Abstract
Slurry pipe jacking was firmly established as a special method for the non-disruptive construction of the underground pipelines of sewage systems. Pipe jacking, in its traditional form, has occasionally been used for short railways, roads, rivers, and other projects. Basically the system involves the pushing or thrusting of concrete pipes into the ground by a number of jacks.
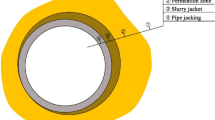
In slurry pipe jacking, during the pushing process, mud slurry and lubricant are injected into the face and the over cutting area that is between the concrete pipes and the surrounding soil. Next, the slurry fills voids and the soil stabilizes due to the created slurry cake around the pipes. Fillings also reduce the jacking force or thrust during operation. When the drivage and pushing processes are finished, a mortar injection into the over cutting area is carried out in order to maintain permanent stability of the surrounding soil and the over cutting area. Successful lubrication around the pipes is extremely important in a large diameter slurry pipe jacking operation.
Control of lubrication and gaps between pipes and soil can prevent hazards such as surface settlement and increases in thrust. Also, to find voids around the pipes after the jacking process, in order to inject mortar for permanent stabilizing, an investigation around the pipes is necessary. To meet these aims, this paper is concerned with the utilization of known methods such as the GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar) system and borehole camera to maintain control of the over cutting area and lubricant distribution around the pipes during a site investigation. From this point of view, experiments were carried out during a tunnel construction using one of the largest cases of slurry pipe jacking in Fujisawa city, Japan. The advantages and disadvantages of each system were clarified during the tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujisawa project data and slurry pipe jacking machine catalogue (2003) KYOWA EXEO Co. Tokyo, Japan
Hume pipe jacking method (2002) Designed data, reference book
Khazaei, S., Shimada, H., Kawai, T., Yotsumoto, J. and Matsui, K. (2003), Over-cutting and lubricant distribution control by RADAR in large diameter slurry pipe jacking method, International Workshop on Earth Science and Technology, Fukuoka, Japan
Kyowa Exeo Co. Ltd. (2003) Control of over-cutting area behind reinforced concrete in Fujisawa project by using RADAR investigation, Report, Japan.
M. Marshall (1998) Pipe-jacked tunneling: jacking loads and ground movements Oxford University England
H. Shimada S. Khazaei K. Matsui (2004) ArticleTitleSmall diameter tunnel excavation method using slurry pipe jacking Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 22 161–186 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:GEGE.0000018365.84174.ea
Shimada, H. and Matsui, K. (1998) A new method for the construction of small-diameter tunnels using pipe-jacking. Proceedings of the Regional Symposium on Sedimentary Rock Engineering, pp. 234–239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khazaei, S., Shimada, H., Kawai, T. et al. Monitoring of Over Cutting Area and Lubrication Distribution in a Large Slurry Pipe Jacking Operation. Geotech Geol Eng 24, 735–755 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-004-5436-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-004-5436-1