Abstract
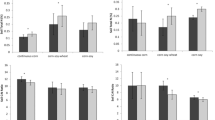
Long-term use of soil, crop residue and fertilizer management practices may affect some soil properties, but the magnitude of change depends on soil type and climatic conditions. Two field experiments with barley, wheat, or canola in a rotation on Gray Luvisol (Typic Cryoboralf) loam at Breton and Black Chernozem (Albic Argicryoll) loam at Ellerslie, Alberta, Canada, were conducted to determine the effects of 19 or 27 years (from 1980 to 1998 or 2006 growing seasons) of tillage (zero tillage [ZT] and conventional tillage [CT]), straw management (straw removed [SRem] and straw retained [SRet]) and N fertilizer rate (0, 50 and 100 kg N ha−1 in SRet, and 0 kg N ha−1 in SRem plots) on pH, extractable P, ammonium-N and nitrate–N in the 0–7.5, 7.5–15, 15–30 and 30–40 cm or 0–15, 15–30, 30–60, 60–90 and 90–120 cm soil layers. The effects of tillage, crop residue management and N fertilization on these chemical properties were usually similar for both contrasting soil types. There was no effect of tillage and residue management on soil pH, but application of N fertilizer reduced pH significantly (by up to 0.5 units) in the top 15 cm soil layers. Extractable P in the 0–15 cm soil layer was higher or tended to be higher under ZT than CT, or with SRet than SRem in many cases, but it decreased significantly with N application (by 18.5 kg P ha−1 in Gray Luvisol soil and 20.5 kg P ha−1 in Black Chernozem soil in 2007). Residual nitrate–N (though quite low in the Gray Luvisol soil in 1998) increased with application of N (by 17.8 kg N ha−1 in the 0–120 cm layer in Gray Luvisol soil and 23.8 kg N ha−1 in 0–90 cm layer in Black Chernozem soil in 2007) and also indicated some downward movement in the soil profile up to 90 cm depth. There was generally no effect of any treatment on ammonium-N in soil. In conclusion, elimination of tillage and retention of straw increased but N fertilization decreased extractable P in the surface soil. Application of N fertilizer reduced pH in the surface soil, and showed accumulation and downward leaching of nitrate–N in the soil profile.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell CA, Zentner RP (1984) Effect of fertilizer on soil pH after 17 years of continuous cropping in southwestern Saskatchewan. Can J Soil Sci 64:710–750
Campbell CA, Lafond G, Zentner RP, Biederbeck VO (1991) Influence of fertilizer and straw baling on soil organic matter in a thin Black Chernozem in western Canada. Soil Biol Biochem 23:443–446
Campbell CA, Selles F, Lafond GP, Biederbeck VO, Zentner RP (2001) Tillage-fertilizer changes: effect on some soil quality attributes under long-term crop rotations in a thin Black Chernozem. Can J Soil Sci 81:157–165
Carter MR, Angers DA, Gregorich EG (1994) Approaches to evaluate organic matter quality in soil management and tillage studies. Proceeding of 13th International Soil Tillage Research Organisation (ISTRO) Conference, Aalborg, Denmark. Vol 1:111–116
Culley JLB (1993) Density and compressibility. In: Carter MR (ed) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton USA
Eckert DJ (1985) Effects of reduced tillage on the distribution of soil pH and nutrients in soil profiles. J Fert Issues 2:86–90
Essington ME, Howard DD (2000) Phosphorus availability and specification in long-term no-till and disc-till soil. Soil Sci 165:144–152
Gregorich EG, Carter MR, Angers DA, Monreal CM, Ellert BH (1994) Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic matter quality in agricultural soils. Can J Soil Sci 74:367–385
Guillard K, Griffin GF, Allinson DW, Yamartino WR, Rafey MM, Pietryzk SW (1995) Nitrogen utilization of selected cropping systems in the U.S. northeast. II. Soil profile nitrate distribution and accumulation. Agron J 87:199–207
Heaney DJ, Nyborg M, Solberg ED, Malhi SS, Ashworth J (1992) Overwinter nitrate loss and denitrification potential of cultivated soils in Alberta. Soil Biol Biochem 24:877–884
Ismail I, Blevins RL, Frye WW (1994) Long-term no-tillage effects on soil properties and continuous corn yields. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:193–198
Janzen HH (1987) Effect of fertilizer on soil productivity in long-term wheat rotations. Can J Soil Sci 67:165–174
Janzen HH, Campbell CA, Izaurralde RC, Ellert BH, Juma N, McGill WB, Zentner RP (1998) Management effects on soil C storage on the Canadian prairies. In: Paustian, K., Elliott, E.T., and Carter, M.R. (eds), Special Issue: Tillage and crop management impacts on soil carbon storage. Soil Tillage Res 47:181–195
Karlen DL, Berry EC, Colvin TS, Kanwar RS (1991) Twelve-year tillage and crop rotation effects on yields and soil chemical properties in northeast Iowa. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 22:1985–2003
Lessard R, Rochette P, Gregorich EG, Patty E, Desjardins RL (1996) N2O fluxes from manure amended soil under maize. J Environ Qual 25:1371–1377
Malhi SS, Lemke R (2007) Tillage, crop residue and N fertilizer effects on crop yield, nutrient uptake, soil quality and greenhouse gas emissions in the second 4-year rotation cycle. Soil Tillage Res 96:269–283
Malhi SS, Harapiak JT, Nyborg M, Flore NA (1991a) Soil chemical properties after long-term fertilization of bromegrass: nitrogen rate. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 22:1447–1458
Malhi SS, Nyborg M, Harapiak JT, Flore N (1991b) Acidification of soil in Alberta by nitrogen fertilizers applied to bromegrass. In: Wright RJ (ed) Plant-soil interactions at low pH. PLSO 61. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 547–553
Malhi SS, Nyborg M, Solberg ED (1996) Influence of source, method of placement and simulated rainfall on the recovery of 15N-labelled fertilizers under zero tillage. Can J Soil Sci 76:93–100
Malhi SS, Brandt SA, Ulrich D, Lemke R, Gill KS (2002) Accumulation and distribution of nitrate-nitrogen and extractable phosphorus in the soil profile under various alternative cropping systems. J Plant Nutr 25:2499–2520
Malhi SS, Brandt SA, Lemke R, Moulin AP, Zentner RP (2009) Effects of input level and crop diversity on soil nitrate-N, extractable P, aggregation, organic C and N, and N and P balance in the Canadian Prairie. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst Online. doi:10.1007/s10705-008-9220-0
Malhi SS, Nyborg M, Goddard T, Puurveen D (2010) Long-term tillage, straw and N rate effects on quantity and quality of organic C and N in a Gray Luvisol soil. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst Online: 16 September 2010. doi:10.1007/s10705-010-9399-8
Malhi SS, Nyborg M, Goddard T, Puurveen D (2011) Long-term tillage, straw management and N fertilization effects on quantity and quality of organic C and N in a Black Chernozem soil. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst In Review
McGill WB, Dormaar JF, Reinl-Dwyer E (1988) New perspectives on soil organic matter quality, quantity, and dynamics on the Canadian Prairies. In: Proceedings of Canadian Society of Soil Science and Canadian Society of Extension Joint Symposium, Land degradation: Assessment and insight into a western Canadian problem. August 23, 1988, Agricultural Institute of Canada, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. pp 30–48
Meek B, Graham L, Donovan T (1982) Long-term effects of manure on soil nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, organic matter and water infiltration rate. Soil Sci Soc Am J 6:1014–1019
Mooleki SP, Malhi SS, Lemke R, Schoenau JJ, Lafond G, Brandt S, Hultgreen G, Wang H, May WE (2010) Effect of nitrogen management, and phosphorus placement on wheat production in Saskatchewan. Can J Plant Sci 90:319–337
Nuttall WF, Bowren KE, Campbell CA (1986) Crop residue management practices, and N and P fertilizer effects on crop response and on some soil physical and chemical properties of a Black Chernozem over 25 years in a continuous wheat rotation. Can J Soil Sci 66:159–171
Nyborg M, Solberg ED, Malhi SS, Izaurralde RC (1995) Fertilizer N, crop residue, and tillage after soil C and N content in a decade. In: Lal R, Kimble J, Levine E, Stewart BA (eds) Soil management and greenhouse effect. Adv Soil Sci. Lewis Publishers, CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA, pp 93–99
Nyborg M, Laidlaw JW, Solberg ED, Malhi SS (1997) Denitrification and nitrous oxide emissions from soil during spring thaw in a Malmo loam, Alberta. Can J Soil Sci 77:53–160
Patra AK, Jarvis SC, Hatch DJ (1999) Nitrogen mineralization in soil layers, soil particles and macro-organic matter under grassland. Biol Fertil Soils 29:38–45
Plante AF, Stewart CE, Conant RT, Paustian K, Six J (2006) Soil management effects on organic carbon in isolated fractions of a Gray Luvisol. Can J Soil Sci 86:141–151
Qian P, Schoenau JJ, Karamanos RE (1994) Simultaneous extraction of phosphorus and potassium with a new soil test: a modified Kelowna extraction. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 25:627–635
SAS Institute (2004) SAS product documentation. Version 8. Available at http://support.sas.com/documentation/onlinedoc/index.html (verified 17 July 2009). SAS Inst., Cary, NC, USA
Singh B, Malhi SS (2006) Response of soil physical properties to tillage and straw management on two contrasting soils in a cryoboreal environment. Soil Tillage Res 85:143–153
Soon YK, Arshad MA (1996) Effects of cropping on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium forms, and soil organic carbon in a Grey Luvisol. Bio Fertil Soils 22:184–190
Technicon Industrial Systems (1973a) Ammonium in water and waste water. Industrial Method No. 90–70 W-B. Revised January 1978. Technicon Industrial Systems, Tarrytown, USA
Technicon Industrial Systems (1973b) Nitrate in water and waste water. Industrial Method No. 100–70 W-B. Revised January 1978. Technicon Industrial Systems, Tarrytown, USA
Technicon Industrial Systems (1977) Industrial/simultaneous determination of nitrogen and/or phosphorus in BD acid digests. Industrial method no. 334-74W/Bt. Tarrytown, USA
Vasconcelos E, Cabral F, Cordovil CMD (1997) Effect of solid phase from pig slurry on soil chemical characteristics, nitrate leaching composition, and yield of wheat. J Plant Nutr 20:939–952
Weil RR, Benedetto PW, Sikora LJ, Bandel VA (1988) Influence of tillage practices on phosphorus distribution and forms in three Ultisols. Agron J 80:503–509
Yuan X, Tong Y, Yang X, Li X, Zhang F (2000) Effect of organic manure on soil nitrate accumulation. Soil Environ Sci 9:197–200
Zhang WL, Tian ZX, Zhang N, Li XO (1996) Nitrate pollution of groundwater in northern China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 59:223–231
Acknowledgments
The authors than Z Zhang and K Strukoff for technical help, D. Leach for statistical analysis, and Dr. K. S. Gill and Dr. H. R. Kutcher for the internal review/revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malhi, S.S., Nyborg, M., Goddard, T. et al. Long-term tillage, straw and N rate effects on some chemical properties in two contrasting soil types in Western Canada. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 90, 133–146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9417-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9417-x