Abstract
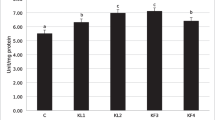
The need to expand aquaculture production has led to other fish to be considered as potential species for culture, such as the sub-Antarctic notothenioid Eleginops maclovinus (Valenciennes, 1830). The aim of this study was to determine the cumulative effect of density and pathogen infection by protein extract of Piscirickettsia salmonis on skeletal muscle metabolism. In a first experiment, specimens were submitted to three different stocking densities: (1) 3.1 kg m−3, (2) 15 kg m−3 and (3) 60 kg m−3, for a period of 10 days. In a second experiment, metabolic changes caused by an infection of P. salmonis protein extract (a single injection of 0.5 μL P. salmonis protein extract g body weight−1 was inoculated in the fish) and its combined effect with stocking density was assessed during a period of 10 days. This study concludes that stress caused by high stocking density led to the reorganization of some metabolic routes to fulfill skeletal muscle energy needs. Furthermore, infection response by pathogen P. salmonis differed when stocking density increased, suggesting an increase of energy needs with density in skeletal muscle of infected fish.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GPT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.2)
- GOT:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.1)
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- GDH:
-
Glutamate dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.2)
- G3PDH:
-
Glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.8)
- LDH-O:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase oxidase (EC 1.1.1.27)
References
Arjona FJ, Vargas-Chacoff L, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Gonçalves O, Páscoa I, Martín del Río MP, Mancera JM (2009) Tertiary stress responses in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858) to osmotic acclimation: implications for osmoregulation, energy metabolism and growth. Aquaculture 287:419–426
Arkush KD, McBride AM, Mendonca HL, Okihiro MS, Andree KB, Marshall S, Henriquez V, Hedrick RP (2005) Genetic characterization and experimental pathogenesis of Piscirickettsia salmonis isolated from white seabass Astractoscion nobilis. Dis Aquat Organ 63:139–149
Athanassopoulou F, Groman D, Prapas T, Sabatakou O (2004) Pathological and epidemiological observations on rickettsiosis in cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) from Greece. J Appl Ichthyol 20:525–529
Barton BA (2002) Stress in fish: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr Comp Biol 42:517–525
Barton BA, Schreck CB, Barton LD (1987) Effects of chronic cortisol administration and daily acute stress on growth, physiological conditions, and stress responses in juvenile rainbow trout. Dis Aquat Organ 2:173–185
Carbonara P, Scolamacchia M, Spedicato MT, Zupa W, McKinley RS, Lembo G (2014) Muscle activity as a key indicator of welfare in farmed European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L. 1758). Aquac Res doi:10.1111/are.12369
Cvitanich JD, Garate O, Smith CE (1991) The isolation of a rickettsia-like organism causing disease and mortality in Chilean salmonids and its confirmation by Koch’s postulate. J Fish Dis 14:121–145
Donaldson MR, Cooke SJ, Patterson DA, Macdonald JS (2008) Cold shock and fish. J Fish Biol 73:1491–1530
Driedzic WR, Vanya Ewart K (2004) Control of glycerol production by rainbow smelt (Osmerus mordax) to provide freeze resistance and allow foraging at low winter water temperatures. Comp Biochem Physiol B Mol Biol 139:347–357
Fryer JL, Hedrick RP (2003) Piscirickettsia salmonis: a Gram-negative intracellular bacterial pathogen of fish. J Fish Dis 26:251–262
Fryer JL, Lannan CN, Garces LH, Larenas JJ, Smith PA (1990) Isolation of a rickettsiales-like organism from diseased coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) in Chile. Fish Pathol 25:107–114
Garces LH, Larenas JJ, Smith PA, Sandino S, Lannan CN, Fryer JL (1991) Infectivity of a rickettsia isolated from coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Dis Aquat Organ 11:93–97
Hegazi MAM, Attia ZIm Hegazi MM (2014) Salinity lessens the impact of high stocking densities and metabolic cost in white muscle and liver of Nile tilapia fingerlings. Aquac Res 45:566–570
Herrera M, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Vargas-Chacoff L, De la Roca E, Mancera JM (2014) Metabolic enzyme activities in relation to crowding stress in the wedge sole (Dicologoglossa cuneata). Aquac Res. doi:10.1111/are.12440
Ibieta P, Tapia V, Venegas C, Hausdorf M, Takle H (2011) Chilean Salmon farming on the horizon of sustainability: review of the development of a highly intensive production, the ISA crisis and implemented actions to reconstruct a more sustainable aquaculture industry. In: Sladonja B (ed) Aquaculture and the environment: a shared destiny. Intech, Croatia, p 246
Keppler D, Decker K (1974) Glycogen determination with amyloglucosidase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 1127–1131
Krasnov A, Koskinen H, Pehkonen P, Rexroad CE, Afanasyev S, Molsa H (2005) Gene expression in the brain and kidney of rainbow trout in response to handling stress. BMC Genomics 6:3
Mancera JM, Vargas-Chacoff L, García-López A, Kleszczyńska A, Kalamarz H, Martínez-Rodríguez G, Kulczykowska E (2008) High density and food deprivation affect arginine vasotocin, isotocin and melatonin in gilthead sea bream (Sparus auratus). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 149:92–97
Mc-Carthy U, Steiropoulos NA, Thompson KD, Adams A, Ellis AE, Ferguson HW (2005) Confirmation of Piscirickettsia salmonis as a pathogen in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax and phylogenetic comparison with salmonid strains. Dis Aquat Organ 64:107–119
Mommsen TP (1984) Metabolism of the fish gill. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish physiology, vol XB. Academic Press, New York, pp 203–238
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW (1999) Cortisol in teleosts: dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fish 9:211–268
Moore S (1968) Amino acid analysis: aqueous dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent for the ninhydrin reaction. J Chem Biol 1242:6281–6283
Nakano K, Tagawa M, Hirano T (1997) Effects of ambient salinities on carbohydrate metabolism in two species of tilapia: Oreochromis mossambicus and O. nicolicus. Fish Sci 63:338–343
Nakano K, Tagawa M, Hirano T (1998) Temporal changes in liver carbohydrate metabolism associated with seawater transfer in Oreochromis mossambicus. Comp Biochem Physiol B Mol Biol 119:721–728
Pequeño G, Pavés H, Bertrán C, Vargas-Chacoff L (2010) Seasonal limnetic feeding regime of the “robalo” Eleginops maclovinus (Valenciennes 1830), in the Valdivia river, Chile. Gayana 74:47–56
Polakof S, Arjona FJ, Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Martín del Río MP, Mancera JM, Soengas JL (2006) Food deprivation alters osmoregulatory and metabolic responses to salinity acclimation in gilthead sea bream Sparus auratus. J Comp Physiol B 176:441–452
Sá R, Gavilán M, Rioseco MJ, Llancabure A, Vargas-Chacoff L, Augsburger A, Bas F (2014) Dietary protein requirement of Patagonian blennie (Eleginops maclovinus, Cuvier 1830) juveniles. Aquaculture 428–429:125–134
Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Laíz-Carrión R, Guzman JM, Martín del Río MP, Miguez JM, Mancera JM, Soengas JL (2003) Acclimation of S. auratus to various salinities alters energy metabolism of osmoregulatory and nonosmoregulatory organs. Am J Physiol 285:R897–R907
Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Arjona FJ, Martín del Río MP, Míguez MP, Mancera JM, Soengas JL (2005) Time course of osmoregulatory and metabolic changes during osmotic acclimation in Sparus auratus. J Exp Biol 208:4291–4304
Skjervold PO, Fjæra SO, Østby PB, Einen O (2001) Live-chilling and crowding stress before slaughter of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 192:267–282
Soengas JL, Moon TW (1995) Uptake and metabolism of glucose, alanine and lactate in red blood cell of American eel Anguilla rostrata. J Exp Biol 198:877–888
Soengas JL, Barciela P, Aldegunde M, Andrés MD (1995) Gill carbohydrate metabolism of rainbow trout is modified during gradual adaptation to sea water. J Fish Biol 46:845–856
Soengas JL, Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Laíz-Carrión R, Mancera JM (2007) Energy metabolism and osmotic acclimation in teleost fish. In: Baldisserotto B, Mancera JM, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish osmoregulation. Science publishers, Enfield, pp 277–308
Trenzado CE, Morales AE, de la Higuera M (2008) Physiological changes in rainbow trout held under crowded conditions and fed diets with different levels of vitamins E and C and highly unsaturated fatty acids (AGAI). Aquaculture 277:293–302
Vanya Ewart K, Richards RC, Driedzic WR (2001) Cloning of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs from two fish species and effect of temperature on enzyme expression in rainbow smelt (Osmerus mordax). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 128:401–412
Vargas-Chacoff L, Arjona FJ, Polakof S, Martín del Río MP, Soengas JL, Mancera JM (2009a) Interactive effects of environmental salinity and temperature on metabolic responses of gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 154:417–424
Vargas-Chacoff L, Arjona FJ, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Páscoa I, Gonçalves O, Martín del Río MP, Mancera JM (2009b) Seasonal variation in osmoregulatory and metabolic parameters in earthen pond cultured gilthead sea bream Sparus auratus. Aquac Res 40:1279–1290
Vargas-Chacoff L, Calvo A, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Villarroel F, Muñoz JL, Tinoco AB, Cárdenas S, Mancera JM (2011) Growth performance, osmoregulatory and metabolic modifications in red porgy fry, Pagrus pagrus, under different environmental salinities and stocking densities. Aquac Res 42:1269–1278
Vijayan MM, Pereira C (1997) Metabolic responses associated with confinement stress in tilapia: the role of cortisol. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 116:89–95
Vijayan MM, Foster GD, Moon TW (1993) Effects of cortisol on hepatic carbohydrate metabolism and responsiveness to hormones in the sea raven Hemitripterus americanus. Fish Physiol Biochem 12:327–335
Vijayan MM, Reddy PK, Leatherland JF, Moon TW (1994) The effects of cortisol on hepatocyte metabolism in rainbow trout: a study using the steroid analogue RU486. Gen Comp Endocrinol 96:75–84
Wendelaar-Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Yañez AJ, Silva H, Valenzuela K, Pontigo JP, Godoy M, Troncoso J, Romero A, Figueroa J, Carcamo JG, Avendaño-Herrera R (2013) Two novel blood-free solid media for the culture of the salmonid pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis. J Fish Dis 36:587–591
Yáñez A, Valenzuela K, Silva H (2012) A broth medium for the successful culture of the fish pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis. Dis Aquat Organ 97:197–205
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out in the framework of FONDECYT Projects 11080168 and 1110235 and FONDAP-INCAR, No. 15110027. We thank Dr. Lafayette Eaton for his help checking this manuscript and the Dirección de Investigación of the Universidad Austral de Chile (DID).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vargas-Chacoff, L., Ortíz, E., Oyarzún, R. et al. Stocking density and Piscirickettsia salmonis infection effect on Patagonian blennie (Eleginops maclovinus, Cuvier 1830) skeletal muscle intermediate metabolism. Fish Physiol Biochem 40, 1683–1691 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9959-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9959-y