Abstract
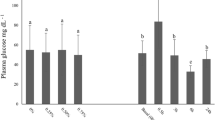
Stocking density is an important factor in cage aquaculture of finfish. Effects of high stocking density (35 fish cubic m−1) on a range of biochemical and immunological parameters in Asian seabass reared in open sea floating net cages were compared to fish held in relatively low density (15 fish cubic m−1). The results revealed that chronic stress due to high stocking density induced variations in most of the parameters studied as evidenced by increased cortisol and glucose levels and decreased activity of lysozyme, myeloperoxidase and complement. Production of reactive oxygen species, total leucocyte count and total serum protein were also decreased, whereas anti-protease, alkaline phosphatase and acid phosphatase activities were increased in high stocking-density group when compared to low stocking-density group. Effects of chronic stress due to high stocking density were discussed in relation to variations in these parameters.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alanara A, Brannas E (1996) Dominance in demand feeding behaviour in Arctic charr and rainbow trout: the effect of stocking density. J Fish Biol 48:242–254
Andersch MA, Szcypinski AJ (1947) Use of p-nitrophenyl-phosphate as the substrate in determination of serum acid phosphatase. Am J Clin Pathol 17:571–574
Anderson DP (1990) Immunological indicators: effects of environmental stress on immune protection and disease outbreaks. Am Fish Soc Symp 8:38–50
Binuramesh R, Michael D (2011) Diel variations in selected serum immune parameters in Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:824–829
Bonga SEW (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Caipang CME, Brinchmann MF, Kiron V (2009) Short-term crowding stress in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L. modulates the humoral immune response. Aquaculture 295:110–115
Caruso G, Genovese L, Maricchiolo G, Modica A (2005) Haematological, biochemical and immunological parameters as stress indicators in Dicentrarchus labrax and Sparus aurata farmed in off-shore cages. Aquac Int 13:67–73
Catherine P, Alexander C, Kirubakaran JW, Michael D (2010) Water soluble fraction of Tinospora cordifolia leaves enhanced the non-specific immune mechanisms and disease resistance in Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:765–772
Cerda-Reverter JM, Zanuy S, Carrillo M, Madrid JA (1998) Time course studies on plasma glucose, insulin and cortisol in seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) held under different photoperiodic regimes. Physiol Behav 64:245–250
Di Marco P, Priori A, Finoia MG, Massari A, Mandich A, Marino G (2008) Physiological responses of European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax to different stocking densities and acute stress challenge. Aquaculture 275:319–328
Ellis AE (2001) Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against virus and bacteria. Dev Comp Immunol 25:827–839
Holm JC, Refstie T, Bo S (1990) The effect of fish density and feeding regimes on individual growth rate and mortality in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 89:3–4
Iguchi K, Ogawa K, Nagae M, Ito F (2003) The influence of rearing density on stress response and disease susceptibility of ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis). Aquaculture 220:515–523
Jorgensen EH, Jobling M (1993) Feeding in darkness eliminates density-dependent growth suppression in Arctic charr. Aquac Int 1:90–93
Kuda T, Matsumoto C, Yano T (2002) Changes in acid and alkaline phosphatase activities during the spoilage of raw muscle from horse mackerel Trachurus japonicus and gurnard Lepidotriga microptera. Food Chem 76:443–447
Magnadottir B (2010) Immunological control of fish diseases. Mar Biotechnol 12:361–379
Magnadottir B, Jonsdottir H, Sigurdur H, Bjornsson B, Jorgensen TO, Pilstrom L (1999) Humoral immune parameters in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) I. The effects of environmental temperature. Comp Biochem Phys B 122:173–180
Mauri I, Romero A, Acerete L, MacKenzie S, Roher N, Callol A, Cano I, Alvarez MC, Tort L (2011) Changes in complement responses in Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) under crowding stress, plus viral and bacterial challenges. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:182–188
Miyazaki T (1998) A simple method to evaluate respiratory burst activity of blood phagocytes from Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Pathol 33:141–142
Montero D, Izqierdo MS, Tort L, Robaina L, Vergara JM (1999) High stocking density produces crowding stress altering some physiological and biochemical parameters in gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata, juveniles. Fish Physiol Biochem 20:53–60
Murray CK, Fletcher TC (1976) The immunohistochemical localisation of lysozyme in plaice (Pleuronectes platessa L.) tissues. J Fish Biol 9:329–334
North BP, Turnbull JF, Ellis T, Porter MJ, Migaud H, Bron J, Bromage NR (2006) The impact of stocking density on the welfare of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 255:466–479
Peake J, Wilson G, Hordern M, Suzuki K, Yamaya K, Nosaka K, Mackinnon L, Coombes JS (2004) Changes in neutrophil surface receptor expression, degranulation, and respiratory burst activity after moderate- and high-intensity exercise. J Appl Physiol 97:612–618
Philipose KK, Sharma SRK, Loka J, Divu D, Sadhu N, Dube PN (2013) Culture of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch) in open sea floating net cages off Karwar, south India. Indian J Fish 60:67–70
Pickering AD, Pottinger TG (1989) Stress responses and disease resistance in salmonid fish: effects of chronic elevation of plasma cortisol. Fish Physiol Biochem 7:253–258
Purcell MK, Kurath G, Garver KA, Herwig RP, Winton JR (2004) Quantitative expression profiling of immune response genes in rainbow trout following infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) infection or DNA vaccination. Fish Shellfish Immunol 17:447–462
Quade MJ, Roth JA (1997) A rapid, direct assay to measure degranulation of bovine neutrophil primary granules. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 58:239–248
Rao VY, Das BK, Jyotyrmayee P, Chakrabarti R (2006) Effect of Achyranthes aspera on the immunity and survival of Labeo rohita infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:263–273
Ross NW, Firth KJ, Wang A, Burka JF, Johnson SC (2000) Changes in hydrolytic enzyme activities of naive Atlantic salmon Salmo salar skin mucus due to infection with the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis and cortisol implantation. Dis Aquat Organ 41:43–51
Sodeberg RW, Meade JW (1987) Effects of rearing density on growth, survival, and fin condition of Atlantic salmon. Progress Fish Cult 49:280–283
Swain P, Dash S, Sahoo PK, Routray P, Sahoo SK, Gupta SB, Meher PK, Sarangi N (2007) Non-specific immune parameters of brood Indian major carp Labeo rohita and their seasonal variations. Fish Shellfish Immunol 22:38–43
Tendencia EA (2002) Vibrio harveyi isolated from cage-cultured sea bass Lates calcarifer, Bloch in the Philippines. Aquac Res 33:455–458
Tort L, Sunyer JO, Gomez E, Molinero A (1996) Crowding stress induces changes in serum haemolytic and agglutinating activity in the gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 51:179–188
Umminger BL (1977) Relation of whole blood sugar concentrations in vertebrates to standard metabolic rate. Comp Biochem Phys A 56:457–460
Vijayan MM, Leatherland JF (1988) Effect of stocking density on the growth and stress-response in brook charr (Salvelinus fontinalis). Aquaculture 75:159–170
Vijayan MM, Ballantyne JS, Leatherland JF (1990) High stocking density alters the energy metabolism of brook charr, Salvelinus fontinalis. Aquaculture 88:371–381
Yin Z, Lam TJ, Sin YM (1995) The effects of crowding stress on the non-specific immune response in fancy carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 5:519–529
Acknowledgments
The results of the study formed part of the Ph.D. research of the first author. The authors are thankful to Dr. G. Syda Rao, Director, CMFRI, for providing facilities to conduct the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadhu, N., Sharma, S.R.K., Joseph, S. et al. Chronic stress due to high stocking density in open sea cage farming induces variation in biochemical and immunological functions in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch). Fish Physiol Biochem 40, 1105–1113 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9909-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9909-8