Abstract
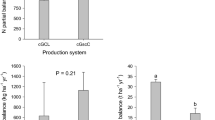
Balances of major nutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in small-scale farming systems are of critical importance to nutrient management and sustainable agricultural development. Mass balances of N, P, and K and some of their influencing factors were studied for two years from July 2003 to July 2005 on small-scale vegetable-farming systems in two contrasting peri-urban areas (Nanjing and Wuxi) of the Yangtze river delta region of China. This balance approach considered organic fertilizer inputs (cow manure, pig manure, and human biosolids), inorganic fertilizer inputs (urea, composite fertilizer, and phosphates), irrigation water, and atmospheric deposition; and considered outputs by vegetables. Input via organic fertilizers was significant for all element balances in the Nanjing area. Inorganic and organic fertilizer, particularly inorganic fertilizer, contributed major nutrient inputs to the system in the Wuxi area. Compared with nutrient output by vegetables, there were significant surpluses of N and P on two vegetable farm systems. Furthermore, N surplus in the Nanjing area was higher than that in the Wuxi area with an inverse relationship to P surplus. In contrast, the general trend of K balances was negative on both sites; hence, the nutrient use efficiency was significantly lower for N and P than K. The nutrient imbalance may be attributed to the differences between fertilizer types and management modes driven by social economic status differences among farmer households. The large N and P net excess creates an environmental threat because of potential losses to ground or surface waters, whereas negative K balance creates soil fertility risks. The results highlight researchers’ and farmers’ need to develop rational fertilization technology to optimize nutrient management on vegetable farmlands to promote sustainable agricultural development in peri-urban areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bengtsson H, Öborn I, Jonsson S, Nilsson I, Andersson A (2003) Field balances of some mineral nutrients and trace elements in organic and conventional dairy farming-a case study at Öjebyn, Sweden. Eur J Agron 20:101–116
Bučienė A, Švedas A, Antanaitis Š (2003) Balances of the major nutrients N, P and K at the farm and field level and some possibilities to improve comparisons between actual and estimated crop yields. Eur J Agron 20:53–62
Chambers R (1994) Participatory rural appraisal (PRA): analysis of experience. World Dev 22:1253–1268
Chang Q, Huang B, Wang HJ, Shi XZ, Zhao YF (2007) Nutrient balances in small-scale vegetable farming system in peri-urban areas—a case study in the Nanjing area and Wuxi, China. Acta Pedologica Sinica (in press) (In Chinese, with English abstract)
Chen ZL, Xu SY, Xu QX, Hu XF, Yu LZ (2001) Pollution patterns and modulating counter measures of surface water environment in the Yangtze River Delta. Resour Environ Yangtze River Drainage Area 10:353–359 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
De Boer W, Kowalchuk GA (2001) Nitrification in acid soils: micro-organisms and mechanisms. Soil Biol Biochem 33:853–866
Ersahin S, Karaman MR (2001) Estimating potential nitrate leaching in nitrogen fertilized and irrigated tomato using the computer model NLEAP. Agric Water Manage 51:1–12
Fierer NG, Gabet EJ (2002) Carbon and nitrogen losses by surface runoff following changes in vegetation. J Environ Qual 31:1207–1213
Ganuza A, Almendros G (2003) Organic carbon storage in soils of the Basque Country (Spain): the effect of climate, vegetation type and edaphic variables. Biol Fertil Soils 37:154–162
Ge XG, Gao H, Zhang EP, Wang XX, Zhang X (2004) Changes of field-vegetable system under long-term fixed fertilizer experiment (III). Acta Hortic Sinica 31(4):456–460 (In Chinese, with English abstract)
Gong ZT, Zhang GL, Chen ZC (2003) Development of soil classification in China. In: Eswaran H, Rice T, Ahrens R, Stewart BA (eds), Soil classification: a global desk reference. CRC Press, Washington, DC, pp 101–125
Goodlass G, Halberg N, Verschuur G (2003) Input-output accounting systems in the European community-an appraisal of their usefulness in raising awareness of environmental problems. Eur J Agron 20:17–24
He FF, Chen Q, Jiang RF, Chen XP, Zhang FS (2007) Yield and nitrogen balance of greenhouse tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.) with conventional and site-specific nitrogen management in Northern China. Nutr Cycle Agroecosys 77:1–14
Huang B, Shi XZ, Yu DS, Öborn I, Blombäck K, Pagella TF, Wang HJ, Sun WX, Sinclair FL (2006) Environmental assessment of small-scale vegetable farming systems in peri-urban areas of the Yangtze river delta region, China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 112:391–402
Janssen BH (1999) Basics of budgets, buffers and balances of nutrients in relation to sustainability of agroecosystems. In: Smaling EMA, Oenema O, Fresco LO (eds) Nutrient disequilibria in agroecosystems: concepts and case studies. CAB International, UK, pp 27–56
Karlen DL, Cambardella CA (1996) Conservation strategies for improving soil quality and organic matter storage. Adv Soil Sci CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, FL
Khai NM, Ha PQ, Öborn I (2006) Nutrient and trace metal cycling in small-scale peri-urban vegetable farming systems in Southeast Asia—a case study in peri-urban Hanoi. Agric Ecosyst Environ (in press)
Ladd J, Amato NM, Oades JM (1985) Decomposition of plant material in Australian Soil III: Residual organic and microbial biomass C and N from isotope- labeled legume material and soil organic matter, decomposing under field conditions. Aust J Soil Res 23:603–611
Lesschen JP, Stoorvogel JJ, Smaling EMA, Henvelink GBM, Veldkamp A (2007) A spatially explicit methodology to quantify soil nutrient balances and their uncertainties at the national level. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 78:111–131
Lu RK, Liu HX, Wen DZ, Qin SW, Zheng JY, Wang ZQ (1996) Nutrient cycling and balance in agricultural ecosystem of some typical areas, China. α Nutrient input parameters in farmlands. Chinese J Soil Sci 27(4):151–154 (In Chinese, with English abstract)
Lu RK (1999) Soil analytical methods of agronomic chemistry. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
Mander U, Forsberg C (2000) Non-point pollution in agricultural watersheds of endangered coastal seas. Ecol Eng 14:317–324
Midmore DJ, Jansen HGP, Dumsday RG (1996) Soil erosion and environmental impact of vegetable production in the Cameron Highlands, Malaysia. Agric Ecosyst Environ 60:29–46
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single-solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chem Acta 27:31–36
Öborn I, Edwards AC, Witter E, Oenema O, Ivarsson K, Withers PJA, Nilsson SI, Richert Stinzing A (2003) Element balances as a tool for sustainable nutrient management: a critical appraisal of their merits and limitations within an agronomic and environmental context. Eur J Agron 20:211–225
Oenema O, Kros H, De Vries W (2003) Approaches and uncertainties in nutrient budgets: implications for nutrient management and environmental policies. Eur J Agron 20:3–16
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis part 2—Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. ASA, Madison
Shi XZ, Yu DS, Warner ED, Sun WX, Petersen GW, Gong ZT, Lin H (2006) Cross-reference system for translating between genetic soil classification of China and soil taxonomy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:78–83
SPSS Inc. (1993) SPSS for windows base system user’s guide release 6.0. Marija J. Norusis/SPSS Inc
Zhang DS, Shi XZ, Yu DS, Huang B, Zhao YC, Huang Y, Öborn I, Martin Larsson (2007a) Numerical simulation of the soil nitrogen circling in peri-urban vegetable farming systems. Acta Pedol Sin 44(3):484–491 (In Chinese, with English abstract)
Zhang QL, Shi XZ, Huang B, Yu DS, Öborn I, Blombäck K, Wang HJ, Pagella TF, Sinclair FL (2007b) Surface water quality of factory-based and vegetable-based peri-urban areas in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Catena 69:57–64
Zhao YF, Shi XZ, Huang B, Yu DS, Wang HJ, Sun WX, Öborn I, Blombäck K (2007) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soils of an industry-based peri-urban area in Wuxi, China. Pedosphere 17(1):44–51
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for funding from the EU (Contract No. ICA4-CT−2002–10021), the National Key Basic Research Support Foundation of China (2002CB410810), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (40773075). The authors would also like to thank the farmers of Nanjing and Wuxi peri-urban areas for their active and valuable participation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HJ., Huang, B., Shi, XZ. et al. Major nutrient balances in small-scale vegetable farming systems in peri-urban areas in China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 81, 203–218 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9157-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9157-8