Abstract
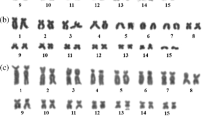
The chromosomes of hylids Hypsiboas albopunctatus, H. raniceps, and H. crepitans from Brazil were analyzed with standard and differential staining techniques. The former species presented 2n = 22 and 2n = 23 karyotypes, the odd diploid number is due to the presence of an extra element interpreted as B chromosome. Although morphologically very similar to the small-sized chromosomes of the A complement, the B was promptly recognized, even under standard staining, on the basis of some characteristics that are usually attributed to this particular class of chromosomes. The two other species have 2n = 24, which is the chromosome number usually found in the species of Hypsiboas karyotyped so far. This means that 2n = 22 is a deviant diploid number, resulted from a structural rearrangement, altering the chromosome number of 2n = 24 to 2n = 22. Based on new chromosome data, some possibilities were evaluated for the origin of B chromosome in Hypsiboas albopunctatus, as well as the karyotypic evolution in the genus, leading to the reduction in the diploid number of 2n = 24 to 2n = 22.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldissera Jr FA, Batistic RF (1992) Estudos citogenéticos em banda C e RON de algumas espécies de anuros brasileiros. In: Abstracts of the 38th Congresso Nacional de Genética, Caxambu, MG, Brasil, September 1992
Baldissera Jr FA, Oliveira PSL, Kasahara S (1993) Cytogenetics of four Brazilian Hyla species (Amphibia-Anura) and description of a case with a supernumerary chromosome. Rev Brasil Gen 16:335–345
Beçak ML (1968) Chromosomal analysis of eighteen species of Anura. Caryologia 21:191–208
Beukeboom LW (1994) Bewildering Bs: an impression of the 1st B-Chromosome Conference. Heredity 73:328–336
Bogart JP (1973) Evolution of anuran karyotypes. In: Vial JL (ed.) Evolutionary biology of the anurans. University of Missouri Press, Columbia
Bogart JP, Bogart JE (1971) Genetic compatibility experiments between some South American anuran amphibians. Herpetologica 27:229–235
Camacho JPM (ed) (2004) B chromosomes in the eukaryote genome. Karger, Basel
Camacho JPM, Sharbel TF, Beukeboon LW (2000) B-chromosome evolution. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355:163–178
Cardoso AJ (1986) Utilização de recursos para reprodução em comunidade de anuros no sudeste do Brasil. Thesis, Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP)
Dutrillaux B, Couturier J (1981) La pratique de l'analyse chromosomique. Masson, Paris
Faivovich J et al (2005) Systematic review of the frog family Hylidae, with special reference to Hylinae: Phylogenetic analysis and taxonomic revision. Bull Am Museum Natural History. New York 294:1–240
Feitosa VLC, Recco-Pimentel SM, Cardoso AJ (1995) Structural chromosomal alterations in Hyla albopunctata and Aplastodiscus perviridis (Anura, Hylidae) from Morro do Ferro region of Minas Gerais. Rev Brasil Genet 18:191–197
Frost DR (2004) Amphibian species of the world: an online reference. Version 3.0 Eletronic database. http://research. amnh.org/herpetology/amphibian/index.html. American Museum of Natural History. Cited 25 Jan 2006
Green DM (1991) Supernumerary chromosomes in amphibians. In: Green DM, Sessions SK (eds) Amphibians Cytogenetics and Evolution. Academic Press, San Diego
Green DM (2004) Structure and evolution of B chromosomes in amphibians. Cytogenet Genome Res 106:235–242
Gruber SL (2002) Estudos citogenéticos em espécies do gênero Hyla (Anura, Hylidae) dos grupos com 2n = 24 e 2n = 30, com técnicas de coloração diferencial. Dissertation, Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP)
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36:1014–1015
Insaurralde DR, Baldo JD, Fenocchio AS et al (1991) Relevamiento cariotípico de la herpetofauna de la provincia de Misiones, Argentina. In: Abstracts of the 37th Congresso Nacional de Genética, Caxambu, MG, Brasil, September 1991
Jones RN, Rees H (1982) B Chromosomes. Academic Press, London
Kasahara S, Yonenaga-Yassuda Y (1982) Chromosomal variability in Akodon sp. Cytologia 47:317–324
Kasahara S, Silva APZ, Gruber SL (1998) Use of lymphocyte cultures for BrdU replication banding patterns in anuran species (Amphibia). Genet Mol Biol 21:471–476
Kasahara S, Silva APZ, Gruber SL et al (2003) Comparative cytogenetic analysis on four tree frog species (Anura, Hylidae, Hylinae) from Brazil. Cytogenet Genome Res 103:155–162
King M (1990) Animal Cytogenetics, vol. 4. Chordata 2, Amphibia. Gerbrüder Borntraeger, Stuttgart and Berlin
Kuramoto M (1990) A list of chromosome numbers of anuran amphibians. Bull Fukuoka Univ Educ 39:87–127
Medeiros LR, Rossa-Feres DC, Jim J et al (2006) B-chromosomes in two Brazilian populations of Dendropsophus nanus (Anura, Hylidae). Genet Mol Biol 29:257–262
Miura I (1995) The late replication banding patterns of chromosomes are highly conserved in the genera Rana, Hyla, and Bufo (Amphibia: Anura). Chromosoma 103:567–574
Rabello MN (1970) Chromosomal studies in Brazilian anurans. Caryologia 23:45–59
Rabello MN, Beçak ML, Beçak W (1971) Contribuição à citotaxonomia da família Hylidae. Arquivos do Museu Nacional LIV:285–286
Rosa C, Aguiar-Jr O, Giaretta AA et al (2003) Karyotypic variation in the genus Megaelosia (Anura, Hylodinae) with the first description of a B-chromosome in leptodactylid frog. Copeia 1:166–174
Schweizer D (1980) Reverse fluorescent chromosome banding with chromomycin and DAPI. Chromosoma 58:307–324
Silva APZ, Haddad CFB, Kasahara S (2000) Chromosomal studies on five species of the genus Leptodactylus Fitzinger, 1826 (Amphibia, Anura) using differential staining. Cytobios 103:25–38
Soma M, Beçak ML, Beçak W et al (1974) Variabilidade de DNA e cariótipo de anfíbios anuros. In: Abstracts of the 26th Reunião Anual da Sociedade Brasileira para o Progresso da Ciência, Brasil, July 1974
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Expl Cell Res 75:304–306
Acknowledgements
The authors are greatly indebted to FAPESP and CNPq for financial support; to Dr. A.S. Abe and Dr. P.C. Garcia for helping in the collection of some specimens used in this study; and to Rogilene Aparecida Prado for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by FAPESP and CNPq
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gruber, S.L., Haddad, C.F.B. & Kasahara, S. Chromosome banding in three species of Hypsiboas (Hylidae, Hylinae), with special reference to a new case of B-chromosome in anuran frogs and to the reduction of the diploid number of 2n = 24 to 2n = 22 in the genus. Genetica 130, 281–291 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-9105-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-9105-6