Abstract
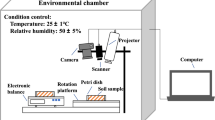
In geotechnical engineering, there is a significant potential of using image analysis technique to study cracking soils by quantifying the characteristics of the crack network. In the current work, the image analysis process was used to obtain comprehensive information about the cracking mechanism and shrinkage during drying. Artificial soil samples investigated in the lab via desiccation tests under different boundary and environment conditions. Soil specimens with smooth and rough bottom contact surfaces were allowed to desiccate under opened and closed environments with specific pressure and temperature conditions. Digital photos were regularly taken during the tests then processed with image j software to characterize the crack patterns. The investigated effects were expressed in terms of crack intensity factor, CIF, and total crack intensity factor, (CIF)tot. The friction of the bottom contact surface, the environment, and the exposition to a saturated salt solution affect cracks formation and affect the cracking mechanism and shrinkage during drying. Smooth and rough boundaries showed significant differences at the end. For rough bottom contact surface, the difference between the values of suction under the opened environment and the closed one may have a small or insignificant effect on (CIF)tot, also the pattern of the cracks did not differ that much. CIF increases with an increase in the friction of the bottom contact surface. Also, samples dried under the open environment exhibit higher CIF and (CIF)tot than those under a closed environment. However, (CIF)tot decreases with an increase in the friction of the bottom surface. For the rough boundary condition under the open environment, the samples exposed to a salt solution had lower CIF and (CIF)tot in comparison with the other one not exposed. Since the orthogonal intersections are more dominant than others, it could be observed that the tensile stresses have a significant effect on desiccation cracks under the investigated conditions.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adem HH, Vanapalli SK (2015) Review of methods for predicting in situ volume change movement of expansive soil over time. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 7:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2014.11.002
Altuhafi F, O’Sullivan C, Cavarretta I (2013) Analysis of an Image-based method to quantify the size and shape of sand particles. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 139:1290–1307. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000855
American Society for testing and Materials (ASTM) (2017) Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Sec. 4, vol. 04.08 and 04.09, West Conshohocken
Auvray R, Rosin-Paumier S, Abdallah A, Masrouri F (2013) Quantification of soft soil cracking during suction cycles by image processing. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 18(1):11–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2013.840250
Barbour SL, Fredlund DG (1989) Mechanisms of osmotic flow and volume change in clay soils. Can Geotech J 26:551–562. https://doi.org/10.1139/t89-068
Bhatia SK, Soliman A (1991) The Application of image analysis techniques to microstructure studies in geotechnical engineering. In: Bennett RH, et al. (eds) Microstructure of fine-grained sediments. Frontiers in sedimentary geology. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4428-8_40
Cordero JA, Useche G, Prat PC, Ledesma A, Santamarina JC (2017) Soil desiccation cracks as a suction–contraction process. Géotech Lett 7(4):279–285. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgele.17.00070
Costa S, Kodikara J (2012) Evaluation of J integral for clay soils using a new ring test. Geotech Test J 35(6):981–989. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ104271
Costa S, Kodikara J, Shannon B (2013) Salient factors controlling desiccation cracking in laboratory experiments. Geotechnique 63(1):18–29. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.9.P.105
El Maarry MR, Watter WA, Yoldi Z, Pommerol A, Fischer D, Eggenberger U, Thoma N (2015) Field investigation of dried lakes in western United States as an analogue to desiccation fractures on Mars. J Geophys Res Planets 120(12):2241–2257. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JE004895
Ferreira T, Rasband W (2012) Image J. User Guide
Gui YL, Zhao ZY, Kodikara J, Bui HH, Yang SQ (2016) Numerical modelling of laboratory soil desiccation cracking using UDEC with a mix-mode cohesive fracture model. Eng Geol 202:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.12.028
Guo Y, Han C, Yu X (2018) Laboratory characterization and discrete element modeling of shrinkage and cracking in clay layer. Can Geotech J 55(5):680–688. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2016-0674
Hartge K, Bachmann J (2000) Angles between cracks developed at primary shrinkage of finegrained soil material. Int Agrophys 14(1): 43–51. https://www.international-agrophysics.org/Angles-between-cracks-developed-at-primary-shrinkage-of-finegrained-soil-material,106868,0,2.html
Horgan GW (1998) Mathematical morphology for analyzing soil structure from Images. Eur J Soil Sci 49:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.1998.00160.x
Ito M, Azam S (2010) Determination of swelling and shrinkage properties of undisturbed expansive soils. Geotech Geol Eng 28:413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-010-9301-0
Julina M, Thyagaraj T (2019) Quantification of desiccation cracks using X-ray tomography for tracing shrinkage path of compacted expansive soil. Acta Geotech 4:35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0647-4
Kaddhour G, Ando E, Salager S, Bésuelle P, Viggiani C, Hall S, Desrues J (2013) Application of X-ray tomography to the characterisation of grain-scale mechanisms in sand. In: Laloui L, Ferrari A (eds) Multiphysical testing of soils and shales. Springer Series in geomechanics and geoengineering, Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32492-5_23
Kodikara J, Costa S (2013) Desiccation cracking in clayey soils: mechanisms and modelling. In: Laloui L, Ferrari A (eds) Multiphysical testing of soils and shales. Springer series in geomechanics and geoengineering, Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32492-5_2
Konrad JM, Ayad R (1997) An idealized framework for the analysis of cohesive soils undergoing desiccation. Can Geotech J 34(4):477–488. https://doi.org/10.1139/t98-069
Lakshmikantha MR (2009) Experimental and theoretical analysis of cracking in drying soils. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Geotechnical Engineering and Geosciences, Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona, Spain
Lakshmikantha MR, Prat PC, Ledesma A (2009) Image analysis for the quantification of a developing crack network on a drying soil. Geotech Test J 32(6):505–515. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ102216
Lakshmikantha MR, Reig R, Prat PC, Ledesma A (2013) Origin and mechanism of cracks seen at the bottom of a desiccating soil specimen. Geo-Congr San Diego California United States. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784412787.079
Laloui L, Ferrari A (2013) Multiphysical testing of soils and shales. Springer, Heidelberg
Li JH, Lu Z, Guo LB, Zhang LM (2017) Experimental study on soil-water characteristic curve for silty clay with desiccation cracks. Eng Geol 218:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.01.004
Miller C, Mi H, Yesiller N (1998) Experimental analysis of desiccation crack propagation in clay liners. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34(3):677–686. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb00964.x
Morris PH, Graham J, Williams DJ (1992) Cracking in drying soils. Can Geotech J 29(2):263–277. https://doi.org/10.1139/t92-030
Nahlawi H, Kodikara J (2006) Laboratory experiments on desiccation cracking of thin soil layers. Geotech Geol Eng 24(6):1641–1664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-005-4894-4
Pelot DD, Jun S, Yarin AL (2015) Bentonite Dispersions: transition from liquid-like to solid-like behavior and cracking. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 219:50–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2015.03.001
Preston S, Griffiths BS, Young IM (1997) An Investigation into sources of soil crack heterogeneity using fractal geometry. Eur J Soil Sci 48:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1997.tb00182.x
Puppala A, Katha B, Hoyos L (2004) Volumetric shrinkage strain measurements in expansive soils using digital imaging technology. Geotech Test J 27(6):547–556. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ12069
Rodríguez R, Sánchez M, Ledesma A, Lloret A (2007) Experimental and numerical analysis of desiccation of a mining waste. Can Geotech J 44(6):644–658. https://doi.org/10.1139/t07-016
Sarmah AK, Pillai-McGarry U, McGarry D (1996) Repair of the structure of a compacted vertisol via wet/dry cycles. Soil Tillage Res 38:17–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-1987(96)01018-5
Scherer GW (1990) Theory of drying. J Am Ceram Soc 73(1):3–14
Serra J (1982) Image analysis and mathematical morphology. Academic Press, London
Shin H, Santamarina JC (2011) Desiccation cracks in saturated fine-grained soils: particle-level phenomena and effective-stress analysis. Géotechnique 61(11):961–972. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.8.P.012
Singh SP, Rout S, Tiwari A (2018) Quantification of desiccation cracks using image analysis technique. Int J Geotech Eng 12(4):383–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2017.1282400
Stirling RA, Glendinning S, Davie T (2017) Modelling the deterioration of the near surface caused by drying induced cracking. Appl Clay Sci 146(15):176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.06.003
Tang C, Shi B, Liu C, Zhao L, Wang B (2008) Influencing factors of geometrical structure of surface shrinkage cracks in clayey soils. Eng Geol 101(3–4):204–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.05.005
Tang CS, Zhu C, Leng T, Shi B, Cheng Q, Zeng H (2019) Three dimensional characterization of desiccation cracking behavior of compacted clayey soil using X ray computed tomography. Eng Geol 255(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.04.014
Velde B (1999) Structure of surface cracks in soil and muds. Geoderma 93(1–2):101–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(99)00047-6
Velde B (2001) Surface cracking and aggregate formation observed in a rendzina soil La Touche (Vienne). Fr Geoderma 99(3–4):261–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(00)00074-4
Vogel H, Hoffmann H, Leopold A, Roth K (2005) Studies of crack dynamics in clay soil: II. A physically based model for crack formation. Geoderma 125(3–4):213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.07.008
Wahyudi S, Miyashita Y, Koseki J (2013) Observation of shear banding characteristics of sand in torsional shear test using image analysis technique. In: Laloui L, Ferrari A (eds) Multiphysical testing of soils and shales. Springer series in geomechanics and geoengineering, Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32492-5_24
Yesiller N, Miller CJ, Inci G, Yaldo K (2000) Desiccation and cracking behavior of three compacted landfill liner soils. Eng Geol 57(1–2):105–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00022-3
Zhao B, Santamarina JC (2019) Desiccation crack formation beneath the surface. Géotechnique. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.18.T.019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Jeznawi, D., Sanchez, M. & Al-Taie, A.J. Using Image Analysis Technique to Study the Effect of Boundary and Environment Conditions on Soil Cracking Mechanism. Geotech Geol Eng 39, 25–36 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01376-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01376-5