Abstract
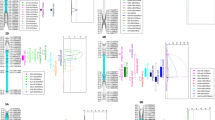
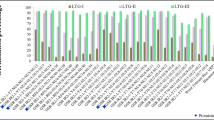
Submergence-induced suppression of seedling vigor is a serious constraint particularly in the direct seeding rice cultivation system. To identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with seedling vigor in rice under submergence, a mapping population of 98 Backcross Inbred Lines derived from a cross of Nipponbare/Kasalath//Nipponbare was used. Phenotypic evaluation of seedling vigor under submergence was based on shoot length (SHL), root length (RTL) and shoot fresh weight (SFW) using a test tube bioassay method. Thirty-two putative QTLs were detected among which 7 were for SHL, 11 for RTL and 14 for SFW. Phenotypic evaluation was also made of the parental lines and a set of 54 chromosome segment substitution lines in which Nipponbare segments were substituted for by their homologous Kasalath segments covering the entire rice genome. Two QTLs with more than 10 % contribution to the total phenotypic variance were verified for SHL, and at least one for RTL and six for SFW on chromosomes 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 at the 1 % significance level. Among these, all but two showed reductions in one, two or all three traits. Our present and previous results suggest that the Nipponbare genome has a potential to improve seedling vigor under submergence and that japonica germplasms can be used to breed for this important trait in indica rice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkhalik AF, Shishido R, Nomura K, Ikehashi H (2005) QTL-based analysis of heterosis for grain shape traits and seedling characteristics in an indica-japonica hybrid in rice. Breed Sci 55:41–48
Bailey PHJ, Currey JD, Fitter AH (2001) The role of root system architecture and root hairs in promoting anchorage against uprooting forces in Alliumcepa and root mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 53:333–340
Bailey-Serres J, Fukao T, Ronald P, Ismail A, Heuer S, Mackill D (2010) Submergence tolerant rice: SUB1’s journey from landrace to modern cultivar. Rice 3:138–147
Banoc DM, Yamauchi A, Kamoshita L, Wade J, Pardales Jr (2000) Genotypic variations in response of lateral root development to fluctuating soil moisture in rice. Plant Prod Sci 3:335–343
Boamfa EI, Ram PC, Jackson MB, Reuss J, Harren FJM (2003) Dynamic aspects of alcoholic fermentation of rice seedlings in response to anaerobiosis and to complete submergence: relationship to submergence tolerance. Ann Bot 91:279–290
Cui KH, Peng SB, Xing YZ, Xu CG, Yu SB, Zhang Q (2002) Molecular dissection of seedling-vigor and associated physiological traits in rice. Theor Appl Genet 105:745–753
Das KK, Sarkar RK, Ismail AM (2005) Elongation ability and non-structural carbohydrate levels in relation to submergence tolerance in rice carbohydrate levels in relation to submergence tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 168:131–136
DeHaan LR, Ehlke NJ, Sheaffer CC (2001) Recurrent selection for seedling vigor in Kura clover. Crop Sci 41:1034–1041
Ella ES, Ismail AM (2006) Seedling nutrient status before submergence affects survival after submergence in rice. Crop Sci 46:1673–1681
Fukao T, Bailey-Serres J (2004) Plant responses to hypoxia—is survival a balancing act? Trends Plant Sci 9:449–456
Fukao T, Bailey-Serres J (2008) Ethylene—a key regulator of submergence responses in rice. Plant Sci 175:43–51
Fukao T, Xu K, Ronald PC, Bailey-Serres J (2006) A variable cluster of ethylene response factor-like genes regulates metabolic and development acclimation responses to submergence in rice. Plant Cell 18:2021–2034
Hattori Y, Nagai K, Ashikari M (2011) Rice growth adapting to deepwater. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:100–105
International Seed Testing Association (ISTA) (1996) http://seedtest.org/en/home.html
Ismail AM, Ella ES, Vergara GV, Mackill DJ (2009) Mechanism associated with tolerance to flooding during germination and early seedling growth in rice (Oryza sativa). Ann Bot 103:197–209
Ito O, Ella E, Kawano N (1999) Physiological basis of submergence tolerance in rainfed lowland rice ecosystem. Field Crop Res 64:75–90
Jackson MB, Ram PC (2003) Physiological and molecular basis of susceptibility and tolerance of rice plants to complete submergence. Ann Bot 91:227–241
Kamolsukyunyong W, Ruanjaichon V, Siangliw M, Kawasaki S, Sasaki T, Vanavichit A, Tragoonrung S (2001) Mapping of quantitative trait locus related to submergence tolerance in rice with aid of chromosome walking. DNA Res 8:163–171
Kamoshita A, Rodriguez R, Yamauchi A, Wade LJ (2004) Genotypic variation in response of rainfed lowland rice to prolonged drought and rewatering. Plant Prod Sci 7:406–420
Lancashire PD, Bleiholder H, van den Boom T, Langeluddeke P, Stauss R, Weber E, Witzenberger A (1991) A uniform decimal code for growth stages of crops and weeds. Ann Appl Biol 119:561–601
Lin SY, Sasaki T, Yano M (1998) Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling seed dormancy and heading date in rice, Oryza sativa L. using backcross inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 96:997–1003
Lu XL, Niu AL, Cai HY, Zhao Y, Liu JW, Zhu YG, Zhang ZH (2007) Genetic dissection of seedling and early vigor in a recombinant inbred line population of rice. Plant Sci 172:212–220
Mackill DJ (ed) (1986) Rainfed lowland rice improvement in South and Southeast Asia: results of a survey. In: Progress in rainfed lowland rice. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos. p 115–144
Manangkil OE, Vu HTT, Yoshida S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2008) A simple, rapid and reliable bioassay for evaluating seedling vigor under submergence in indica and japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 163:267–274
McCouch SR (2008) Gene nomenclature system for rice. Rice 1:72–84
McDonald MB Jr (1993) The history of seed vigour testing. J Seed Technol 17:93–104
Nakagawa H, Yamagishi J, Miyamoto N, Motoyama M, Yano M, Nemoto K (2005) Flowering response of rice to photoperiod and temperature: a QTL analysis using a phonological model. Theor Appl Genet 110:778–786
Perata P, Voesenek LACJ (2007) Submergence tolerance in rice requires Sub1A, an ethylene-response-factor-like gene. Trends Plant Sci 12:43–46
Rahman A, Roytman L, Krakauer NY, Nizamuddin M, Goldberg M (2009) Use of vegetation health data for estimation of aus rice yield. Sensors 9:2968–2975
Ram PC, Singh BB, Singh AK, Ram P, Singh PN, Singh HP, Boamfa EI, Harren FJM, Santosa E, Jackson MB (2002) Submergence tolerance in rainfed lowland rice: physiological basis and prospects for cultivar improvement through marker-aided breeding. Field Crop Res 76:131–152
Redona ED, Mackill DJ (1996) Mapping quantitative trait loci for seedling vigor in rice using RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 92:395–402
Rice Genome Resource Center (2005) Materials for genetic analysis [Online]. Available at http://www.rgrc.dna.affrc.go.jp/stock.html. National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Tsukuba, Japan
Richnaria RH, Misro B (1960) Flood and deep water rices and the future plan of their improvement. Indian Agric 4:135–143
Sasahara T, Ikarashi H, Kambayashi M (1986) Genetic variations in embryo and endosperm weights, seedling growth parameters and α-amylase activity of the germinated grains in rice (Oryza sativa). Jpn J Breed 36:248–261
Setter TL, Laureles EV (1996) The beneficial effect of reduced elongation growth on submergence tolerance of rice. J Exp Bot 47:1551–1559
Siangliw M, Toojinda T, Tragoonrung S, Vanavichit A (2003) Thai jasmine rice carrying QTLch9 (SubQTL) is submergence tolerant. Ann Bot 91:255–261
Suge H (1985) Ethylene and gibberellin: regulation of internodal elongation and nodal root development in floating rice. Plant Cell Physiol 26:607–614
Suralta RR, Inukai Y, Yamauchi A (2008) Utilizing chromosome segment substitution line (CSSLs) for evaluation of root response to transient moisture stresses in rice. Plant Prod Sci 11:457–465
Toojinda T, Siangliw M, Tragoonrung S, Vanavichit A (2003) Molecular genetics of submergence tolerance in rice: QTL analysis of key traits. Ann Bot 91:243–253
Voesenek LACJ, Benschop JJ, Bou J, Cox MCH, Groeneveld HW, Millenaar FF, Vreeburg RAM, Peeters AJM (2003) Interactions between plant hormones regulate submergence-induced shoot elongation in the flooding-tolerant dicot Rumex palustris. AnnBot 91:205–211
Voesenek LACJ, Rijnders JHGM, Peeters AJM, Van de Steeg HM, de Kroon H (2004) Plant hormones regulate fast shoot elongation under water: from genes to communities. Ecology 85:16–27
Voesenek LACJ, Colmer TD, Pierik R, Millenaar FF, Peeters AJM (2006) How plants cope with complete submergence. New Phytol 170:213–226
Vriezen WH, Zhou Z, Van der Straeten D (2003) Regulation of submergence-induced enhanced shoot elongation in Oryza sativa L. Ann Bot 91:263–270
Vu HTT, Manangkil OE, Mori N, Yoshida S, Nakamura C (2009) Submergence-induced adh and aldh gene expression in japonica and indica rice with contrasting levels of seedling vigor under submergence stress. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 23:1469–1473
Vu HTT, Manangkil OE, Mori N, Yoshida S, Nakamura C (2010) Post-germination seedling vigor under submergence and submergence-induced SUB1 gene expression in indica and japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Aust J Crop Sci 4:264–272
Wade LJ, Kamoshita A, Yamauchi A, Azhiri-Sigari T (2000) Genotypic variation in response of rainfed lowland rice to drought and rewatering. I. Growth and water use. Plant Prod Sci 3:173–179
Wang S, Basten CJ, Gaffney P, Zeng ZB (2003) Windows QTL Cartographer Version 2.0. Statistical Genetics. North Carolina State University, USA
Williams JF, Peterson ML (1973) Relation between alpha-amylase activity and growth of rice seedlings. Crop Sci 13:612–614
Won JG, Yoshida T (2000) Screening cultivars at low dissolved oxygen level for water-seeded rice. Plant Prod Sci 3:112–113
Xu K, Mackill D (1996) A major locus for submergence tolerance mapped on rice chromosome 9. Mol Breed 2:219–224
Xu K, Xu X, Fukao T, Canlas P, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Bailey-Serres J, Ronald PC, Mackill DJ (2006) Sub1A is an ethylene-response-factor-like gene that confers submergence tolerance in rice. Nature 442:705–708
Gramene Genes. http://www.gramene.org/db/genes/search_gene?acc=GR:0060043
Zhang ZH, Qu XS, Wan S, Chen LH, Zhu YG (2005) Comparison of QTL controlling seedling vigor under different temperature conditions using recombinant inbred lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ann Bot 95:423–429
Zhou L, Wang JK, Qiong Y, Wang YZ, Zhu YG, Zhang ZH (2007) Quantitative trait loci for seedling vigor in rice under field conditions. Field Crops Res 100:294–301
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. We thank the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, Tsukuba, Japan for kindly providing us with BILs and CSSLs. The experiments comply with the current laws of Japan in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manangkil, O.E., Vu, H.T.T., Mori, N. et al. Mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling seedling vigor in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under submergence. Euphytica 192, 63–75 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0857-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0857-z