Abstract
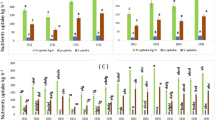
A 3-year multi-site study was carried out on rainfed Vertisols under Mediterranean conditions in southern Europe to determine the influence of the N fertilizer rate on soil nitrates, N uptake and N use efficiency in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. Durum Desf.) in rotation with sunflower (Heliathus annuus L.). Nitrogen fertilizer rates were 0, 100, 150 and 200 kg N ha−1 applied in equal proportions at sowing, tillering and stem elongation. The experiment was designed as a randomized complete block with a split plot arrangement and four replications. Nitrogen harvest index (NHI), N uptake/grain yield (NUp/GY), N use efficiency (NUE), N utilization efficiency (NUtE), N uptake efficiency (NUpE) and N apparent recovery fraction (NRF) were calculated. Differences were observed in N use efficiency between the two modern bread wheat and durum wheat cultivars studied. In comparison to durum, bread wheat displayed greater N accumulation capacity and a more efficient use of N for grain production. While under N-limiting conditions, the behavior was similar for both wheat types. No difference was noted between wheat types with regard to changes in soil residual \( {\text{NO}}^{ - }_{{\text{3}}} - {\text{N}} \) levels over the study period at the various sites. The 100-kg ha−1 N fertilizer rate kept soil nitrates stable at a moderate level in plots where both wheat types were sown.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad A, Lloveras J, Michelena A (2004) Nitrogen fertilization and foliar urea effects on durum wheat yield and quality and on residual soil nitrate in irrigated Mediterranean conditions. Field Crops Res 87:257–269
Analytical Software (2003) Statistix 8.0. Analytical Software, Tallahassee, FL
Ashraf M, Azam F (1998) Fate and interaction with soil N of fertilizer 15N applied to wheat at different growth stages. Cereal Res Commun 26:397–404
Barnes H, Folkard AR (1951) The determination of nitrates. Analyst 76:599–603
Corbeels M, Hofman G, Van Cleemput O (1998) Residual effect of nitrogen fertilization in a wheat-sunflower cropping sequence on a Vertisol under semi-arid Mediterranean conditions. Eur J Agron 9:109–116
Delogu G, Cattivelli L, Pecchioni N, De Falcis D, Maggiore T, Stanca AM (1998) Uptake and agronomic efficiency of nitrogen in winter barley and winter wheat. Eur J Agron 9:11–20
Dhugga KS, Waines JG (1989) Analysis of nitrogen accumulation and use in bread and durum wheat. Crop Sci 29:1232–1239
Ehdaie B, Shakiba MR, Waines JG (1999) Path analysis of genotype × environment interactions of wheats to nitrogen. Agronomie 19:45–56
Ehdaie B, Shakiba MR, Waines JG (2001) Sowing date and nitrogen input influence nitrogen-use efficiency in spring bread and durum wheat genotypes. J Plant Nutr 24:899–919
Ehdaie B, Waines JB (2001) Sowing date and nitrogen rate effects on dry matter and nitrogen partitioning in bread and durum wheat. Field Crops Res 73:47–61
Geleto T, Tanner DG, Mamo T, Gebeyehu G (1995) Response of rainfed bread and durum wheat to source, level, and timing of nitrogen fertilizer on two Ethiopian vertisols. I. Yield and yield components. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 26:1773–1794
Geleto T, Tanner DG, Mamo T, Gebeyehu G (1996) Response of rainfed bread and durum wheat to source, level, and timing of nitrogen fertilizer on two Ethiopian Vertisols. II. N uptake, recovery and efficiency. Fertilizer Res 44:195–204
Gómez KA, Gómez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. Wiley, New York
Huggins DR, Pan WL (1993) Nitrogen efficiency component analysis: an evaluation of cropping system differences in productivity. Agron J 85:898–905
Ladha JK, Pathak H, Krupnik TJ, Six J, Kessel C (2005) Efficiency of fertilizer nitrogen in cereal production: retrospects and prospects. Adv Agron 87:86–157
López-Bellido RJ, López-Bellido L (2001) Efficiency of nitrogen in wheat under Mediterranean conditions: effect of tillage, crop rotation and N fertilization. Field Crops Res 71:31–46
López-Bellido L, López-Bellido RJ, Castillo JE, López-Bellido FJ (2000) Effects of tillage, crop rotation and nitrogen fertilization on wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions. Agron J 92:1054–1063
López-Bellido L, López-Bellido RJ, Redondo R (2005) Nitrogen efficiency in wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions as affected by split nitrogen application. Field Crops Res 94:86–97
López-Bellido L, López-Bellido RJ, López-Bellido FJ (2006) Fertilizer nitrogen efficiency in durum wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions: effect of split application. Agron J 98:55–62
McIntosh MS (1983) Analysis of combined experiments. Agron J 75:153–155
Moll RH, Kamprath EJ, Jackson WA (1982) Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization. Agron J 74:562–564
Sinclair TR (1998) Historical changes in harvest index and crop nitrogen accumulation. Crop Sci 38:638–643
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the ERDF Program and Spain’s “Plan Nacional I + D” (projects 1FD1997-0228 and AGL2001-2549). The authors thank the Fertiberia company for their excellent cooperation and Assistant Technicians Joaquín Muñoz, José Muñoz and Auxiliadora López for their invaluable help and cooperation in the laboratory and field work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Bellido, R.J., Castillo, J.E. & López-Bellido, L. Comparative response of bread and durum wheat cultivars to nitrogen fertilizer in a rainfed Mediterranean environment: soil nitrate and N uptake and efficiency. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 80, 121–130 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9125-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9125-3