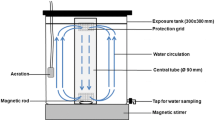
Abstract
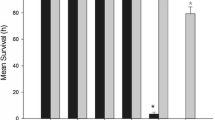
Dispersant use is a controversial technique used to respond to oil spills in nearshore areas. In order to assess the toxicity of this technique, this study evaluated the cardiac toxicological effects on juvenile golden grey mullets Liza aurata exposed for 48 h to either dispersant alone, chemically dispersed oil, mechanically dispersed oil, the water-soluble fraction of oil or a control condition. Following exposure, the positive inotropic effects of adrenaline were assessed in order to evaluate a potential impairment on the cardiac performance. The results revealed an impairment of the positive inotropic effects of adrenaline for all the contaminants (single dispersant, dispersed and undispersed oil, water-soluble fraction of oil). This suggests that: (1) cardiac performance is a valuable parameter to study the physiopathological effects of dispersed oil; (2) dispersant application is likely to impair cardiac performance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas E, Baussant T, Balk L, Liewenborg B, Andersen OK (2000) PAH metabolites in bile, cytochrome P4501A and DNA adducts as environmental risk parameters for chronic oil exposure: a laboratory experiment with Atlantic cod. Aquat Toxicol 51:241–258
Camus L, Aas E, Børseth JF (1998) Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity and fixed wavelength fluorescence detection of PAH metabolites in bile in Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) exposed to a dispersed topped crude oil in a continuous flow system. Mar Environ Res 46:29–32
Churchill PF, Dudley RJ, Churchill SA (1995) Surfactant-enhanced bioremediation. Waste Manag 15:371–377
Claireaux G, Davoodi F (2010) Effect of exposure to petroleum hydrocarbons upon cardio-respiratory function in the common sole (Solea solea). Aquat Toxicol 98:113–119
Cormack D (1977) Oil pollution. Chem Ind 14:605–608
Goanvec C, Poirier E, Le Floch S, Théron M (2011) Branchial structure and hydromineral equilibrium in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) exposed to heavy fuel oil. Fish Physiol Biochem 37:363–371
Incardona JP, Collier TK, Scholz NL (2004) Defects in cardiac function precede morphological abnormalities in fish embryos exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196:191–205
Jung JH, Yim UH, Han GM, Shim WJ (2009) Biochemical changes in rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli, exposed to dispersed crude oil. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 150:218–223
Klabunde RE (2011) Cardiovascular physiology concepts, 2nd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, New York
Lewis A, Daling P (2001) Oil spill dispersants. In: Consultant ALOS. SINTEF, Staines
Milinkovitch T, Kanan R, Thomas-Guyon H, Le Floch S (2011) Effects of dispersed oil exposure on bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and mortality of juvenile Liza ramada. Sci Total Environ 409:1643–1650
Milinkovitch T, Lucas J, Le Floch S, Thomas-Guyon H, Lefrançois C (2012) Effect of dispersed crude oil exposure upon the aerobic metabolic scope in juvenile golden grey mullet (Liza aurata). Mar Pol Bull 64:865–871
Petersen LH, Gamperl K (2009) A comprehensive examination of the effects of chronic hypoxia on the cardiorespiratory physiology of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 153:S56–S63
Ramachandran SD, Hodson PV, Khan CW, Lee K (2004) Oil dispersant increases PAH uptake by fish exposed to crude oil. Ecotox Environ Saf 59:300–308
Shiels HA, Farrell AP (1997) The effect of the temperature and adrenaline on the relative importance of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in contributing Ca2+ to force development in isolated ventricular trabeculae from rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 200:1607–1621
Spooner MF (1970) Oil spill in Tarut Bay, Saudi Arabia. Mar Pol Bull 1:166–167
Thiem A (1994) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the presence of synthetic surfactants. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:258–263
Thomaz JM, Martins ND, Monteiro DA, Rantin FT, Kalinin AL (2009) Cardio-respiratory function and oxidative stress biomarkers in Nile tilapia exposed to the organophosphate insecticide trichlorfon (NEGUVON®). Ecotox Environ Saf 72:1413–1424
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milinkovitch, T., Thomas-Guyon, H., Lefrançois, C. et al. Dispersant use as a response to oil spills: toxicological effects on fish cardiac performance. Fish Physiol Biochem 39, 257–262 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-012-9696-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-012-9696-z