Abstract
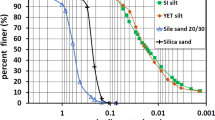
Loose saturated cohesionless soils are most susceptible to liquefaction, however there are strong historical evidence suggesting that soils containing fines such as silty sands are also prone to liquefaction during earthquakes. The liquefaction of silty sands has been observed in a number of recent case studies. This paper presents the effects of fine silts on liquefaction potential of sandy soil. Tests have been conducted on the vibration table at different accelerations and pore water pressure is measured. During the lab investigation, locally (Roorkee, India) available Solani Sand and Dhanauri Silt have been used. The soil samples have been prepared by varying silt content and the initial relative density. The results of the study performed are used to clarify the effects of non-plastic fines content on the Solani sand. As the silt content increases, the number of cycles required to produce maximum pore water pressure increases. For a particular level of excitation, rate of pore water pressure generation is maximum at critical silt content. It is observed that critical silt content to generate maximum pore water pressure is different for different accelerations. Further, effect of silt content is very much dependent on relative density.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carraro JAH, Bandini P, Salgado R (2003) Liquefaction resistance of clean and nonplastic silty sands based on cone penetration resistance. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 129(11):965–976
Chang NY, Yeh ST, Kaufman LP (1982) Liquefaction potential of clean and silty sands. Proceedings of 3rd International Earthquake Microzonation Conference, vol 2. Seattle, USA, pp 1017–1032
Dezfulian H (1984) Effects of silt content on dynamic properties of sandy soils. Proceedings of the 8th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering. San Francisco, USA, pp 63–70
El Hosri MS, Biarez H, Hicher PY (1984) Liquefaction characteristics of silty slay. Proceedings of 8th World Conference of Earthquake Engineering. San Francisco, USA, pp 277–284
Finn WL (1982) Soil liquefaction studies in the Peoples Republic of China. In: Soil mechanics—transient and cyclic loads, John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 609–626
Finn WDL, Ledbetter RH, Wu G (1994) Liquefaction in silty soils: design and analysis. In: Ground failures under seismic conditions, Geotechnical special publication, No. 44, ASCE, pp 51–76
Guo T, Prakash S (1999) Liquefaction of silts and silt-clay mixtures. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 125(8):706–710
Gupta MK (1977) Liquefaction of saturated sands during earthquakes. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Earthquake Engineering, University of Roorkee, Roorkee, India
Jennings PC (1980) Earthquake engineering and hazards reduction in china. CSCPRC, Report No. 8, National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D.C
Koester JP (1994) The influence of fine type and contents on cyclic resistance. In: Ground failures under seismic conditions, Geotechnical special publication, No. 44, ASCE, pp 17–33
Kramer SL (1996) Geotechnical earthquake engineering. Pearson Education, First Indian reprint 2003
Okashi Y (1970) Effects of sand compaction on liquefaction during Tokachioki earthquake. Soils Found JSSMFE 10(2):112–128
Patel AK (2006) Effect of fines on liquefaction potential. M. Tech. Dissertation, Department of Earthquake Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee, India
Polito CP, Martin JR (2001) Effects of nonplastic fines on the liquefaction resistance of sands. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 127(5):408–415
Prakash S (1981) Soil dynamics. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Prakash S, Sandoval JA (1992) Liquefaction of low plasticity silts. J. of Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, Elsevier Science Publishers Ltd., 11:373–379
Sandoval J (1989) Liquefaction and settlement characteristics of silt soils. Ph.D. thesis, University of Missori-Rolla, Rolla, USA
Seed HB, Idriss IM (1971) Simplified procedure for evaluating soil liquefaction potential. J Soil Mech Found Div ASCE 97(9):1249–1274
Seed HB, Martin PP, Lysmer J (1975) The generation and dissipation of pore water pressure during soil liquefaction. Earthquake Engineering Research Centre, California, Report No. 75/26
Seed HB, Tokimatsu K, Harder LF, Chung RM (1985) Influence of SPT procedures in soil liquefaction resistance evaluations. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE 111(12):1425–1445
Shen CK, Vrymoed JL, Uyeno CK (1977) The effects of fines on liquefaction of sands. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, vol 2. Tokyo, Japan, pp 381–385
Tatsuoka F, Iwasaki T, Tokida K, Yasuda S, Hirose M, Imai T, Kon-No M (1980) Standard penetration tests and soil liquefaction potential evaluation. Soils Found JSSMFE 20(4):95–111
Tokimatsu K, Yoshimi Y (1983) Empirical correlation of soil liquefaction based on SPT N-value and fines content. Soils Found JSSMFE 23(4):56–74
Tronsco JH, Verdugo R (1985) Silt content and dynamic behavior of tailing sands. Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. San Francisco, USA, pp 1311–1314
Vaid VP (1994) Liquefaction of silty soils. Ground failures under seismic conditions, Geotechnical special publication, No. 44, ASCE, pp 1–16
Yamamuro JA, Kelly MC (2001) Monotonic and cyclic liquefaction of very loose sands with high silt content. J of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Eng, ASCE 127(4):314–324
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Prof. and Head of Department of Earthquake Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India for providing laboratory facilities and assistance for conducting of tests. This support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maheshwari, B.K., Patel, A.K. Effects of Non-Plastic Silts on Liquefaction Potential of Solani Sand. Geotech Geol Eng 28, 559–566 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-010-9310-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-010-9310-z