Abstract
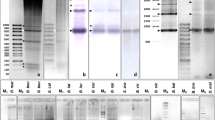
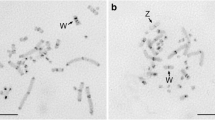
We have cloned and sequenced a 321bp band of repetitive DNA from Eptesicus fuscus and E. serotinus observed after gel electrophoresis of EcoRI digested genomic DNA in both species. Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA (from both species) digested with the same enzyme showed the existence of a ladder pattern indicating that the repetitive DNA is arrayed in tandem. The repetitive sequences have a monomer unit of 321bp which is composed of two subunits of 160bp, suggested by the existence of a 160bp band in the ladder of E. fuscus and by the presence of some direct repeats found in the analysis of the consensus sequence. Analysis of the methylation status demonstrated that cytosines in CCGG sequences in this satellite DNA are methylated in E. fuscus but not in the E. serotinus. Alignment of the sequenced clones showed that several nucleotide positions are diagnostic species-specific and consequently the phylogenetic analysis grouped the monomer units from both species in two clearly separated groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S. F., T. L. Madden, A. A. Schäffer, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, W. Miller & D. J. Lipman, 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 3389–3402.
Baker, R. J., J. L. Longmire, M. Maltbie, M. J. Hamilton & R. A. Van Den Bussche, 1997. DNA synapomorphies for a variety of taxonomic levels from a cosmid library from the New World bat Macrotus waterhousii. Syst. Biol. 46: 579–589.
Barragán, M. J. L., S. Martínez, J. A. Marchal, M. Bullejos, R. Díaz de la Guardia & A. Sánchez, 2002a. Highly repeated DNA sequences in three species of the genus Pteropus (Megachiroptera, Mammalia). Heredity 88: 366–370.
Barragán, M. J. L., S. Martínez, J. A. Marchal, M. Bullejos, R. Díaz de la Guardia & A. Sánchez, 2002b. Highly repeated DNA sequences in Miniopterus schreibersi (Vespertilioni-dae;Chiroptera). Hereditas 137: 65–71.
Barragán, M. J. L., S. Martínez, J. A. Marchal, M. R. Fernández, M. Bullejos, R. Díaz de la Guardia & A. Sánchez, 2003. Pericentric satellite DNA sequences in Pipistrellus pipistrel-lus (Vespertilionidae;Chiroptera;Mammalia). Heredity 91: 232–238.
Borodulina, O. R. & D. A. Kramerov, 1999. Wide distribution of short interspersed elements among eukaryotic genomes. FEBS 457: 409–413.
Burton, D. W., J. W. Bickhan & H. H. Genoways, 1989. Flow-cytometric analysis of nuclear DNA content in four families of Neotropical bats. Evolution 34: 756–765.
Capanna, E. & M. G. Manfredi Romanini, 1971. Nuclear DNA content and morphology of the karyotype in certain palearctic Microchiroptera. Caryologia 24: 471–482.
Capanna, E. & M. G. Manfredi Romanini, 1973. Contenu en ADN des noyaux postkinétiques et évolution du caryotype chez les chiroptères. Periodicum Biologorum 75: 55–60.
Gregory, T. R., 2001. Animal Genome Size Database. http:// www. genomesize. com.
Kimura, M., 1980. A simple method for estimating evo-lutionary rates of base substitution through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16: 111–120.
Kumar, S., K. Tamura & M. Nei, 1993. MEGA: Mole-cular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, Version 1.01. The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802.
Lee, C. & C. C. Lin, 1996. Conservation of a 31-bp bovine subrepeat in centromeric satellite DNA monomers of Cervus elaphus and other cervid species. Chromosome Res. 4: 427–435.
Lorite, P., M. F. García & T. Palomeque, 1999. Satellite DNA in the ant Messor structor. Genome 42: 881–886.
Nei, M., 1987. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York.
Pettigrew, J. D.& J. A. Kirsch, 1995. Flying primates revisited: DNA hybridization with fractionated, GC-enriched DNA. S. Afr. J. Sci. 91: 477–482.
Rojas-Rousse, D., Y. Bigot & G. Periquet, 1993. DNA insertions as a component of the evolution of unique satellite DNA families in two genera of parasitoid wasps: Diadromus and Eupelmus (Hymenoptera). Mol. Biol. Evol. 10: 383–396.
Romanini, M. G., C. Pellicciari, F. Bolchi & E. Capanna, 1975. New data on the DNA content of postkinetic nuclei of the bats. Mammalia 39: 675–683.
Rozas, J. & R. Rozas, 1999. DnaSP version 3: and inte-grated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15: 174–175.
Saitou, N. & M. Nei, 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4: 406–425.
Sambrook, J., E. F. Fritsch & T. Maniatis, 1989. Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Sonoda, S., T. Yamada, T. Naito & F. Nakasuji, 1995. Repetitive DNA sequences families in Hemitaxonus minom-ensis and H. athyrii (Hymenoptera;Tenthredinidae). Jpn. J. Genet. 70: 7–16.
Tarès, S., J. Cornuet & P. Abad, 1993. Characterization of an unusually conserved Alu I highly reiterated DNA sequence family from the Honeybee, Apis mellifera. Genetics 134: 1195–1204.
Thompson, J. D., D. G. Higgins & T. J. Gibson, 1994. CLUS-TAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-speci c gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 22: 4673–4680.
Van Den Bussche, R. A., J. L. Longmire & R. J. Baker, 1995. How bats achieve a small C-value: frequency of repetitive DNA in Macrotus. Mammal Genome 6: 521–525.
Zhang, X. Y. & W. Horz, 1984. Nucleosomes are positioned on mouse satellite DNA in multiple highly speci c frames that are correlated with a diverged subrepeat of nine base-pairs. J. Mol. Biol. 176: 105–129.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchal, J., Martínez, S., Acosta, M. et al. Characterization of an EcoRI family of satellite DNA from two species. Genetica 122, 303–310 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-004-2220-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-004-2220-3