Abstract
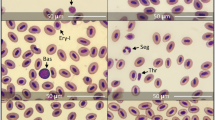
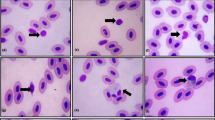
The aim of this study was a comparison of key haematological features of diploid (2n) and triploid (3n) Caspian salmon (Salmo trutta caspius). Morphometric indices of erythrocytes were determined on blood smears by light microscopy. Triploidy significantly (P < 0.001) increased all morphometric indices measured in the erythrocytes including cell size, cell surface area, and cell volume. The increase in cell size was larger for the major (27%) axis than for the minor (22%) axis, thus making erythrocytes of 3n Caspian salmon more ellipsoidal. The estimated increase in erythrocyte nuclear volume (87%) was bigger than the theoretical expected 50% increase. Haematological indices were measured manually by hemocytometry. Triploids had lower numbers of red blood cells (RBC: 1,120,000 cells/mL in 2n vs. 700,000 cells/mL in 3n; P < 0.001) but they were larger in size (mean erythrocytic volume [MEV]: 363.1 nm3 in 2n vs. 483.3 nm3 in 3n; P < 0.001). The decrease in RBC number was not compensated by the increase in MEV and, thus, triploidy affected the haematocrit (Hct: 38.8% in 2n vs. 33.06% in 3n; P < 0.05). Total blood hemoglobin concentration was lower in triploid fish (Hb: 9.9 g/dL in 2n vs. 8.9 g/dL in 3n; P < 0.05). In contrast, mean erythrocytic hemoglobin (MEH: 95 μg in 2n vs. 133.2 μg in 3n; P < 0.001) was higher for 3n Caspian salmon as a result of their larger erythrocytes, although MEH concentration (MEHC: 0.26 g/dL in 2n vs. 0.27 g/dL in 3n) did not significantly differ (P > 0.05). White blood cell (WBC) counts (lymphocytes and neutrophiles) were measured and WBC/RBC ratios were calculated. There were no significant differences in WBC (15,710 cells/mL in 2n vs. 12,683 cells/mL in 3n; P > 0.05), lymphocytes, and neutrophils as %WBC as well as WBC/RBC ratios between two ploidy levels (P > 0.05). Triploid Caspian salmon showed higher erythrocyte abnormalities such as ‘twisted’, ‘tailed’, and ‘anucleated’ cells as well as high portions of immature RBC in blood smears in comparison with diploids (P < 0.001).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktins ME, O’Keefe RA, Benfey TJ (2000) The effect of exercise on the growth and haematology of diploid and triploid brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). Aquacul Assoc Canada Spec Publ 4:19–21
Benfey TJ (1999) The physiology and behaviour of triploid fishes. Rev Fish Sci 7:39–67
Benfey TJ, Sutterlin AM (1984) The haematology of triploid landlocked Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar, L. J Fish Biol 24:333–338
Benfey TJ, Sutterlin AM, Thompson RJ (1984) Use of erythrocyte measurements to identify triploid salmonids. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 41:980–984
Benfey TJ, Biron M (2000) Acute stress response in triploid rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). Aquaculture 184:167–176
Beyea MM, Benfey TJ, Kieffer JD (2005) Haematology and stress physiology of juvenile diploid and triploid shortnose sturgeon (Acipenser brevirostrum). Fish Physiol Biochem 31:303–313
Cal RM, Vidal S, Camacho T, Piferrer F, Guitian FJ (2005) Effect of triploidy on turbot haematology. Comp Biochem Physiol A 141:35–41
Cogswell AT, Benfey TJ, Sutterlin AM (2002) The haematology of diploid and triploid transgenic Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Physiol Biochem 24:271–277
Felip A, Piferrer F, Zanuy S, Carrillo M (2001) Comparative growth performance between diploid and triploid sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) over the first four spawning seasons. J Fish Biol 58:76–88
Flajshans M (1997) A model approach to distinguish diploid and triploid fish by means of computer-assisted image analysis. Acta Vet Brno 66:101–110
Houston AH (1990) Blood and circulation. In: Schreck CB, Moyle PB (eds) Methods in fish biology. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, Maryland, pp 273–335
Houston AH (1997) Review: are the classical haematological variables acceptable indicators of fish health? Trans Am Fish Soc 126:879–893
Hulata G (2001) Genetic manipulations in aquaculture: a review of stock improvement by classical and modern technologies. Genetica 111:155–173
Kiabi BH, Abdoli A, Naderi M (1999) Status of fish fauna in the south Caspian basin of Iran. Zool Middle East 18:57–65
Lemoine LH, Smith TL (1980) Polyploidy induced in brook trout by cold shock. Tran Am Fish Soc 109:626–631
O’Keefe R, Stillwell E, Benfey TJ (2000) The effect of transportation and handling on the haematology of diploid and triploid Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquac Assoc Canada Spec Publ 4:25–27
Quillet E, Faure A, Chevassus B, Kreig F, Harache Y, Arzel J, Metailler R, Boeuf G (1992) The potential of brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) for mariculture in temperate waters. ICEL Agric Sci 6:63–76
Sedgwick SD (1995) Trout farming handbook, 5th edn. Fishing News Books, Alden Press, Oxford
Scheerer PD, Thorgaard GH (1983) Increased survival in salmonid hybrids by induced triploidy. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 40:2040–2044
Sezaki K, Kobayasi H, Nakamura M (1977) Size of erythrocytes in the diploid and triploid specimens of Carassius auratus langsdorfi. Jap J Ichthyol 24:135–140
Sezaki K, Watabe S, Tsukamoto K, Hashimoto K (1991) Effects of increase in ploidy status on respiratory function of ginbuna, Carassius auratus langsdorfi (Cyprinidae). Comp Biochem Physiol 32:123–127
Svobodova Z, Kolarova J, Flajshans M (1998) The first finding of the differences in complete blood count between diploid and triploid tench, Tinca tinca L. Acta Vet Brno 67:243–248
Thorgaard GH (1983) Chromosome set manipulation and sex control in fish. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ, Donaldson EM (eds) Fish physiology, vol IXB. Academic Press, New York, pp 405–434
Tiwary BK, Kirubagaran R, Ray AK (2004) The biology of triploid fish. Rev Fish Biol Fish 14:391–402
Virtanen E, Forsman L, Sundby A (1990) Triploidy decreases the aerobic swimming capacity of rainbow trout (Salmo garidneri). Comp Biochem Physiol 96A:117–121
Wlasow T, Kuzminski H, Woznicki P, Ziomek E (2004) Blood cell alterations in triploid brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis. Acta Vet Brno 73:115–118
Yamamoto A, Iida T (1994) Haematological characteristics of triploid rainbow trout. Fish Pathol 29:239–243
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank A. Pasha Zanousi, M. Rezvani, and H. Golshahi, manager and staff of Dr. Bahonar Culture and Breeding Centre of Salmonids, Kelardasht, Mazandaran, Iran. Thanks also to Dr. A. M. Abedian, Tarbiat Modares University, Iran and Dr. M. Flajshans, South Bohemia University, Czech Republic for their kind assistance. Special thanks to Mr. Kh. Rahimi for his helpful assistance in blood parameter measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorafshan, S., Kalbassi, M.R., Pourkazemi, M. et al. Effects of triploidy on the Caspian salmon Salmo trutta caspius haematology. Fish Physiol Biochem 34, 195–200 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-007-9176-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-007-9176-z