Abstract
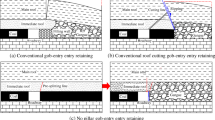
Aiming at the serious deformation problem of the roadway supported along gob-side by stowing with high-water-content packing on the engineering background of No. 1200 working face, the technologies of supporting beside the roadway by stowing with high-water-content packing and relieving pressure by roof-cutting along gob-side entry are applied in different sections respectively. Based on the engineering geological conditions of the working face, the roof-cutting parameter is calculated and some technologies have been put into use in the project: high constant resistance and large deformation (CRLD) cable supporting technology; bilateral cumulative tensile explosion technology; gangue blocking supporting technology. Arm-shortening beam resulting from roof-cutting cuts down the cantilever beam length of roadway roof. CRLD cable supporting can effectively improve the mechanical properties of roof strata. The roof collapses smoothly within the height of cutting seam along the gob-side entry, filling the gob with gangue quickly. The point where the gob roof touches the collapsed gangue moves toward the remained roadway side and the subsiding and rotary deformation problem of gangue-formed wall gets under control and the subsiding level is reduced. Compared with the original backfilling body, the collapsed gangue weakens the level of stress concentration. Meanwhile, the subsiding of minor roofs and the roof strengthening can dramatically reduce the bottom heave. Engineering practice has proved that in such mining geological conditions, the method of releasing pressure by roof-cutting along gob-side entry can effectively decrease the deformation of the retained roadways, greatly reduce the workload, enhance productivity and guarantee the remarkable benefit of retaining roadway economy.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
He M (2014) Progress and challenges of soft rock engineering in depth. J China Coal Soc 39(8):1409–1417 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He M, Guo Z (2014) Mechanical property and engineering application of anchor bolt with constant resistance and large deformation. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31(7):12971–1308 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He M, Cao W, Shan R et al (2003) New blasting technology-bilateral cumulative. Chin J Rock Mechan Eng 22(12):2047–2051 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He M, Qian Q et al (2010) The basis of deep rock mechanics. Science Press, Beijing
He M, Gong W, Wang J et al (2014a) Development of a novel energy-absorbing bolt with extraordinarily large elongation and constant resistance. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 67:29–42
He M, Wang J, Sun X et al (2014b) Mechanics characteristics and applications of prevention and control rack bursts of the negative Poisson’s ratio effect anchor. Rock Mech Eng 39(2):214–221 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hua X (2006) Development status and improved proposals on gob-side entry retaining support technology in China. Coal Sci Technol 34(12):78–81 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kang H, Niu D, Zhang Z et al (2010) Deformation characteristic of surrounding rock and supporting technology of gob-side entry retaining in deep coal mine. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 29(10):1978–1987 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li H (2000) Control design of roof rocks for gob-side entry. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 19(5):651–654 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu Y (2014) Study on floor heave mechanism of gob-side entry retaining in Zhongxing Colliery. China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu X (2013) Research on controlling mechanism of surrounding rock around gob-side entry retaining in deep coal mine with large section. China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu X, Hua X, Zhao M (2011) Calculation and analysis of immediate roof subsidence in gob-side Entry Retaining. J Min Saf Eng 28(1):34–38 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Miao X, Mao Z, Hu G et al (1997) Research on broken expand and press solid characteristics of rocks and coals. Exp Mech 12(3):394–400 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qian M, Shi P, Xu J (2010) Coal mine ressure and strata control. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Song Z, Cui Z, Xia H et al (2010) The fundamental theoretical and engineering research on the green safe non-coal pillar mining model by mainly using coal gangue backfill. J China Coal Soc 35(5):705–710 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun H, Zhao B (1993) Theory and practice of gob-side entry retaining. China Coal Industry Publishing House, Beijing, pp 67–75
Sun X, Liu X, Liang G et al (2014a) Key parameters of gob-side entry retaining formed by roof-cutting and pressure releasing in thin coal seams. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 33(8):1449–1456 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun X, Wang D, Wang C et al (2014b) Tensile properties and application of constant resistance and large deformation bolts. Rock Mech Eng 33(9):1765–1771 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu Y, Zhou H, Bai J et al (2015) Characteristics and control method of floor heave in god-side entry retaining. J Min Saf Eng 34(S2):4235–4244 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yuan L (2009) Theory and practice on integrated pillarless coal production and methane extraction in multi seams of low permeability. Eng Sci 11(5):72–80 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yuan SC, Harrison JP (2004) An empirical dilatancy index for the dilatant deformation of rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(4):679–686 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang G, He M, Yu X et al (2011) Research on the technique of non-pillar mining with gob-side entry formed by advanced roof caving in the protective seam in Baijiao coal mine. J Min Saf Eng 28(4):511–516 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang G, Yu X, Yang C (2016) Study on deformation control of gob-side entry retaining with roof-cutting and engineering application. J China Coal Soc 41(S1):35–43 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the basic theory and key technology of shaft construction and hoisting in deep coal mines of China (2016YFC0600900), Yue Qi outstanding scholar award program of China University of Mining & Technology, Beijing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao-ming, S., Gan, L., Peng, S. et al. Application Research on Gob-Side Entry Retaining Methods in No. 1200 Working Face in Zhongxing Mine. Geotech Geol Eng 37, 185–200 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0602-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0602-z