Abstract
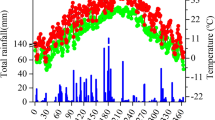
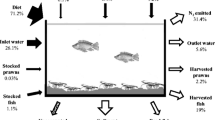
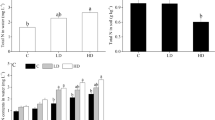
Management of nitrogen (N) in rice-fish culture is of great significance in order to exploit synergies between rice and fish. However, detailed and systematic studies on N cycling in rice-fish systems are rare. An experiment was carried out at the Bangladesh Agricultural University using the fish species common carp, Cyprinus carpio L., and Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Efficiencies of fertilizer and feed as N inputs were evaluated by establishing an apparent N balance. The different N input strategies for rice-fish (RF) treatments were: (1) with fish, with urea (101 kg N ha−1, RF Urea), (2) with fish, with feed (22.6 kg N ha−1, RF Feed I), and (3) with fish, with feed (41.5 kg N ha−1, RF Feed II). Rice only (var. BR28) with urea (101.2 kg N ha−1) was added as the control (Rice only). Urea as N input (Rice only, RF Urea) resulted in negative apparent N balances (N output–N input), whereas N input in the form of feed (RF Feed I, RF Feed II) led to positive apparent N balances due to the lower N input. The presence of fish increased the grain and straw N output in RF Urea compared to Rice only, the effect being significant for straw (P < 0.05). Moreover, a significant difference in nitrogen uptake by rice was seen between the two feeding levels. The higher feeding rate in the RF Feed II treatment led to higher N outputs of grain, straw and fish compared to the RF Feed I treatment, a significant difference occurring for straw (P < 0.05). An apparent recovery efficiency of 48.7% was determined for the additional N input in RF Feed II compared to the RF Feed I teatment. An economic analysis revealed that the RF Urea treatment was the most profitable, as reflected by the highest gross margin. In conclusion, the results indicate that fish can improve nitrogen uptake by rice plants. Moreover, the supply of supplementary feed has a fertilizing effect on the rice due to the utilization of excreted feed nutrients by rice plants.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis, 15th edn, vol 2. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, Virginia, USA
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen–total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy Inc. Soil Science Society of America Inc, Madison, USA
BRRI (2004) Cultivation procedures of modern rice, 12th revision. Booklet No. 5 (in Bangla) Bangladesh Rice Research Institute, Gazipur, Bangladesh, pp 66
Cassman KG, Pingali PL (1995) Intensification of irrigated rice systems: learning from the past to meet future challenges. GeoJournal 35(3):299–305
Cassman KG, Peng S, Olk DC, Ladha JK, Reichardt W, Dobermann A, Singh U (1998) Opportunities for increased nitrogen-use efficiency from improved resource management in irrigated rice systems. Field Crop Res 56:7–39
Chapman G, Fernando CH (1994) The diets and related aspects of feeding of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) in lowland rice fields in northeast Thailand. Aquaculture 123:281–307
Choudhury ATMA, Kennedy IR (2005) Nitrogen fertilizer losses from rice soils and control of environment pollution problems. Commun Soil Sci Plan 36:1625–1639
CIA (2006) The world factbook. https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/bg.html, accessed on 21st September 2006
Dobermann A, Witt C (2000) The potential impact of crop intensification on carbon and nitrogen cycling in intensive rice systems. In: Kirk GJD, Olk DC (eds) Carbon and nitrogen dynamics in flooded soils. Proceeding of the workshop on carbon and nitrogen dynamics in flooded soils, 19–22 April 1999. Los Banos, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, Makati City (Philippines), pp 1–25
FAO (2006). FAOSTAT database. http://faostat.fao.org. Accessed on 21st September 2006
Fernando CH (1993) Rice field ecology and fish culture—an overview. Hydrobiologia 259:91–113
Frei M, Becker K (2005a) Integrated rice-fish culture: coupled production saves resources. Nat Resour Forum 29:135–143
Frei M, Becker K (2005b) A greenhouse experiment on growth and yield effects in integrated rice-fish culture. Aquaculture 244:199–128
Frei M, Razzak MA, Hossain MM, Oehme M, Dewan S, Becker K (2007a) Performance of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. and Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) in intergrated rice-fish culture in Bangladesh. Aquaculture 262:250–259
Frei M, Razzak, MA, Hossain MM, Oehme M, Dewan S, Becker K (2007b) Methane emissions and related physicochemical soil and water parameters in rice-fish systems in Bangladesh. Agric Ecosyst Environ doi:10.1016/j.agee.2006.10.013
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Gupta MV, Sollows MA, Mazid A, Rahman MG, Hussain MG, Dey MM (1998) Integrating aquaculture with rice farming in Bangladesh: feasibility and economic viability, its adoption and impact. ICLARM Tech. Rep.55, 90 pp
Kirk GJD, Kronzucker HJ (2000) Nitrogen uptake by rice roots. In: Kirk GJD, Olk DC (eds) Carbon and Nitrogen dynamics in flooded soils. Proceeding of the workshop on Carbon and Nitrogen dynamics in flooded soils, 19– 22 April 1999. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Philippines.Makati City (Philippines), pp 147–162
Koyama T, App A (1979) Nitrogen balance in flooded rice soils. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Nitrogen and rice. IRRI, Los Banos, Philippines, pp 95–104
Kronzucker HJ, Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM, Kirk GJD (1999) Nitrate-ammonium synergism in rice. A subcellular flux analysis. Plant Physiol 119:1041–1045
Kyaw KM, Toyota K, Okazaki M, Motobayashi T, Tanaka H (2005) Nitrogen balance in a paddy field planted with whole crop rice (Oryza sativa cv. Kusahonami) during two rice-growing seasons. Biol Fertil Soils 42:72–82
Li K (1988) Rice-fish culture in China: a review. Aquaculture 71:173–186
Little DC, Surintaraseree P, Innes-Taylor N (1996) Fish culture in rainfed rice fields of northeast. Thailand Aquac 140:295–321
Lightfoot C, Van Dam A, Costa-Pierce B (1992) What’s happening to rice yields in rice-fish systems? In: dela Cruz CR, Lightfoot C, Costa-Pierce BA, Carangal VR, Bimbao MP (eds) Rice-fish research and development in Asia. ICLARM Conf. Proc. 24, pp 177–183
Pagiola S (1995) Environmental and natural resource degradation in intensive agriculture in Bangladesh. Environment Department Papers No. 15, World Bank, Washington, DC, USA
Panda MM, Ghosh BC, Sinhababu DP (1987) Uptake of nutrients by rice under rice-cum-fish culture in intermediate deep water situation (upto 50-cm water depth). Plant Soil 102:131–132
Patnaik S, Rao MV (1979) Source of nitrogen for rice production. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Nitrogen and rice. IRRI, Los Banos, Philippines, pp 25–43
Pingali PL, Hossain M, Pandey S, Price LL (1998) Economics of nutrient management in Asian rice systems: towards increasing knowledge intensity. Field Crop Res 56:157–176
Rothius AJ, Vromant N, Xuan VT, Richter CJJ, Ollevier F (1999) The effect of rice seeding rate and fish production, and weed abundance in direct-seeded rice-fish culture. Aquaculture 172:255–274
Samonte SOPB, Wilson LT, Medley JC, Pinson SRM, McClung AM, Lales JS (2006) Nitrogen utilization efficiency: relationship with grain yield, grain protein, and yield-related traits in rice. Agron J 98:168–176
Sastradiwirja F (1992) Resource utilization in rice-fish farming. In: dela Cruz CR, Lightfoot C, Costa-Pierce BA, Carangal VR, Bimbao MP (eds) Rice-fish research and development in Asia. ICLARM Conf. Proc. 24, pp 201–206
Steffens W (1989) Principles of fish nutrition. Ellis Horwood Limited, England, p 66
Terjesen BF, Chadwick TD, Verreth JAJ, Rønnestad I, Wright PA (2001) Pathways for urea production during early life of an air-breathing teleost, the African catfish Clarias gariepinus Burchell. J Exper Biol 204:2155–2165
Vromant N, Chau NTH, Ollevier F (2001) The effect of rice-seeding rate and fish stocking on the floodwater ecology of the trench of a concurrent, direct-seeded rice-fish system. Hydrobiologia 457:105–117
Zhong X, Peng S, Sanico AL, Liu H (2003) Quantifying the interactive effect of leaf nitrogen and leaf area on tillering of rice. J Plant Nutr 26:1203–1222
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this study was granted by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) and the Father-and-Son-Eiselen Foundation Ulm (M.O.). The authors wish to thank Md. Akterruzzaman for technical help with the chemical analysis and our field laborers, Md. Abdul Khaled, Md. Mamunur Rashid, and Md. Alam Tofael for their reliable service. Dr. Harinder Makkar gave constructive comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oehme, M., Frei, M., Razzak, M.A. et al. Studies on nitrogen cycling under different nitrogen inputs in integrated rice-fish culture in Bangladesh. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 79, 181–191 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9106-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9106-6