Abstract
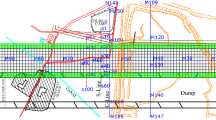
Surface ground movements are usually described by a number of characteristic indices such as vertical displacement, horizontal strain and slope, which are an inevitable consequence of underground mining. Every point at the surface over a panel is subjected to strain and slope during mining and its investigation is essential to assess the safety of surface structures. Therefore, the behaviour of dynamic active and residual subsidence was studied for a few panels of Jharia coalfield. The subsidence and slope were linearly related to time. Compressive and tensile strains showed typical fluctuating characteristic behaviour. The rate of mining being a key and controlling parameter for rate of subsidence their inter-relationship was developed, which showed a rational trend. Compressive and tensile strains and slope showed poor correlation with rate of face advance.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACARP (2002) Impacts of mine subsidence on the strata & hydrology of river valleys—management guidelines for undermining cliffs, gorges and river systems, Australian Coal Association Research Program, Final Report C9067 Stage 2, June
Agricola G (1950) De Re Metallica. Translated from the first Latin edition of 1556. In: Hoover H, Hoover LH (eds) Dover Publications, New York, 378 p
Anon (2007a) Narrabri Coal Project Subsidence Assessment, Prepared by Mining Geotechnical Services Pty Ltd, specialist consultant studies compendium volume 2, part 8, ABN: 76 107 813 963, Narrabri Coal Pty Ltd, Narrabri Coal Project Report No. 674/05, March, pp 1–18
Anon (2007b) General discussion on systematic and non systematic mine subsidence ground movements. Mine subsidence engineering consultants level 1/228 Victoria Avenue—Chatswood—NSW 2067 PO Box 3047—Willoughby North—NSW, August
Anon (2009) Subsidence assessment for longwall mining in the Hebden and Barret seams, Strata Control Technology Operations Pty Ltd., GLEN 3253, March, pp 1–55
Booth CJ, Spande ED, Pattee CT, Miller JD, Bertsch LP (1998) Positive and negative impacts of longwall mine subsidence on a sandstone aquifer. Environ Geol 34:223–233
Fox CS (1930) The Jharia coalfield, Mem. Geol. Surv. India, 255 p
Gregory C (1987) A concise history of mining. Pergamon Press, UK, 195 p
Hartman HL (1992) SME mining engineering handbook. Society of mining, metallurgy and exploration, Inc. Port City Press, Baltimore
Holla L (1987) The response of domestic structures to ground movements caused by mine subsidence. In: Proceedings Nat. Structural Engr. Conf., The Institution of Engineers, Australia, pp 427–477
Holla LE (2000) Mine subsidence in the Southern Coalfield, NSW, Australia, Mineral Resources of NSW, Sydney
Karaman A, Carpenter PJ, Booth CJ (2001) Type-curve analysis of water-level changes induced by a longwall mine. Environ Geol 40:897–901
Karmis M, Agioutantis Z (1998) Correlation of subsidence parameters and damage assessment due to underground mining. In: Proceedings, 5th symposium on environmental issues and waste management in energy and mineral production, Ankara, Turkey, May pp 18–20, 195–201
Kratzsch H (1983) Mining subsidence engineering (Trans: Fleming RFS). Springer, New York, pp 1–40, 183–185, 250–251, 283–286, 332–334, 363–442 and 501–503
Mehnert BB, Van Roosendaal DJ, Bauer RA (1992) Long-term subsidence monitoring over a longwall coal mine in southern Illinois. In: Peng SS (ed) Proceedings of third workshop on surface subsidence due to underground mining, Dept. of Mining Engr. West Virginia Univ. Morgantown, WV, pp 311–316
Mining Environmental Handbook (1997) Marcus, Jerrold J. Imperial College Press, London
Prakash A, Singh KB, Kumar A, Lokhande RD (2005) Residual subsidence over abandoned mine: a case study. Min Eng J 7(1):17–21
Prakash A, Singh AK, Mandal PK, Singh KB (2008) Damage to surface structures due to triggered subsidence—a case study. Mine Tech 29(2):17–24
Schenk J (1999) Measurement of movements and deformations in subsidence depression (in Czech), Ostrava, VŠB-TUO, 144 s, ISBN 80-7078-711-2
Shadbolt CH (1978) Mining subsidence-historical review and state of the art. In: Proceedings, conference on large ground movements and structures, Cardiff, Wales, pp 705–748
Sheorey PR, Loui JP, Singh KB, Singh SK (2000) Ground subsidence observations and a modified influence function method for complete subsidence prediction. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 37:801–818
Singh KB, Singh TN (1998) Ground movements over longwall workings in the Kamptee coalfield, India. Eng Geol 50:125–139
Soliman M (1998) Environmental Hydrogeology, CRC Press LLC, US, pp 81–101
Wagner H, Schomann EHR (1991) Surface effects of total coal-seam extraction by underground mining methods. JS Astr Inst Min Metal 91(7):221–231
Whittaker BN, Reddish DJ (1989) Subsidence—occurrence, prediction and control. Elsevier, Lennningrad, p 528
Whittaker BN, Reddish DJ (1993) Subsidence behaviour of rock structures. In: Brown ET, Pairhurst C, Hoek E (eds) Comprehensive rock engineering: principles, practice and projects, 4, excavation, support and monitoring. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 751–780
Acknowledgments
The financial support extended by Tata Steel to undertake this study is sincerely acknowledged. The authors are highly thankful to the Director, Central Institute of Mining and Fuel Research, Dhanbad, for permitting to publish the paper. Subsidence monitoring team are also sincerely acknowledged for data generation at regular intervals to carry out this study. The views expressed in this paper are those of authors and not necessarily of the organizations they represent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, A., Kumar, A. & Singh, K.B. Dynamic Subsidence Characteristics in Jharia Coalfield, India. Geotech Geol Eng 32, 627–635 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9738-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9738-7