherent scatter observations of the equatorial daytime ionosphere. Geophys Res Lett 33(8):L08108. doi:10.1029/2005GL025180
Kutepov AA, Feofilov AG, Marshall BT, Gordley LL, Pesnell WD, Goldberg RA, Russell JM III (2006) SABER temperature observations in the summer polar mesosphere and lower thermosphere: importance of accounting for the CO2 V2 quanta V-V exchange. Geophys Res Lett 33:L21809. doi:10.1029/2006GL026591
La Hoz C, Havnes O (2008) Artificial modification of polar mesospheric winter echoes with an RF heater: do charged dust particles play an active role? J Geophys Res 113:D19205. doi:10.1029/2008JD010460
Laštovička J (1977) Seasonal variation in the asymmetry of diurnal variation of absorption in the lower ionosphere. J Atmos Terr Phys 39:891–894
Laštovička J, Akmaev RA, Beig G, Bremer J, Emmert JT (2006) Global change in the upper atmosphere. Science 314(5803):1253–1254
Lehmacher GA, Croskey CL, Mitchell JD, Friedrich M, Lübken F-J, Rapp M, Kudeki E, Fritts DC (2006) Intense turbulence observed above a mesospheric temperature inversion at equatorial latitude. Geophys Res Lett 33:L08808. doi:10.1029/2005GL024345
Leslie RJ (1885) Sky glows. Nature 33:245
Lübken F-J (1997) Seasonal variation of turbulent energy dissipation rates at high latitudes as determined by in situ measurements of neutral density fluctuations. J Geophys Res 102:13441–13456
Lübken F-J (1999) Thermal structure of the arctic summer mesosphere. J Geophys Res 104:9135–9149
Lübken F-J, Rapp M, Blix T, Thrane E (1998) Microphysical and turbulent measurements of the Schmidt number in the vicinity of polar mesosphere summer echoes. Geophys Res Lett 25:893–896
Lübken F-J, Jarvis MJ, Jones GOL (1999) First in situ temperature measurements at the Antarctic summer mesopause. Geophys Res Lett 26:3581–3584
Lübken FJ, Strelnikov B, Rapp M, Singer W, Latteck R, Brattli A, Hoppe U-P, Friedrich M (2006) The thermal and dynamical state of the atmosphere during polar mesosphere winter echoes. Atmos Chem Phys 6:13–24
Lübken F-J, Lautenbach J, Höffner J, Rapp M, Zecha M (2009) First continuous temperature measurements within polar summer echoes. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 71(6–7):453–463. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.06.001
Lynch KA, Gelinas LJ, Kelley MC, Collins RL, Widholm M, Rau D, MacDonald E, Liu Y, Ulwick J, Mace P (2005) Multiple sounding rocket observations of charged dust in the polar winter mesosphere. J Geophys Res 110:A03302. doi:10.1029/2004JA01050
Lynch K, Bracikowksi P, Gelinas L, Plane J, Friedrich M, Rapp M, Havnes O (2008) Recent sounding rocket flights of a mesospheric charged dust detector, Poster SA41A-1584, AGU Fall meeting, San Francisco
Marsh D, Roble R (2002) TIME-GCM simulations of lower-thermospheric nitric oxide seen by the halogen occultation experiment. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 64:8–11. doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(02)00044-5
Marsh DR, Russell JM III (2000) A tidal explanation for the sunrise/sunset anomaly in HALOE low-latitude nitric oxide observations. Geophys Res Lett 27(19):3197–3200
Mathews JD (1978) The effect of negative ions on collision-dominated thomson scattering. J Geophys Res 83:505–512
Mathews JD, Breakall JK, Ganguly S (1982) The measurement of diurnal variations of electron concentration in the 60 to 100 km ionosphere at Arecibo. J Atmos Terr Phys 44:41–448
McKinnell L-A, Friedrich M (2007) A neural network-based ionospheric model for the auroral zone. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 69:1459–1470
McNamara LF (1979) A statistical model of the D-region. Radio Sci 14:1165–1173
Mechtly EA (1974) Accuracy of rocket measurements of lower ionosphere electron density concentration. Radio Sci 9:373–378
Mechtly EA, Bowhill SA, Smith LG, Knoebel HW (1967) Lower ionosphere electron concentrations and collision frequency from rocket measurements of Faraday rotation, differential absorption, and probe current. J Geophys Res 72:5239–5245
Megner L, Gumbel J (2009) Charged meteoritic particles as ice nuclei in the mesosphere: part 2—a feasibility study. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys (in press). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2009.05.002
Megner L, Rapp M, Gumbel J (2006) Sensitivity of meteoric smoke distribution to microphysical properties and atmospheric conditions. Atmos Chem Phys 6:4415–4426
Megner L, Siskind DE, Rapp M, Gumbel J (2008) Global and temporal distribution of meteoric smoke: a two-dimensional simulation study. J Geophys Res 113:D03202. doi:1029/2007JD009054
Mendis D, Wong W-H, Rosenberg M, Sorasio G (2005) Micrometeoroid flight in the upper atmosphere: electron emission and charging. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 67:1178–1189
Mitchell J, Croskey C (2001) Electrical structure of Noctilucent clouds and polar mesospheric summer echo regions. Adv Space Res 28(7):1027–1036
Mitchell J, Croskey C, Goldberg R (2001) Evidence for charged aerosol particles and associated meter-scale structure in identified PMSE/NLC regions. Geophys Res Lett 28:1423–1426
Næsheim LI, Havnes O, La Hoz C (2008) A comparison of polar mesosphere summer echo at VHF (224 MHz) and UHF (930 MHz) and the effects of artificial electron heating. J Geophys Res 113:D08205. doi:10.1029/2007JD009245
Natanson GL (1960) On the theory of the charging of a microscopic aerosol particles as a result of capture of gas ions. Sov Phys Tech Phys (English Transl) 5:538–551
Offermann D (1979) A study of D-region winter anomaly in western Europe, 1975/76. J Atmos Terr Phys 41:1–13
Offermann D, Jarisch M, Schmidt H, Oberheide J, Grossmann KU, Gusev O, Russell JM III, Mlynczak MG (2006) The wave turbopause. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 69:2139–2158
Osepian A, Smirnova N (1997) Modelling of absorption layer during absorption events. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 59(8):951–960
Pedersen A, Trøim J, Kane J (1969) Rocket measurement showing removal of electrons above the mesopause in summer at high latitudes. Planet Space Sci 18:945–947
Philbrick CR, McIsaac JP, Fryklund DH, Buck RF (1981) Atmospheric structure measurements from accelerometer instrumented falling spheres. In: Offermann D, Thrane EV (eds) “Sounding rocket program aeronomy project: energy budget campaign 1980, experiment summary”, BMFT-FB-W 81-052, pp 244–255
Picone JM, Hedin AE, Drob DP, Aikin AC (2002) NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: statistical comparisons and scientific issues. J Geophys Res 107(A12):1468. doi:10.1029/2002JA009430
Plane JMC (2003) Atmospheric chemistry of meteoric metals. Chem Rev 103:4963–4984
Rapp M, Lübken F-J (2000) Electron temperature control of PMSE. Geophys Res Lett 27:3285–3288
Rapp M, Lübken F-J (2001) Modelling of particle charging in the polar summer mesosphere: part 1–general results. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 63:759–770
Rapp M, Lübken F-J (2003a) Comment on “The response time of PMSE to ionospheric heating” by E Belova et al. J Geophys Res 108(D23):4727. doi:10.1029/2003JD003638
Rapp M, Lübken F-J (2003b) On the nature of PMSE: electron diffusion in the vicinity of charged particles revisited. J Geophys Res 108(D8):8437. doi:10.1029/2002JD002857
Rapp M, Lübken F-J (2004) Polar mesosphere summer echoes (PMSE): review of observations and current understanding. Atmos Chem Phys 4:2601–2633
Rapp M, Strelnikova I (2008) Measurements of meteor smoke particles during the ECOMA-2006 campaign: 1. Particle detection by active photoionization. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys (in press). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.06.002
Rapp M, Thomas GE (2006) Modelling the microphysics of mesospheric ice particles: assessment of current capabilities and basic sensitivities. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 68:715–744
Rapp M, Gumbel J, Lübken F-J (2001) Absolute density measurements in the middle atmosphere. Ann Geophys 19:571–580
Rapp M, Strelnikova I, Gumbel J (2007) Meteoric smoke particles: evidence from rocket and radar techniques. Adv Space Res 40:809–817
Rapp M, Lübken F-J, Hoffmann P, Latteck R, Baumgarten G, Blix TA (2003) PMSE dependence on aerosol charge number density and aerosol size. J Geophys Res 108(D8):8450. doi:10.1029/2002JD002650
Rapp M, Hedin J, Strelnikova I, Friedrich M, Gumbel J, Lübken F-J (2005) Observations of positively charged nanoparticles in the nighttime polar mesosphere. Geophys Res Lett 32:L23821. doi:10.1029/2005GL02467
Rapp M, Strelnikova I, Strelnikov B, Latteck R, Baumgarten G, Megner L, Gumbel J, Friedrich M, Hoppe U-P, Robertson S (2009) First in situ measurement of the vertical distribution of ice volume/mass density in a mesospheric ice cloud during the ECOMA/MASS rocket-campaign. Ann Geophys 27(2):755–766
Reid GC (1977) The production of water-cluster positive ions in the quiet daytime D region. Planet Space Sci 25:275–290
Robertson S, Horányi M, Knappmiller S, Sternovsky Z, Holzworth R, Shimogawa M, Friedrich M, Torkar K, Gumbel J, Megner L, Baumgarten G, Latteck R, Rapp M, Hoppe U-P, Hervig ME (2009). Mass analysis of charged aerosol particles in NLC and PMSE during the ECOMA/MASS campaign. Ann Geophys 27:1213–1232
Rosinski J, Snow RH (1961) Secondary particulate matter from meteor vapors. J Meteorol 18:736–745
Röttger J, Rietveld M, La Hoz C, Hall C, Kelley MC, Swartz W (1990) Polar mesosphere summer echoes observed with the EISCAT 933 MHz radar and the CUPRI 46.9 MHz radar, their similarity to 224 MHz radar echoes and their relation to turbulence and electron density profiles. Radio Sci 25:671–687
Rycroft M, Keating GM, Rees D (eds) (1990) Upper atmosphere models and research. Adv Space Res 10(6)
Schulte P, Arnold F (1992) Detection of upper atmospheric negatively charged microclusters by a rocket borne mass spectrometer. Geophys Res Lett 19:2297–2300
Schunk RW, Nagy AF (2000) Ionospheres: physics, plasma physics and chemistry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Semeter J, Butler T, Heinselman C, Nicolls M, Kelly J, Hampton D (2009) Volumetric imaging of the auroral ionosphere: initial results from PFISR. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 71(6–7):738–743. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.08.0142009
Shimogawa M, Holzworth RH (2009) Electric field measurements in a NLC/PMSE region during the MASS/ECOMA campaign. Ann Geophys 27:1423–1430
Singer W, Latteck R, Holdsworth DA (2008) A new narrow beam Doppler radar at 3 MHz for studies of the high-latitude middle atmosphere. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 41:1487–1493
Siskind DE, Bacmeister JT, Summers ME, Russell JM III (1997) Two-dimensional model calculations of nitric oxide transport in the middle atmosphere and comparison with halogen occultation experiment data. J Geophys Res 102(D3):3527–3545
Siskind DE, Barth CA, Russell JM III (1998) A climatology of nitric oxide in the mesosphere and thermosphere. Adv Space Res 21(10):1353–1362
Smiley B, Robertson S, Horányi M, Blix T, Rapp M, Latteck R, Gumbel J (2003) Measurement of negatively and positively charged particles inside PMSE during MIDAS SOLSTICE 2001. J Geophys Res 108(D8):8444. doi:10.1029/2002JD002425
Solomon SC, Barth CA, Bailey SM (1999) Auroral production of nitric oxide measured by the SNOE satellite. Geophys Res Lett 26(9):1259–1262
Stebel K, Blum U, Fricke K-H, Kirkwood S, Mitchell N, Osepian A (2004) Joint radar/lidar observations of possible aerosol layers in the winter mesosphere. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 66(11):957–970
Steiner RJ (2003) Novel procedures for modelling the high-latitude ionosphere. PhD Thesis, Graz University of Technology
Sternovsky Z, Holzworth RH, Horányi M, Robertson S (2004) Potential distribution around sounding rockets in mesospheric layers with charged aerosol particles. Geophys Res Lett 31:L22101. doi:10.1029/2004GL020949
Strelnikov B, Rapp M, Blix TA, Engler N, Höffner J, Lautenbach J, Lübken F-J, Smiley B, Friedrich M (2006) In Situ observations of small scale neutral and plasma dynamics in the mesosphere/lower thermosphere at 79°N. Adv Space Res 38:2388–2393
Strelnikova I, Rapp M (2007) Meteoric smoke particle signatures in D-region incoherent scatter radar spectra. ESA SP–647:629–638
Strelnikova I, Rapp M, Raizada S, Sulzer M (2007) Meteor smoke particle properties derived from Arecibo incoherent scatter radar observations. Geophys Res Lett 34:L15815. doi:10.1029/2007GL030635
Strelnikova I, Rapp M, Strelnikov B, Baumgarten G, Brattli A, Svenes K, Hoppe U-P, Friedrich M, Gumbel J, Williams BP (2009) Measurements of meteor smoke particles during the ECOMA-2006 campaign: 2. results. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 71:486–496. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.07.011
Szuszczewicz EP (1972) Area influences and floating potentials in Langmuir probe measurements. J Appl Phys 43(3):874–880
Thomas GE, McKay CP (1985) On the mean particle size and water content of polar mesospheric clouds. Planet Space Sci 33:1209–1224
Thomas GE, Olivero JJ, Jensen EJ, Schröder W, Toon OB (1989) Relation between increasing methane and the presence of ice clouds at the mesopause. Nature 338:490–492
Thomas GE, Olivero JJ, DeLand M, Shettle EP (2003) A response to the article by U. von Zahn, ‘‘Are Noctilucent clouds truly a miner’s canary of global change?’’. Eos Trans AGU 84(36):352–353
Thrane EV (1974) Ionospheric profiles up to 160 km: a review of techniques and profiles. In: Rawer K (ed) Methods of measurements and results of lower ionosphere structure. Verlag, Berlin
Torkar KM, Friedrich MF, Stauning P (1980) Evidence of coupling between auroral zone activity and mid-latitude absorption. J Atmos Terr Phys 42(2):183–188
Ulwick JC, Baker KD, Kelley MC, Balsley BB, Ecklund WL (1988) Comparison of simultaneous MST radar and electron density probe measurements during STATE. J Geophys Res 93:6989–7000
Viggiano AA, Hunton DE (1999) Airborne mass spectrometers: four decades of atmospheric and space research at the air force research laboratory. J Mass Spectrom 34:1107–1129
von Zahn U, Herwig T (1977) Inert gas abundances as indicators for the strength of eddy diffusion at turbopause altitudes. In: Grandal B, Holtet JA (eds) Dynamical and chemical coupling between the neutral and ionized atmosphere. D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, pp 49–52
von Zahn U, von Cossart G, Fiedler J, Fricke KH, Nelke G, Baumgarten G, Rees D, Hauchecorne A, Adolfsen K (2000) The ALOMAR Rayleigh/Mie/Raman lidar: objectives, configuration, and performance. Ann Geophys 18:815–833
Vondrak T, Plane JMC, Meech SR (2006) Photoemission from sodium on ice: a mechanism for positive and negative charge coexistence in the mesosphere. Phys Chem B Lett 110:3860–3863
Wayne RP (2000) Chemistry of atmospheres, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Williams BP, Fritts DC, She CY, Goldberg RA (2006) Gravity wave propagation through a large semidiurnal tide and instabilities in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere during the winter 2003 MacWAVE rocket campaign. Ann Geophys 24(4):1199–1208
Zadorozhny AM, Tyutin AA, Witt G, Wilhelm N, Wälchli U, Cho J, Swartz WE (1993) Electric field measurements in the vicinity of Noctilucent clouds and PMSE. Geophys Res Lett 20:2299–2302
Zadorozhny AM, Vostrikov AA, Witt G, Bragin OA, Dubov DY, Kazakov VG, Kikhtenko VN, Tyutin AA (1997) Laboratory and in situ evidence for the presence of ice particles in a PMSE region. Geophys Res Lett 24:841–844
Zeller O, Zecha M, Bremer J, Latteck R, Singer W (2006) Mean characteristics of mesosphere winter echoes at mid- and high-latitudes. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 68(10):1087–1104
Acknowledgments
A significant part of the results presented in Sect. 5 were achieved in the frame of the European sounding rocket project ECOMA. MR acknowledges corresponding support by the German Aerospace Centre under the grants 50OE0301 and 50OE0801, the participation of MF in these same activities was funded by grant P170848 of the Austrian Research Funds. In addition, the new radar techniques to study MSPs based on properties of ISR-spectra were developed under a grant provided by the German Science Foundation (RA 1400 2/1 and RA 1400 2/2) in the frame of the CAWSES priority program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedrich, M., Rapp, M. News from the Lower Ionosphere: A Review of Recent Developments. Surv Geophys 30, 525–559 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-009-9074-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-009-9074-2