Abstract
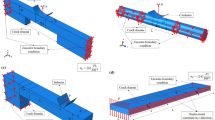
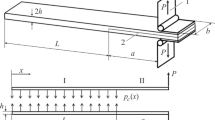
A direct energy balance approach has been developed and used to determine energy release rates in three and four point bend end notched flexure tests. This study was performed in the context of the larger goal of understanding the wide variation in mode II toughnesses that have been obtained by the two tests when used on the same material. The primary motivation for developing the direct energy balance approach was to fully account for the effects of friction, large deformations, and other geometric nonlinearities that occur during these tests. The direct energy balance approach simulates crack advance as it occurs in physical testing. Most significantly, this approach accounts for frictional dissipation that occurs during crack advance, which is an effect that has been neglected in previous analyses of these tests. The direct energy balance approach is used to show that, for most cases of practical interest, the virtual crack closure technique is quite accurate, and predictions by this latter approach are only in error when moderately large geometric nonlinearities occur prior to crack advance. Based on these results, a “cut-off value,” expressed in terms of the maximum slope in the specimen as predicted by classical beam theory, is suggested for the upper limit of applicability of the virtual crack closure technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AECMA prEN 6034. (1995). Carbon fiber reinforced plastics: determination of interlaminar fracture toughness energy mode II-GIIc.
Broek, D. (1986). Elementary engineering fracture mechanics, 4th revised edition, Kluwer Academic Publishers Inc.
L.A. Carlsson J.W. Gillespie R.B. Pipes (1986) ArticleTitleOn the analysis and design of the end notched flexure (ENF) specimen for mode II testing Journal of Composite Materials 20 594–604
B.D. Davidson H. Hu R.A. Schapery (1995) ArticleTitleAn analytical crack tip element for layered elastic structures Journal of Applied Mechanics 63 IssueID6 243–253
B.D. Davidson X. Sun (2005) ArticleTitleEffects of friction, geometry and fixture compliance on the perceived toughness from three and four point bend end notch flexure tests Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites 24 IssueID15 1611–1628 Occurrence Handle10.1177/0731684405050402 Occurrence Handle2005JRPC...24.1611D
Davidson B.D., Sun X., Vinciquerra A.J. (2005). Influence of friction, geometric nonlinearity and fixture compliance on experimentally observed toughness from three and four point bend end notched flexure tests. Journal of Composite Materials. (submitted).
P. Davies B.R.K. Blackman A.J. Brunner (1998) ArticleTitleStandard test method for delamination resistance of composite materials: current status Applied Composite Materials 5 345–364 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008869811626
P. Davies G.D. Sims B.R.K. Blackman A.J. Brunner K. Kageyama M. Hojo K. Tanaka G. Rousseau R.H. Martin (1999) ArticleTitleComparison of test configurations for determination of mode II interlaminar fracture toughness results from international collaborative test programme Plastics, Rubber and Composites 28 IssueID9 432–437
A.T. Dibenedetto M.R. Gurvich (1998) ArticleTitleEffect of friction between fiber and matrix on the fracture toughness of the composite interface Journal of Materials Science 33 4239–4248 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004486026347
A.A. Griffith (1920) ArticleTitleThe phenomena of rupture and flow in solids Philosophical Transactions, Series A 221 163–198 Occurrence Handle1921RSPTA.221..163G
S. Hashemi A.J. Kinloch J.G. Williams (1990) ArticleTitleThe analysis of interlaminar fracture in uniaxial fiber-polymer composites Proceedings of the Royal society of London A A427 173–199 Occurrence Handle1990RSPSA.427..173H
JIS 7086. (1993). Testing methods for interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon fiber reinforced plastics.
M.J. Johnson S. Sriharan (1999) ArticleTitleEvaluation of strain energy release rates in delaminated laminates under compression AIAA Journal 37 IssueID8 954–963 Occurrence Handle10.2514/2.816
S. Mall N.K. Kochhar (1986) ArticleTitleFinite-element analysis of end-notched flexure specimens Journal of Composites Technology and Research 8 IssueID2 54–57
R.H. Martin B.D. Davidson (1999) ArticleTitleMode II fracture toughness evaluation using four point bend end notched flexure test Plastics, Rubber and Composites 28 IssueID8 401–406
R.H. Martin T. Elms S. Bowron (1998) Characterization of mode II delamination using the 4ENF. Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Composite Materials: Testing and Standardization Institute of Materials London 161–170
O’Brien, T.K., Murri, G.B. and Salpekar, S.A. (1989). Interlaminar shear fracture toughness and fatigue thresholds for composite materials. Composite Materials: Fatigue and Fracture, Second Volume, ASTM STP 1012, (Edited by Lagace, P.A.) American Society for Testing and Materials, 222–250.
A. Pieracci B.D. Davidson V. Sundararaman (1998) ArticleTitleNonlinear analysis of homogeneous, symmetrically delaminated single leg bending specimens Journal of Composites Technology and Research 20 IssueID3 170–178
E.F. Rybicki M.F. Kanninen (1977) ArticleTitleA finite element calculation of stress intensity factors by a modified crack closure integral Engineering Fracture Mechanics 9 931–938 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0013-7944(77)90013-3
C. Schuecker B.D. Davidson (2000a) ArticleTitleEvaluation of the accuracy of the four-point bend end-notched flexure test for mode II delamination toughness determination Composites Science and Technology 60 2137–2146 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0266-3538(00)00113-5
Schuecker, C. and Davidson, B.D. (2000b). Effect of friction on the perceived mode II delamination toughness from three and four-point bend end notched flexure tests. Composite Structure: Theory and Practice, ASTM STP 1383, (Edited by Grant, P. and Rousseau, C.Q.) American Society for Testing and Materials, 334–344.
Sun, X. and Davidson, B.D. (2005). Numerical evaluation of the effects of friction and geometric nonlinearities on the energy release rate in three and four point end notched flexure test. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. (submitted).
Vinciquerra, A.J. and Davidson, B.D. (2002). Effect of crack length measurement technique and data reduction procedures on the perceived toughness from four-point bend end-notched flexure tests. Proceedings of the 17th Annual American Society for Composites Technical Conference, Paper No. 182, (Edited by Sun, C.T. and Kim, H.) CRC Press (2002). Also To Appear in Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites.
Y. Wang J.G. Williams (1992) ArticleTitleCorrections for mode II fracture toughness specimens of composites materials Composites Science and Technology 43 251–256 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0266-3538(92)90096-L
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Davidson, B.D. A Direct Energy Balance Approach for Determining Energy Release Rates in Three and Four Point Bend End Notched Flexure Tests. Int J Fract 135, 51–72 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-005-3746-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-005-3746-9