Abstract
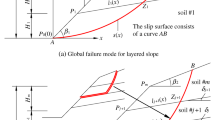
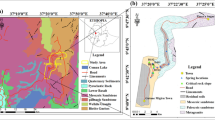
The preferred plane often exists in a layered slope, which has a main influence on the slope stability. Such a plane can evolve into the failure surface, due to the internal and external triggers of landslides. This paper proposes a case study of the failure of a highway slope in Sichuan, China. The site investigations were conducted using a number of methods, such as geological survey, unmanned aerial vehicle survey, slope monitoring, in-situ and laboratory tests. Through the case study, the failure mechanism of the layered slope was discussed, where the slope stability analysis was conducted using the limit equilibrium method (slip-wedge method) and strength reduction method (SRM). According to the circumstance of the landslide area and the requirement for the highway, this paper also proposes the stabilization measures, which was subsequently validated by SRM. Finally, the sliding mechanism of the landslide was discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the study is all included in the article.
References
Gokceoglu C, Aksoy H (1996) Landslide susceptibility mapping of the slopes in the residual soils of the Mengen region (Turkey) by deterministic stability analyses and image processing techniques. Eng Geol 44:147–161
Huang RQ (2007) Large-scale landslides and their occurrence mechanism in China since the 20th century. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 182:433–454
Huang ZQ, Tim Law K et al (2009) The chaotic characteristics of landslide evolution: a case study of Xintan landslide. Environ Geol 56:1585–1591
Li XP, Wang T, Xie QM et al (2007) Study on stability analysis and treatment optimization of expressway landslide. Rock Soil Mech 28:981–990
Li S, Wang YL, Zhu Q et al (2020) Comprehensive treatment plan for bedding traction cutting landslide. Sci Technol Eng 20:303–311
Liu DP, Chen T (2019) Study on stability analysis and treatment of a landslide in Gannan expressway. J Catastr 34:174–179
Müller L (1964) The rock slide in the Vajont Valley. Rock Mech Eng Geol 2:148–212
Müller L (1968) New considerations on the Vaiont slide. Rock Mech Eng Geol 6:1–91
Müller L (1987) The Vaiont catastrophe-a personal review. Eng Geol 24:423–444
Song DR, Ren Weizhong R et al (2013) Discussion on the failure mechanism of towed landslide and its reinforcement measures. Rock Soil Mech 34:3587–3593
Tao LJ, Wang QH (2016) The damage mechanism and treatment of highway landslide in red bed area. J Civil Eng Manag 33:12–17
Wang ZF, Liu HD, He SM (2013) Dynamic deformation monitoring and three-dimensional numerical analysis of K62 landslide on the approach road of Ahaihai hydropower station. Chin J Geotech Eng 35:94–100
Xian YJ, Chen XJ, Wang ZG (2015) Rock-soil slope stability analysis and anti-slide pile design based on finite element strength reduction coefficient method. Geol Sci Technol Inf 34:176–182
Xiong CZ, Shi YC, Ji F et al (2019) Deformation failure mechanism and stability evaluation of a highway landslide in Guizhou. Geol Hazards Environ Prot 30:3–7
Xu Q, Huang RQ et al (2009) The Jiweishan landslide of June 5 2009 in Wulong, Chongqing: characteristics and failure mechanism. J Eng Geol 17:432–444
Yin YP, Sun P, Zhang M et al (2011) Mechanism on apparent dip sliding of oblique inclined bedding rockslide at Jiweishan, Chongqing, China. Landslides 8:49–65
Zhang LY, Zheng YR, Zhao SY (2003) Study on the accuracy of the finite element strength reduction coefficient method for calculating the safety factor of soil slope stability. J Hydraul Eng 1:21–27
Zhang ZR, Lu HP, Zhou SZ (2016) Analysis and treatment design of a highway landslide in Xiangxi. J Railw Sci Eng 13:1068–1074
Zhang DQ, Jiang XY, Zou NN et al (2019) Numerical simulation of the influence of rainfall seepage on the stability of accumulation landslides. Sci Technol Eng 19:338–344
Zhao JL, Li GF, Hu W et al (2017) Experimental study on anti-sliding effect and deformation characteristics of straight roots of arbor in shallow landslide_parallel double roots. Sci Technol Eng 17:163–169
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Central Plains Science and technology innovation leader Project (214200510030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design, ZH and LM; Writing-original draft, CW and XL; Writing-review & editing, TR and ZH. All the authors participated in the critical revision, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ran, T., Huang, Z., Meng, L. et al. Mechanisms and Stabilization Measures of Layered Slope: A Study Case of a Layered Slope in Sichuan, China. Geotech Geol Eng 40, 785–794 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-021-01924-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-021-01924-7