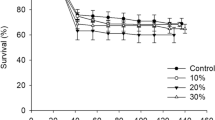
Abstract
Enterocytes of the anterior to midsection of the intestine in grouper Epinephelus coioides larvae were compared among different treatments: unfed to the point-of-no-return (PNR), fed natural food only, and co-fed natural food and artificial diet. On day 3, the nutritional condition of unfed grouper larvae regressed with its reduced enterocyte heights which were further degraded on day 4, the PNR, when all the enterocytes were in advanced stages of apoptosis. The apoptosis appeared to be internally directed via the mitochondria. Among day 3 fed larvae, enterocyte heights of those fed artificial diet did not differ from those fed natural food only. Dietary phospholipid deficiency was indicated in larvae co-fed artificial diet on day 3 with an unusually large chylomicron opening into the inter-enterocyte space, and on days 6 and 33 by intestinal steatosis. On day 19, scant to absent lipid droplets in enterocytes of larvae disclosed heightened nutritional requirement preparatory to metamorphosis. As observed in unfed day 3 and premetamorphic day 19 E. coioides, larvae undergoing critical periods and starvation during development employ apoptosis to dispose of degenerated enterocytes that are phagocytosed by adjacent healthy enterocytes without causing inflammatory distress. Upon metamorphosis, grouper larval gut develops better immunity fitness with eosinophilic granule cells observed in the intestinal epithelia of day 33 larvae. Future studies on grouper larval nutrition may consider the appropriate dietary phospholipid levels and larval competence to biosynthesize highly unsaturated fatty acid from linoleic acid vis-à-vis the use of plant ingredients in artificial diet formulations. In vivo challenge tests may validate appropriate dietary nutrient supplementation and lead to better feed formulation, matching the varying energetic demands and digestive capacities of developing E. coioides larvae.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC (1980) Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC. In: Horwitz W (ed), 13th edn. The Association of Official Analytical Chemists. 1038 p. http://ia600303.us.archive.org/22/items/gov.law.aoac.methods.1980/aoac.methods.1980.pdf Accessed 13 Aug 2013
Bates JM, Mittge E, Kuhlman J, Baden KN, Cheesman SE, Guillemin K (2006) Distinct signals from the microbiota promote different aspects of zebrafish gut differentiation. Dev Biol 297:374–386
Blaxter JHS, Hempel G (1963) The influence of egg size on herring larvae (Clupea harengus L.). ICES J Mar Sci 28:211–240
Cahu CL, Zambonino Infante JL, Barbosa V (2003) Phospholipid level in dietary lipid fraction is determining for sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larval development. Br J Nutr 90:21–28
Cahu CL, Gisbert E, Villeneuve LA, Morais S, Hamza N, Wold P-A, Zambonino Infante JL (2009) Influence of dietary phospholipids on early ontogenesis of fish. Aquac Res 40:989–999
Calzada A, Medina A, Gonzales ML (1998) Fine structure of the intestine development in cultured sea bream larvae. J Fish Biol 53:340–365
Cunha ME, Quental H, Barradas A, Pousao-Ferreira P, Cabrita E, Engrola S (2009) Rearing larvae of dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus (Lowe, 1834), (Pisces:Serranidae) in a semi extensive mesocosm. Sci Mar 73S1:201–212. doi:10.3989/scimar.2009.73s1201
Dapra F, Geurden I, Corraze G, Bazin D, Zambonino Infante JL, Fontagne-Dicharry S (2011) Physiological and molecular responses to dietary phospholipids vary between fry and early juvenile stages of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 319:377–384
Deplano M, Connes R, Diaz JP, Paris J (1989) Intestinal steatosis in the farm-reared sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax. Dis Aquat Org 6:121–130
Diaz J-P, Guyot E, Vigier S, Connes R (1997) First events in lipid absorption during post-embryonic development of the anterior intestine in gilt-head seabream. J Fish Biol 51:180–192
Diaz J-P, Mani-Ponset L, Blasco C, Connes R (2002) Cytological detection of the main phases of lipid metabolism during early post-embryonic development in three teleost species: Dicentrarchus labrax, Sparus aurata and Stizostedion lucioperca. Aquat Living Resour 15:169–178
Duray MN, Estudillo CB, Alpasan LG (1996) The effect of background color and rotifer density on rotifer intake, growth and survival of the grouper (Epinephelus suillus) larvae. Aquaculture 146:217–224
Duray MN, Estudillo CB, Alpasan LG (1997) Larval rearing of the grouper Epinephelus suillus under laboratory conditions. Aquaculture 115:361–367
Elbal MT, Garcia Hernandez MP, Lozano MT, Aguilleiro B (2004) Development of the digestive tract of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Light and electron microscopic studies. Aquaculture 234:215–238
Eusebio PS, Toledo JD, Mamauag REP, Bernas MJG (2004) Digestive enzyme activity in developing grouper (Epinephelus coioides) larvae. In: Williams KC, Rimmer MA, McBride S (eds) Advances in grouper aquaculture. ACIAR, Canberra, pp 35–40
FAOSTAT (2009) Grouper aquaculture, capture and global production. http://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/en. Accessed 15 Nov 2011
Frøyland L, Madsen L, Vaagenes H, Totland GK, Auwerx J, Kryvi H, Staels B, Berge RK (1997) Mitochondrion is the principal target for nutritional and pharmacological control of triglyceride metabolism. J Lipid Res 38:1851–1858
Gisbert E, Villeneuve L, Zambonino-Infante JL, Quazuguel P, Cahu CL (2005) Dietary phospholipids are more efficient than neutral lipids for long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supply in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax larval development. Lipids 40(6):609–618
Gisbert E, Ortiz-Delgado JB, Sarasquete MC (2008) Nutritional cellular biomarkers in early life stages of fish. Histol Histopathol 23:1525–1539
Hamre K (2006) Nutrition in cod (Gadus morhua) larvae and juveniles. ICES J Mar Sci 63:267–274
Iwai T (1968) The comparative study of the digestive tract of teleost larvae-V. Fat absorption in the gut epithelium of goldfish larvae. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 34(11):973–978
Iwai T (1969) Fine structure of gut epithelial cells of larval and juvenile carp during absorption of fat and protein. Arch Histol Jpn 30(2):183–199
Iwai T, Tanaka M (1968) The comparative study of the digestive tract of teleost larvae-IV. Absorption of fat by the gut of halfbeak larvae. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 34(10):871–875
Izquierdo MS, Socorro J, Arantzamendi L, Hernandez-Cruz CM (2000) Recent advances in lipid nutrition in fish larvae. Fish Physiol Biochem 22:97–107
Jones BA, Gores GJ (1997) Physiology and pathophysiology of apoptosis in epithelial cells of the liver, pancreas and intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 273:G1174–G1188
Kjørsvik E, Van der Meeren T, Kryvi H, Arnfinnson J, Kvenseth PG (1991) Early development of the digestive tract of cod larvae, Gadus morhua L., during start-feeding and starvation. J Fish Biol 38:1–15
Kuz’mina VV, Gelman AG (1997) Membrane-linked digestion in fish. Rev Fish Sci 5(2):99–129
Lazo JP, Darias MJ, Gisbert E (2010) New approaches to assess the nutritional condition of marine fish larvae. In: Cruz-Suarez LE, Ricque–Marie D, Tapia-Salazar M, Nieto-Lopez MG, Villareal-Cavazos DA, Gamboa-Delgado J (eds) Avances en nutrición acuícola X- memorias del X Simposio Internacional de Nutrición Acuícola, 8–10 de Nov, San Nicolas de los Garza, NL México. Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo de León, Monterrey, México, pp 283–296
Li WS, Chen D, Wong AOL, Lin HR (2005) Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, and ontogeny of mRNA expression of growth hormone in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Gen Comp Endocrinol 144:78–89
Liao IC, Su HM, Chang EY (2001) Techniques in finfish larviculture in Taiwan. Aquaculture 200:1–31
MacQueen Leifson R, Homme JM, Jøstensen JP, Lie O, Myklebust R, Strøm T (2003) Phospholipids in formulated start-feeds- effect on turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) larval growth and mitochondrial alteration in enterocytes. Aquac Nutr 9:43–54
Mani-Ponset L, Diaz JP, Schlumberger O, Connes R (1994) Development of yolk complex, liver and anterior intestine in pike perch larvae, Stizostedion lucioperca (Percidae), according to the first diet during rearing. Aquat Living Resour 7:191–202
McBride S (2004) The activity of digestive enzymes in larval grouper and live feed. In: Rimmer MA, McBride S, Williams KC (eds) Advances in grouper aquaculture. ACIAR, Canberra, pp 41–46
McFadzen IRB, Lowe DM, Coombs SH (1994) Histological changes in starved turbot larvae (Scophthalmus maximus) quantified by digital image analysis. J Fish Biol 44:255–262
Morais S, Conceicao LEC, Ronnestad I, Koven W, Cahu C, Zambonino Infante JL, Dinis MT (2007) Dietary neutral lipid level and source in marine fish larvae: effects on digestive physiology and food intake. Aquaculture 268:106–122
Mulero I, Pilar Sepulcre N, Meseguer J, Garcia-Ayala A, Mulero V (2007) Histamine is stored in mast cells of most evolutionarily advanced fish and regulates the fish inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19434–19439
Niu J, Liu YJ, Tian LX, Mai KS, Yang HJ, Ye CX, Zhu Y (2008) Effects of dietary phospholipid level in cobia (Rachycentron canadum) larvae: growth, survival, plasma lipids and enzymes of lipid metabolism. Fish Physiol Biochem 34:9–17. doi:10.1007/s10695-007-9140-y
O’Conell CP (1976) Histological criteria for diagnosing the starving condition in early post yolk sac larvae of the northern anchovy, Engraulis mordax Girard. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 25:285–312
Olsen RE, Myklebust R, Kaino T, Ringø E (1999) Lipid digestibility and ultrastructural changes in the enterocytes of Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus L.) fed linseed oil and soybean lecithin. Fish Physiol Biochem 21:35–44
Olsen RE, Myklebust R, Ringø E, Mayhew TM (2000) The influences of dietary linseed oil and saturated fatty acids on caecal enterocytes in Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus L.): a quantitative ultrastructural study. Fish Physiol Biochem 22:207–216
Ordonio-Aguilar RS (1995) Survival mechanisms of tropical marine fish larvae during changeover from endogenous to exogenous feeding. Dissertation, Tokyo University of Fisheries
Ordonio-Aguilar R, Kohno H, Ohno A, Moteki M, Taki Y (1995) Development of grouper, Epinephelus coioides, larvae during changeover of energy sources. J Tokyo Univ Fish 82:103–108
Phleger CF (1998) Buoyancy in marine fishes: direct and indirect role of lipids. Am Zool 38:321–330
Piper RC, Katzmann DJ (2007) Biogenesis and function of multivesicular bodies. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:519–547. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123319
Qu M, Ding S, Xu X, Shen M, You Y, Su Y (2012) Ontogenetic development of the digestive system and growth in coral trout (Plectropomus leopardus). Aquaculture 334–337:132–141
Quinitio GF, Sa-an AC, Toledo JD, Tan-Fermin JD (2004a) Changes in the gastrointestinal tract and associated organs during early development of the grouper (Epinephelus coioides). In: Rimmer MA, McBride S, Williams KC (eds) Advances in grouper aquaculture. ACIAR, Canberra, pp 26–29
Quinitio GF, Sa-an AC, Toledo JD, Tan-Fermin JD (2004b) Localisation of enzymes in the digestive system during early development of the grouper (Epinephelus coioides). In: Rimmer MA, McBride S, Williams KC (eds) Advances in grouper aquaculture. ACIAR, Canberra, pp 30–34
Reinecke M, Muller C, Segner H (1997) An immunohistochemical analysis of the ontogeny, distribution and coexistence of 12 regulatory peptides and serotonin in endocrine cells and nerve fibers of the digestive tract of the turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (Teleostei). Anat Embryol 195:87–101. doi:10.1007/S004290050028
Rimmer MA, McBride S, Williams KC (2004) Advances in grouper aquaculture. ACIAR, Canberra
Ringø E, Olsen RE, Mayhew TM, Myklebust R (2003) Electron microscopy of the intestinal microflora of fish. Aquaculture 227:395–415
Ringø E, Myklebust R, Mayhew TM, Olsen RE (2007) Bacterial translocation and pathogenesis in the digestive tract of larvae and fry. Aquaculture 268:251–264
Russo T, Boglione C, De Marzi P, Cataudella S (2009) Feeding preferences of the dusky grouper (Epinephelus marginatus, Lowe 1834) larvae reared in semi-intensive conditions: a contribution addressing the domestication of this species. Aquaculture 289:289–296
Rust MB (2002) Nutritional physiology. In: Halver JE, Hardy RW (eds) Fish nutrition, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 367–452
Sadovy YJ, Donaldson TJ, Graham TR, McGilvray F, Muldoon GJ, Phillips MJ, Rimmer MA, Smith A, Yeeting B (2003) While stocks last: the live reef food fish trade. Asian Development Bank, Manila
Sarasquete MC, Polo A, Yufera M (1995) Histology and histochemistry of the development of the digestive system of larval gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata L. Aquaculture 130:79–92
Sarker MAA, Yamamoto Y, Haga Y, MSA Sarker, Miwa M, Yoshizaki G, Satoh S (2011) Influences of low salinity and dietary fatty acids on fatty acid desaturase and elongase expression in red sea bream Pagrus major. Fish Sci 77:385–396
Segner H, Rösch R, Verreth J, Witt U (1993) Larval nutritional physiology: studies with Clarias gariepinus, Coregonus lavaretus and Scophthalmus maximus. J World Aquac Soc 24(2):121–133
Sire M-F, Lutton C, Vernier J-M (1981) New views on intestinal absorption of lipids in teleostean fishes: an ultrastructural and biochemical study in the rainbow trout. J Lipid Res 22:81–94
Sternini C, Anselmi L, Rozengurt E (2008) Enteroendocrine cells: a site of ‘taste’ in gastrointestinal chemosensing. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 15:73–78. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e3282f43a73
Suen D-F, Norris KL, Youle RJ (2008) Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev 22:1577–1590
Sumule O, Koshio S, Teshima S, Ishikawa M (2003) Energy budget of the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck and Schlegel) larvae fed HUFA-enriched and non-enriched Artemia nauplii. Aquac Res 34:877–886
Sun Y, Yang H, Ling Z, Chang J, Ye J (2009) Gut microbiota of fast and slow growing grouper Epinephelus coioides. Afr J Microbiol Res 3(11):713–720
Theilacker GH, Watanabe Y (1989) Midgut cell height defines nutritional status of laboratory raised larval northern anchovy, Engraulis mordax. Fish Bull 87:457–469
Tocher DR (2003) Metabolism and functions of lipids and fatty acids in teleost fish. Rev Fish Sci 11(2):107–184
Tocher DR (2010) Fatty acid requirements in ontogeny of marine and freshwater fish. Aquac Res 41:717–732
Tocher DR, Bendiksen EA, Campbell PJ, Bell GJ (2008) The role of phospholipids in nutrition and metabolism of teleost fish. Aquaculture 280:21–34
Toledo JD, Golez, Doi M, Ohno A (1999) Use of copepod nauplii during early feeding stage of grouper Epinephelus coioides. Fish Sci 65:390–397
Yamaoka K, Nanbu T, Miyagawa M, Isshiki T, Kusaka A (2000) Water surface tension-related deaths in prelarval red-spotted grouper. Aquaculture 189:165–176
Zambonino Infante JL, Cahu CL (2007) Dietary modulation of some digestive enzymes and metabolic processes in developing marine fish: applications to diet formulation. Aquaculture 268:98–105
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Commission on Higher Education, the Philippine Council for Agriculture, Aquatic Natural Resources Research and Development and the Science Education Institute of the Department of Science and Technology, and the Bureau of Agricultural Research-Department of Agriculture of the Government of the Philippines for financial support (extended to Y.H. Primavera-Tirol) and to the Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center-Aquaculture Department for the use of its aquaculture facilities. Thanks are given to V. Balinas for statistical advice, to T. Billena-Hagy, C. Sombito, and N. Bautista for technical assistance with the transmission electron microscopy, and to I. Tendencia for the artwork. Helpful advice from two anonymous reviewers that improved the manuscript is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Primavera-Tirol, Y.H., Coloso, R.M., Quinitio, G.F. et al. Ultrastructure of the anterior intestinal epithelia of the orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides larvae under different feeding regimes. Fish Physiol Biochem 40, 607–624 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9870-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9870-y