Abstract
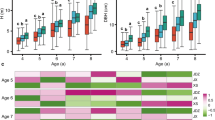
Growth characteristics have a complex inheritance pattern, and gene–environment interactions make predicting tree responses to environmental change difficult. In this study, we planted 44 Betula platyphylla families at three different sites (Mao er shan forestry center in Shangzhi, Jilin experiment forestry center in Jilin, Lang xiang forestry center in Langxiang) in northeastern China. Variation and stability of genotype–environment interactions of different families were analyzed using additive main effect and multiplicative interaction models. Variation analysis indicated significant differences between site × family interaction mean values for height, diameter at breast height, volume, and stem straight degree, suggesting that most genotypes responded differently according to location. The phenotypic coefficients of variation of different traits ranged from 12.84 % (stem straight degree in Langxiang) to 53.34 % (volume in Langxiang) and heritabilities of the different traits varied from 0.485 (diameter at breast height in Mao er shan) to 0.781 (height in Jilin). Correlation analysis showed a significantly positive association between tree height, diameter at breast height, and volume at the same and different sites, but stem straight degree showing a weaker correlation with other traits. Stability analysis indicated that some families had high tree heights but were sensitive to environmental conditions, whereas others had average tree heights but were resistant to environmental conditions. These results suggest that families should be bred in various habitats to assess growth under favorable and unfavorable environments. Under a selection ratio of 10 %, four families (family 1–7, 4–7, 3–12 and 4–13) were rated as superior families. The average height, diameter at breast height, volume, and stem straight degree of these four families were higher than average of all the families by 12.24, 16.82, 32.28 and 6.28 % in the four test sites, respectively.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annicchiarico P (2002) Genotype × environment interactions: challenges and opportunities for plant breeding and cultivar recommendations. Washington (DC): Food and Agriculture Org. p 101
Balestre M, Pinho R, Soouza J, Oliverira R (2009) Genotypic stability and adaptability in tropical maize based on AMMI and GGE biplot analysis. Genet Mol Res 8:1311–1322
Bi CX, Guo JZ, Wang HW, Shu QY (2000) The correlation and path analysis on the quantity characters of Chinese pine. J Northwest For Univ 15(2):7–12
Burdon R (1977) Genetic correlation as concept for studying genotype-environment interactions in forest breeding. Silvae Genet 26:168–175
Codesido V, Lopez F (2009) Implication of genotype × site interaction on Pinus radiata breeding in Galicia. New Forest 37:17–34
Dhillon G, Singh A, Sidhu DS, Brar HS (2012) Variation among poplar clones for growth and crown traits under field conditions at two sites of north-western India. J For Res 24:61–67
Fang SZ, Xu XZ, Lu SX, Tang LZ (1999) Growth dynamics and biomass production in short-rotation poplar plantations: 6-year results for three clones at four spacings. Biomass Bioenergy 17:415–425
Frew M (2003) Yield stability in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes. Euphytica 130:147–153
Hai PH, Jansson G, Harwood C, Hannrup B, Thinh HH (2008) Genetic variation in growth, stem straightness and branch thickness in clonal trials of Acacia auriculiformis at three contrasting sites in Vietnam. For Ecol Manag 255:156–167
Hansen J, Roulund H (1997) Genetic parameters for spiral grain, stem form, pilodyn and growth in 13 years old clones of Sitka Spruce (Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr.). Silvae Genet 46:107–113
Jiang J, Yang G, Zhu ZB, Yang YL, Yang SZ (2011) Family selection from intensive seed orchard of Betula Platyphylla. J Northeast For Univ 39:1–4
Kang M, Pham H (1991) Simultaneous selection for high yielding and stable crop genotypes. Agron J 83:161–165
Kempton R (1984) The use of the biplots in interpreting variety by environment interactions. J Agric Sci 103:123–135
Kien ND, Jansson G, Harwood C, Almqvist C, Thinh HH (2008) Genetic variation in wood basic density and pilodyn penetration and their relationships with growth, stem straightness and branch size for Eucalyptus urophylla S. T. Blake in Northern Vietnam. NZ J For Sci 38:160–175
Li P, Fang G, Sun C (1995) Wood characteristics of pulpwood. Chem Indus For Prod 15:13–18
Liu DK, Liu MR, Li ZX, Wang GY, Li Y, Zheng M, Liu GF, Zhao XY (2015a) Variation analysis of growth traits of transgenic Populous simonii × P.nigra clones carrying TaLEA Gene. Bull Bot Res 35:540–546
Liu MR, Yin SP, Si DJ, Shao LT, Li Y, Zheng M, Wang FW, Li SC, Liu GF, Zhao XY (2015b) Variation and genetic stability analyses of transgenic TaLEA poplar clones from four different sites in China. Euphytica. doi:10.1007/s10681-015-1471-7
Lynch M, Walsh B (1998) Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits. Mass. Sinauer, Sunderland
Maniee MD, Kahrizi MD, Mohammadi R (2009) Genetic variability of some morphophysiological traits in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum var. durum). J Appl Sci 9:1383–1387
Marron N, Ceulemans R (2006) Genetic variation of leaf traits related to productivity in a Populus deltoides × Populus nigra family. Can J For Res 36:390–400
Marron N, Ricciotti L, Bastien C, Beritognolo L, Gaudet M, Paolucci I, Fabbrini F, Salani F, Dillen SY, Ceulemans R, Pinel M, Taylor G, Mugnozza GS, Sabatti M (2010) Plasticity of growth and biomass production of an intraspecific Populus alba family grown at three sites across Europe during three growing seasons. Can J For Res 40:1887–1903
Misra RC, Das S, Patnaik MC (2009) AMMI model analysis of stability and adaptability of late duration finger millet (Eleusine coracana) genotypes. World Appl Sci J 6:1650–1654
Montes CS, Hernandez RE, Beaulieu J, Weber JC (2008) Genetic variation in wood color and its correlations with tree growth and wood density of Calycophyllum spruceanum at an early age in the Peruvian Amazon. New Forest 35:57–73
Namkoong G, Kang HC, Brouard JS (1988) Tree breeding: principles and strategies. Springer, New York, p 180
Nicolas M, Sophie Y, Reinhart C (2007) Evaluation of leaf traits for indirect selection of high yielding poplar hybrids. Environ Exp Bot 61:103–116
Pliura A, Zhang YS, Mackay J, Bousquet J (2007) Genotypic variation in wood density and growth traits of poplar hybrids at four clonal trials. For Ecol Manag 238:92–106
Safavi SA, Pourdad SA, Mohmmad T, Mahmoud K (2010) Assessment of genetic variation among safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) accessions using agro-morphological traits nand molecular markers. J Food Agric Environ 8:616–625
Sumida A, Miyaura T, Hitoshi T (2013) Relationships of tree height and diameter at breast height revisited: analyses of stem growth using 20-year data of an even-aged Chamaecyparis obtuse stand. Tree Physiol 33:106–118
Yang CP, Liu GF, Wei ZG, Wu YL, Zhou YM (2004) Study on intensive breeding technique of accelerating Betula platyphylla flowering and seeding early. Sci Silvae Sin 40:14–17
Yu QB, Pulkkien P (2003) Genotype-environment interaction and stability in growth of aspen hybrid clones. For Ecol Manag 173:25–35
Zeng J, Zou YP, Bai JY, Zheng HS (2003) RAPD analysis of genetic variation in natural populations of Betula alnoides from Guangxi, China. Euphytica 134:33–41
Zhao XY, Li Y, Zhao L, Wu RL, Zhang ZY (2013) Analysis and evaluation of growth and adaptive performance of white poplar hybrid clones in different sites. J Beijing For Univ 35:7–14
Zhao XY, Bian XY, Li ZX, Wang XW, Yang CP, Liu GF, Jiang J, Kentbayev Y, Kentbayeva B, Yang CP (2014a) Genetic stability analysis of introduced Betula pendula, Bentula kirghisorum, and Betula pubescens families in saline-alkali soil of northeastern china. Scand J For Res 29:619–639
Zhao XY, Bian XY, Liu MR, Li ZX, Li Y, Zheng M, Teng WH, Jiang J, Liu GF (2014b) Analysis of genetic effects on complete diallel cross test of Betula platyphylla. Euphytica 200:221–229
Zhao XY, Hou W, Zheng HQ, Zhang ZY (2014c) Analyses of genotypic variation in white poplar clones at four sites in China. Silvae Genet 62:187–195
Zobel RW, Madison JW, Gauch HG (1988) Statistical analysis of a yield trial. Agron J 80:388–393
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the grants of the National Science and Technology Pillar Program of China (No. 2012BAD21B02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiyang Zhao and Hui Xia have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Xia, H., Wang, X. et al. Variance and stability analyses of growth characters in half-sib Betula platyphylla families at three different sites in China. Euphytica 208, 173–186 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1617-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1617-7