Abstract
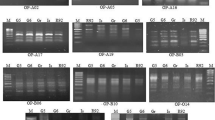
An assessment of genetic diversity studies was undertaken to understand the level and pattern of diversity in 65 mango (Mangifera indica L.) genotypes of India including 20 commercial cultivars, 18 hybrids, 25 local genotypes and two exotic cultivars based on qualitative and quantitative fruit characters as well as RAPD and ISSR profiles. A considerable variation was observed in respect of three important qualitative characters namely table quality, fruit attractiveness and storage life of ripe fruits and potentially superior genotypes for the above traits were identified. A wide variation was noticeable regarding metabolite composition of pulp of ripe mango fruit with respect to total soluble solids, total sugar, reducing sugar, acidity, sugar:acid ratio, ascorbic acid and phenolic content. Fifteen RAPD primers yielded 27 monomorphic and 129 polymorphic bands with percent polymorphism averaging 82.7%. Of a total 70 ISSR bands generated from eight ISSR primers, 60 bands (85.71%) were found to be polymorphic. Cumulative band data from these two methods precisely arranged accessions into eight clusters which correspond well with their pedigree relationship. UPGMA dendrograms drawn using RAPD, ISSR and cumulative data showed highly similar grouping of genotypes on the basis of their parental origin. No clear-cut geographical separation was revealed among East, West, North and South Indian mango cultivars by neither of these molecular markers nor their combinations. This supports the common gene pool origin of mango as well as operation of similar selection pressure as the cultivar preferences in these areas are largely similar.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitchitt M, Thangavelu M, Mantell SH (2000) The reproducibility of RAPD profiles: effect of PCR components on RAPD analysis of date palm DNA. Proc 1st International Conference on Date Palm, United Arab Emirates University Al-Ain, UAE, pp 225-233
A.O.A.C (1990) Official Methods of Analysis. The Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 15th Edn. Arlington, West Virginia, Washington DC, USA, p 1400
Bajpai A, Srivastava N, Rajan S, Chandra R (2008) Genetic diversity and discrimination of mango accessions using RAPD and ISSR markers. Indian J Horticult 65(4):377–382
Bookstein FL (1991) Morphometric tools for landmark data: geometry and biology. Cambridge University Press, New York, p 435
Brown N, Venkatasamy S, Khittoo G, Bahorun T, Jawaheer S (2009) Evaluation of genetic diversity between 27 banana cultivars (Musa spp.) in Mauritius using RAPD markers. Afr J Biotechnol 8(9):1834–1840
Chundet R, Cutler RW, Tasanon M, Anuntalabhochai S (2007) Hybrid detection in Lychee (Litchee chinensis Sonn.) cultivars using HAT-RAPD markers. Sci Asia 33:307–311
Degani C, Rowland LJ, Saunders JA, Hokanson SC, Ogden E, Golan-Goldhirsh A, Galetta GL (2001) A comparison of genetic relationship measures in strawberry (Frageria ananassa Duch.) based on AFLPs, RAPDs and pedigree data. Euphytica 117:1–12
Dehesdtani A, Kazemitabar SK, Rahimian H (2007) Assessment of genetic diversity of navel sweet orange cultivars grown in mazandaran province using RAPD markers. Asian J Plant Sci 6:1119–1124
Devos KM, Gale MD (1992) The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84:567–572
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Gupta M, Chyi YS, Romero-Severson J, Owen JL (1994) Amplification of DNA markers from evolutionarily diverse genomes using simple primers of simple sequence repeats. Theor Appl Genet 18:44–48
Harris SA (1999) RAPDs in systematics—a useful methodology ? In: Hollingsworth PM, Bateman RM, Gornall RJ, Taylor and Francis (eds), Molecular systematics and plant evolution. London, pp 211–228
Hemanth KNV, Vasanthaiah N (2009) Paternity analysis of mango (Mangifera indica L.) hybrids with their parents. Int J Fruit Sci 9(1):1–10
Ishtiaq AR, Nabila T, Aman UM, Saeed AM, Mehboob-ur-Rahmanc Yusuf Z (2008) Assessment of genetic diversity among mango (Mangifera indica L.) genotypes using RAPD markers. Sci Horti 117(3):297–301
Karihaloo JL, Dwivedi YK, Archak S, Gaikwad AB (2003) Analysis of genetic diversity of Indian mango cultivars using RAPD markers. J Hort Sci Biotech 78:285–289
Krishna H, Singh SK (2007) Biotechnological advances in mango (Mangifera indica L.) and their future implication in crop improvement. Biotechnol Adv 25:223–243
Mantel N (1967) The deduction of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Mitra S, Tarafdar J (2006) Nutritional assessment of some mango varieties grown in West Bengal. Abs. International conference on biotechnology approaches for alleviating malnutrition and human health. University of Agriculture Science, Bangalore, India, p 175
Pandey KK, Kumar N (2007) Quality characters of some mango hybrids at Sabour. Hortic J 18(2):84–85
Pandit SS, Mitra S, Giri AP, Pujari KH, Patil PB (2007) Genetic diversity analysis of mango cultivars using inter simple sequence repeat markers. Curr Sci 93(8):1135–1141
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A (1996) The comparison of RAPD, ISSR, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2:225–238
PPV, FRA (2008) Guidelines for the conduct of tests for distinctness, uniformity, stability of mango (Mangifera indica L.), protection of plant varieties and farmers’ right authority, Ministry of Agriculture, Govt of India, New Delhi, India, pp 17
Ram S, Rajan S (2003) Status report on genetic resources of mango in Asia-Pacific region. IPGRI office for South Asia, New Delhi, India, pp 64–68
Ranganna S (1986) Handbook of analysis and quality control for fruit and vegetable products. Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company, New Delhi, India, p 1152
RI IPG (1989) Descriptors for mango (Mangifera indica L.). International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Rome, Italy, p 21
RI IPG (2006) Descriptors for mango (Mangifera indica L.). International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Rome, Italy, p 45
Ribeiro SMR, Queiroz JH, Ribeiro MEL, Campos FM, Sant’Ana HMP (2007) Antioxidant in mango (Mangifera indica L.) pulp. Plant Food Human Nutr 62(1):13–17
Rohlf FJ (1993) NTSYS pc Numerical taxonomy and multivariate system Ver. 21 Exeter Publ Ltd, Setauket, New York
Samal KC (2011) Studies on genetic diversity of mango (Mangifera indica L.) using morphological, biochemical and molecular markers and development of protocol for mass propagation through in vitro culture. PhD Thesis, Utkal University, India, p 132
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Springer Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, Vol 1–3, p 1659
Singh S, Gaikwad AB, Karihaloo JL (2009) Morphological and molecular analysis of intracultivar variation in Indian mango (Mangifera indica L.) cultivars. Acta Horti 829:205–212
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. Freeman, San Fransisco, p 573
Srivastava AP, Chandra R, Saxena S, Ranjan S, Ranade S, Prasad V (2007) A PCR based assessment of genetic diversity and parentage analysis among commercial mango cultivars and hybrids. J Hortic Sci Biotech 82:951–959
Sulan L, Puchao He, Xueqin Z, Peng Z (2002) Inheritance of RAPD markers in an interspecific F1 hybrid of grape between Vitis quinquangularis and V. vinifera. Sci Horti 93:19–28
Uddin MZ, Rahim MA, Alam MA, Barman JC, Wadud MA (2006) A Study on the physical characteristics of some mango germplasms grown in Mymensingh condition. Int J Sustain Crop Prod 1(2):33–38
Uzun A, Gulsen O, lu TY, Aka-Ka Y, Tuzcu O (2010) Distinguishing grapefruit and pummelo accessions using ISSR markers. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 46(4):170–177
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucl Acid Res 18:7213–7218
Williams JGK, Hanafey MK, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1993) Genetic analysis using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Methods Enzymol 218:704–741
Wolff K, Schoen ED, Peters-Van RJ (1993) Optimizing the generation of random amplified polymorphic DNAs in chrysanthemum. Theor Appl Genet 86:1033–1037
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Acknowledgments
Financial assistance received through a project grant from the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperation, Govt. of India, New Delhi is duly acknowledged. We wish to thank Dr. Jatindra K. Nayak, Professor of English, Utkal University, Bhubaneswar (India) for going through the manuscript and making useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samal, K.C., Jena, R.C., Swain, S.S. et al. Evaluation of genetic diversity among commercial cultivars, hybrids and local mango (Mangifera indica L.) genotypes of India using cumulative RAPD and ISSR markers. Euphytica 185, 195–213 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0522-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0522-y