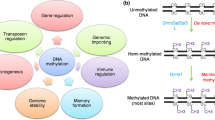
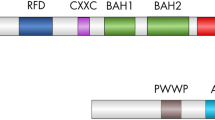
Abstract
DNA methylation has been studied abundantly in vertebrates and recent evidence confirms that this phenomenon could be disseminated among some invertebrates groups, including Drosophila species. In this paper, we used the Methylation-Sensitive Restriction Endonuclease (MSRE) technique and Southern blot with specific probes, to detect methylation in the Drosophila willistoni species. We found differential cleavage patterns between males and females that cannot be explained by Mendelian inheritance, pointing to a DNA methylation phenomenon different from the Drosophila melanogaster one. The sequencing of some of these bands showed that these fragments were formed by different DNA elements, among which rDNA. We also characterized the D. willitoni dDnmt2 sequence, through a Mega Blast search against the D. willistoni Trace Archive Database using the D. melanogaster dDnmt2 nucleotide sequence as query. The complete analysis of D. willistoni dDnmt2 sequence showed that its promoter region is larger, its dDnmt2 nucleotide sequence is 33% divergent from the D. melanogaster one, Inverted Terminal Repeats (ITRs) are absent and only the B isoform of the enzyme is produced. In contrast, ORF2 is more conserved. Comparing the D. willistoni and D. melanogaster dDnmt2 protein sequences, we found higher conservation in motifs from the large domain, responsible for the catalysis of methyl transfer, and great variability in the region that carries out the recognition of specific DNA sequences (TRD). Globally, our results reveal that methylation of the D. willistoni genome could be involved in a singular process of species-specific dosage compensation and that the DNA methylation in the Drosophila genus can have diverse functions. This could be related to the evolutionary history of each species and also to the acquisition time of the dDnmt2 gene.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avner P, Heard E (2001) X-chromosome inactivation: counting, choice and initiation. Nat Rev Genet 2: 59–67
Baylin SB, Esteller M, Rountree MR, et al. (2001) Aberrant patterns of DNA methylation, chromatin formation and gene expression in cancer. Hum Mol Genet 10(7): 687–692
Bernstein E, Allis CD (2005) RNA meets chromatin. Genes Dev 19: 1635–1655
Bestor TH (2000) The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum Mol Gen 9(16): 2395–2402
Bird A (2002) DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev 16(1): 6–21
Bongiorni S, Cintio O, Prantera G (1999) The relationship between DNA methylation and chromosome imprinting in the Coccid Planococcus citri. Genetics 151: 1471–1478
Busslinger M, Hurst J, Flavell RA (1983) DNA methylation and the regulation of globin gene expression. Cell 34: 197–206
Colot V, Rossignol JL (1999) Eukaryotic DNA methylation as an evolutionary device. Bioessays 21: 402–411
Dahl C, Guldberg P (2003). DNA methylation analysis techniques. Biogerontology 4: 233–250
Dong A, Yoder JA, Zhang X, et al. (2001). Structure of human DNMT2, an enigmatic DNA methyltransferase homolog that displays denaturant-resistent binding to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 29(2): 439–448
Ehrlich M, Jackson K, Weemaes C (2006). Immunodeficiency, centromeric region instability, facial anomalies syndrome (ICF). Orphanet J Rare Dis 1: 1–2
Field LM (2000) Methylation and expression of amplified esterase genes in the aphid Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Biochem J 349: 863–868
Field LM, Devonshire AL, French-Constant RH, et al. (1989) Changes in DNA methylation are associated with loss of insecticide resistence in the peach-potato aphid Myzus persicae (Sulz.). FEBS Lett. 243: 323–327
Field LM, Lyko F, Mandrioli M, et al. (2004) DNA methylation in insects. Insect Mol Biol 13(2): 109–115
Fisher O, Siman-Tov R, Ankri S (2004) Characterization of cytosine methylated regions and 5-cytosine DNA methyltransferase (Ehmeth) in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Nucleic Acids Res 32(1): 287–297
Ghoshal K, Majumder S, Datta J, et al. (2004) Role of human ribosomal RNA (rRNA) promoter methylation and of methyl-CpG-binding protein MBD2 in the suppression of rRNA gene expression. J Biol Chem 279:6783–6793
Gilfillan GD, Dahlsveen IK, Becker PB (2004) Lifting a chromosome: dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster. FEBS Lett 567: 8–14
Gruenbaum Y, Stein R, Cedar H, et al. (1981) Methylation of CpG sequences in eukariotic DNA. FEBS Lett 124: 67–71
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41: 95–98
Heard E (2004) Recent advances in X-chromosome inactivation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16: 247–255
Hick CA, Field LM, Devonshire AL (1996) Changes in the methylation of amplified esterase DNA during loss and reselection of insecticide resistence in peach-potato aphids, Myzus persicae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 26: 41–47
Higgins DG, Bleasby AJ, Fuchs R (1994) Clustal W: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Computer applications in the Bioscience. CABIOS 8: 189–191
Jowett T (1986) Preparation of nucleic acids. In: Roberts DB (ed). Drosophila: a practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford
Kumar S, Cheng X, Klimasauskas S, et al. (1994) The DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res 22(1): 1–10
Kunert N, Marhold J, Stanke J, et al. (2003). A Dnmt2-like protein mediates DNA methylation in Drosophila. Development 130: 5083–5090
Li E, Bestor TH, Jaenisch R (1992) Targed mutation of the DNA methyltranferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell 69: 915–926
Lloyd V. (2000) Parental imprinting in Drosophila. Genetica 109: 35–44
Lyko F (2001) DNA methylation learns to fly. Trends Genet 17(4): 169–172
Lyko F, Beisel C, Marhold J, et al. (2006) Epigenetic regulation in Drosophila. Curr Trop Microbiol Immunol 310: 23–44
Lyko F, Ramsahoye BH, Jaenisch R (2000) DNA methylation in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 408(30): 538–540
Mandrioli M, Volpi N (2003) The genome of the lepidopteran Mamestra brassicae has a vertebrate-like content of methyl-cytosine. Genetica 119: 187–191
Marhold J, Rothe N, Pauli A (2004) Conservation of methylation in dipteran insects. Insect Mol Biol 13(2): 117–123
Marques EK, Napp M, Winge H (1966) A corn meal, soybean fluor, wheat germ medium for Drosophila. Drosoph Inf Serv 41: 187
Nicholas KB, Nicholas HB Jr, Deerfield DW II (1997) GeneDoc: analysis and visualization of genetic variation EMBNEW. NEWS 4:1–4
Norris DP, Patel D, Kay GF, et al. (1994) Evidence that random and imprinted Xist expression is controlled by preemptive methylation. Cell 77: 41–51
Nur U (1990) Heterochromatinization and euchromatinization of whole genomes in scale insects (Coccoidea: Homoptera). Development Suppl: 29–34
Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA, et al. (1999) DNA methyltransferasesDnmt3a and Dnmt3b are assential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell 99: 247–257
Okano M, Xie S, Li E (1998) Dnmt2 is not required for de novo and maintenance methylation of viral DNA in embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 26: 2536–2540
Paz MF, Fraga MF, Ávila S, et al. (2003) A systematic profile of DNA methylation in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 63(5): 1114–1121
Ponger L, Li W (2005) Evolutionary diversification of DNA methyltransferases in eukaryotic genomes. Mol Biol Evol 22(4): 1119–1128
Riggs AD (1975) X inativation, differentiation, and DNA metylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet 14: 9–25
Russo VEA, Martienssen RA, Riggs AD (1996) Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Santoro R, Grummt I (2001) Molecular mechanisms mediating methylation-dependent silencing of ribosomal gene transcription. Mol Cell 8: 719–725
Santoro R, Grummt I (2005) Epigenetic mechanism of rDNA gene silencing: temporal order of NoRC-mediated histone modification, chromatin remodelling, and DNA methylation. Mol Cell Biol 25: 2539–2546
Scarbrough K, Hattman S, Nur U (1984) Relationship of DNA methylation level to the presence of heterochromatin on mealybugs. Mol Cell Biol 4: 599–603
Shiota K, Kogo Y, Ohgane J (2002). Epigenetic marks by DNA methylation specific to stem germ and somatic cells in mice. Genes Cells 7(9):961–969
Staden R (1996) The Staden sequence analysis package. Mol Biotechnol 5(3): 233–241
Straub T, Dahlsveen IK, Becker PB (2005) Dosage compensation in flies: mechanism, models, mystery. FEBS Lett 579: 3258–3263
Tang L, Reddy MN, Rasheva V, et al. (2003) The eukaryotic DNMT2 genes encode a new class of cytosine-5 DNA methyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 278(36): 33613–33616
Tautz D, Hancock J, Webb D, et al. (1988) Complete sequences of the rRNA genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 5: 366–376
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W. Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tweedie S, Charlton J, Clarck V, et al. (1997) Methylation of genomes and genes at the invertebrate-vertebrate boundary. Mol Cell Biol 17: 1469–1475
Urieli-Shoval S, Gruenbaum Y, Sedat J, et al. (1982) The absence of detectable methylated bases in Drosophila melanogaster DNA. FEBS Lett 146(1): 148–152
Wade PA (2001) Methyl CpG binding proteins: coupling chromatin architecture to gene regulation. Oncogene 20: 3166–3173
Weinhold B (2006) Epigenetics: the science of change. Environ Health Perspect 114(3): A160–167
Yoder JA, Soman NS, Verdine GL, et al. (1997) DNA(cytosine-5)-methyltransferase in mouse cells and tissues. Studies with a mechanism-based probe. J Mol Biol 270: 385–395
Acknowledgements
To CNPq, FAPERGS and PROPESQ-UFRGS for fellowships and grants; to Dr. Carlos Polanco de la Puente (University of Leicester) for supplying rDNA probe. To Dr. Henrique B. Ferreira (Cestódeos Molecular Biology Laboratory, UFRGS) for support the cloning process. We thank Dr. Wolfgang J. Miller (Laboratories of Genome Dynamics Center of Anatomy and Cell Biology, Vienna, Austria) for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, R.N., D’Ávila, M.F., Robe, L.J. et al. First evidence of methylation in the genome of Drosophila willistoni . Genetica 131, 91–105 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-9116-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-9116-3