Abstract
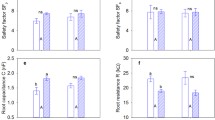
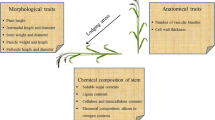
Lodging results in serious yield and quality reductions in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Among summer crops, foxtail millet is a high density and soft stalked crop that is prone to lodging. Field selection for lodging resistance is difficult because the occurrence of lodging depends on the environmental conditions. A practical method for the evaluation of lodging is not available for foxtail millet, so an understanding of lodging-associated traits and identifying a suitable method to assess lodging are essential to select for lodging resistance and to predict the risk of lodging in a cultivar. In the present study, six stem and root traits associated with lodging was measured in the field and lodging coefficients were determined to evaluate lodging resistance in landrace and improved cultivars. Based on the results of correlation analysis, lodging coefficient is a suitable indicator for field selection for lodging resistance in both classes of cultivars tested for breeding purpose. Statistical analyses demonstrated that lodging was associated with stem quality rather than plant height and internode length at the stem base. The most important trait that directly impacted on lodging coefficient was mechanical strength of the stem and plant height in the landraces, while the weights of the above- and under-ground tissues, in combination with mechanical strength of the stem, were the most important contributors to lodging coefficient in the improved cultivars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker CJ, Berry PM, Spink JH, Sylvester-Bradley R, Griffin JM, Scott RK, Clare RW (1998) A method for the assessment of the risk of wheat lodging. J Theor Biol 194:587–603
Berry PM, Spink JH, Sterling M, Pickett A (2003a) A comparison of root and stem lodging risks among winter wheat cultivars. J Agric Sci 141:191–202
Berry PM, Spink JH, Sterling M, Pickett A (2003b) Methods for rapidly measuring the lodging resistance of wheat cultivars. J Agron Crop Sci 189:390–401
Berry PM, Sterling M, Spink JH, Baker CJ, Sylvester-Bradley R, Mooney SJ, Tams, Ennos AR (2005) Understanding and reducing lodging in cereals. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advance in agronomy. Academic Press, Salt Lake City, pp 218–263
Crook MJ, Ennos AR (1994) Stem and root characteristics associated with lodging resistance in four winter wheat cultivars. J Agric Sci 123:167–174
Harlan JR (1975) Crops and man. ASA, Inc, Madison, pp 150–189, Chapter 7
Huang ZW, Zhao TJ, Yu DY, Chen SY, Gai JY (2008) Lodging resistance indices and related QTLs in soybean. Acta Agron Sin 34:605–611
Ibrahim M, Erskine W, Hanti G, Fares A (1993) Lodging in lentil as affected by plant population, soil moisture, and genotype. Exp Agric 29:201–206
Inoue M, Gao ZS, Cai HW (2004) QTL analysis on lodging resistance and related traits in Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1576–1585
Jezowski S (1981) Variation, correlation and heritability of characters determining lodging of spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). II. Analysis of relationship between lodging grade and some morphological characters of spring barley varieties. Genet Pol 22:45–61
Kelbert AJ, Spaner D, Griggs KG, King JR (2004) Screening for lodging resistance in spring wheat breeding programmes. Plant Breed 123:349–354
Li Y, Wu SZ (1996) Traditional maintenance and multiplication of foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv) landraces in China. Euphytica 87:33–38
Li Y, Wu SZ, Cao YS, Zhang XZ (1996) A phenotypic diversity analysis of foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv) landraces of Chinese origin. Genet Resour Crop Evol 43:377–384
Pu DF, Zhou JR, Li BF, Li Q, Zhou Q (2000) Evaluation method of root lodging resistance in wheat. Acta Agric Boreali-Occidentalis Sin 9:58–61
Sakata I, Sakai M, Imbe T (2003) The correlation of the resistance to root lodging with growth angle, diameter and pulling strength of grown roots in rice seedlings. Jpn J Crop Sci 72:56–61
Sterling M, Baker CJ, Wade A (2003) An experimental investigation of the lodging of wheat. Agric Forest Meteorol 119:149–165
Terashima K, Sakai K, Kabaki N (2002) Relationship between biomass of an individual hill and root lodging tolerance in direct seeded rice. Jpn J Crop Sci 71:161–168
Tian BH, Wang SY, Li YJ, Wang JG, Zhang LX, Liang FQ, Zhai YZ, Liu JR (2008) Response to sodium chloride stress at germination and seedling and identification of salinity tolerance genotypes in foxtail millet landraces originated from China. Acta Agron Sin 34:2218–2222
Tottman DR (1987) The decimal code for the growth stages of cereals, with illustrations. Ann Appl Biol 110:441–454
Wang Y, Du JL (2001) Evaluation method of root lodging resistance and its path analysis in barley. Acta Agron Sin 27:941–945
Acknowledgments
The financial support provided by the Ministry of Agriculture of China (no. 2006BAD02B02-01-04) is gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, B., Wang, J., Zhang, L. et al. Assessment of resistance to lodging of landrace and improved cultivars in foxtail millet. Euphytica 172, 295–302 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-009-9999-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-009-9999-z