Abstract
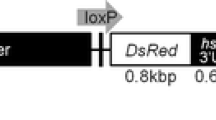
One cannot seek permission to market transgenic fish mainly because there is no field test or any basic research on technological developments for evaluating their biosafety. Infertility is a necessary adjunct to exploiting transgenic fish unless completely secure land-locked facilities are available. In this study, we report the generation of a Cre transgenic zebrafish line using a cytomegalovirus promoter. We also produced fish carrying the Bax1 and Bax2 plasmids; these genes were separated by two loxP sites under a zona pellucida C promoter or were driven by an anti-Müllerian hormone promoter. We inserted a red fluorescent protein gene between the two loxP sites. After obtaining transgenic lines with the two transgenic fish crossed with each other (Cre transgenic zebrafish x loxP transgenic zebrafish), the floxed DNA was found to be specifically eliminated from the female or male zebrafish, and apoptosis gene expressions caused ovarian and testicular growth cessation and degeneration. Overexpression of the Bax1 and Bax2 genes caused various expression levels of apoptosis-related genes. Accordingly, this transgenic zebrafish model system provides a method to produce infertile fish and may be useful for application to genetically modified fish.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams MV, Sutterlin A (1999) The foraging and antipredator behaviour of growth-enhanced transgenic Atlantic salmon. Anim Behav 58:933–942
Abremski K, Hoess R, Sternberg N (1983) Studies on the properties of P1 site-specific recombination: evidence for topologically unlinked products following recombination. Cell 32:1301–1311
Bailey JM, Creamer BA, Hollingsworth MA (2009) What a fish can learn from a mouse: principles and strategies for modeling human cancer in mice. Zebrafish 6:329–337
Bunting M, Bernstein KE, Greer JM, Capecchi MR, Thomas KR (1999) Targeting genes for self-excision in the germ line. Genes Dev 13:1524–1528
Chen JY, Chiou MJ, Chen LK, Wu JL (2010) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the zebrafish follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)beta promoter. Comp Biochem Physiol B-Biochem Mol Biol 155:155–163
Ciruna B, Weidinger G, Knaut H, Thisse B, Thisse C, Raz E, Schier AF (2002) Production of maternal-zygotic mutant zebrafish by germ-line replacement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14919–14924
Devlin RH, Biagi CA, Smailus DE (2001) Genetic mapping of Y-chromosomal DNA markers in Pacific salmon. Genetica 111:43–58
Devlin RH, D’andrade M, Uh M, Biagi CA (2004) Population effects of growth hormone transgenic coho salmon depend on food availability and genotype by environment interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9303–9308
Devlin RH, Sundström LF, Muir WM (2006) Interface of biotechnology and ecology for environmental risk assessments of transgenic fish. Trends Biotechnol 24:89–97
Eimon PM, Ashkenazi A (2010) The zebrafish as a model organism for the study of apoptosis. Apoptosis 15:331–349
Eimon PM, Kratz E, Varfolomeev E, Hymowitz SG, Stern H, Zha J, Ashkenazi A (2006) Delineation of the cell-extrinsic apoptosis pathway in the zebrafish. Cell Death Differ 13:1619–1630
Fischer JA, Giniger E, Maniatis T, Ptashne M (1988) GAL4 Activates transcription in Drosophila. Nature 332:853–856
Foresta C, Flohe L, Garolla A, Roveri A, Ursini F, Maiorino M (2002) Male fertility is linked to the selenoprotein phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase. Biol Reprod 67:967–971
Golling G, Amsterdam A, Sun ZX, Antonelli M, Maldonado E, Chen WB, Burgess S, Haldi M, Artzt K, Farrington S, Lin SY, Nissen RM, Hopkins N (2002) Insertional mutagenesis in zebrafish rapidly identifies genes essential for early vertebrate development. Nature Genet 31:135–140
Gossen M, Bujard H (1992) Tight control of gene-expression in mammalian-cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5547–5551
Hu SY, Lin PY, Liao CH, Gong HY, Lin GH, Kawakami K, Wu JL (2010) Nitroreductase-mediated gonadal dysgenesis for infertility control of genetically modified Zebrafish. Mar Biotechnol 12:569–578
Imai H, Narashima K, Arai M, Sakamoto H, Chiba N, Nakagawa Y (1998) Suppression of leukotriene formation in RBL-2H3 cells that overexpressed phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase. J Biol Chem 273:1990–1997
Imai H, Hakkaku N, Iwamoto R, Suzuki J, Suzuki T, Tajima Y, Konishi K, Minami S, Ichinose S, Ishizaka K, Shioda S, Arata S, Nishimura M, Naito S, Nakagawa Y (2009) Depletion of selenoprotein GPx4 in spermatocytes causes male infertility in mice. J Biol Chem 284:32522–32532
Kapuscinski AR, Hayes KR, Li S, Dana G (2007) Environmental risk assessment of genetically modified organisms, volumn 3: methodologies for transgenic fish. CABI international, USA
Kawakami K, Takeda H, Kawakami N, Kobayashi M, Matsuda N, Mishina M (2004) A transposon-mediated gene trap approach identifies developmentally regulated genes in zebrafish. Dev Cell 7:133–144
Kratz E, Eimon PM, Mukhyala K, Stern H, Zha J, Strasser A, Hart R, Ashkenazi A (2006) Functional characterization of the Bcl-2 gene family in the zebrafish. Cell Death Differ 13:1631–1640
Langenau DM, Feng H, Berghmans S, Kanki JP, Kutok JL, Look AT (2005) Cre/lox-regulated transgenic zebrafish model with conditional myc-induced T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:6068–6073
Meeker ND, Hutchinson SA, Ho L, Trecle NS (2007) Method for isolation of PCR-ready genomic DNA from zebrafish tissues. Biotechniques 43:610–614
Ogorman S, Fox DT, Wahl GM (1991) Recombinase-mediated gene activation and site-specific integration in mammalian-cells. Science 251:1351–1355
Pan XF, Wan HY, Chia W, Tong Y, Gong ZY (2005) Demonstration of site-directed recombination in transgenic zebrafish using the Cre/loxP system. Transgenic Res 14:217–223
Pyati UJ, Look AT, Hammerschmidt M (2007) Zebrafish as a powerful vertebrate model system for in vivo studies of cell death. Semin Cancer Biol 17:154–165
Reichhardt T (2000) Will souped up salmon sink or swim? Nature 406:10–12
Rodriguez-Mari A, Canestro C, Bremiller RA, Nguyen-Johnson A, Asakawa K, Kawakami K, Postlethwait JH (2010) Sex reversal in zebrafish fancl mutants is caused by Tp53-mediated germ cell apoptosis. PLoS Genet 6:e1001034
Rodriguez-Mari A, Wilson C, Titus TA, Canestro C, Bremiller RA, Yan YL, Nanda I, Johnston A, Kanki JP, Gray EM, He XJ, Spitsbergen J, Schindler D, Postlethwait JH (2011) Roles of brca2 (fancd1) in oocyte nuclear architecture, gametogenesis, gonad tumors, and genome stability in zebrafish. PLoS Genet 7:e1001357
Thummel R, Burket CT, Brewer JL, Sarras MP, Li L, Perry M, Mcdermott JP, Sauer B, Hyde DR, Godwin AR (2005) Cre-mediated site-specific recombination in zebrafish embryos. Dev Dyn 233:1366–1377
Wong AC, Draper BW, Van Eenennaam AL (2011) FLPe functions in zebrafish embryos. Transgenic Res 20:409–415
Yabu T, Kishi S, Okazaki T, Yamashita M (2001) Characterization of zebrafish caspase-3 and induction of apoptosis through ceramide generation in fish fathead minnow tailbud cells and zebrafish embryo. Biochem J 360:39–47
Zheng BH, Mills AA, Bradley A (1999) A system for rapid generation of coat color-tagged knockouts and defined chromosomal rearrangements in mice. Nucleic Acids Res 27:2354–2360
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Development Program of Industrialization for Agricultural Biotechnology (money provided by Academia Sinica), called “Study and development of novel pattern of transgenic fluorescent ornamental fish and infertility technology” to Dr. Jyh-Yih Chen in 2010 and 2011. The Cre–loxP plasmid was kindly provided as a gift from Dr. Allan Bradley (Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Cambridge, UK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, HJ., Lee, SH., Wu, JL. et al. Development of Cre–loxP technology in zebrafish to study the regulation of fish reproduction. Fish Physiol Biochem 39, 1525–1539 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9806-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9806-6