Abstract
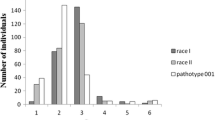
The objective of this study was to identify polymorphic molecular markers associated with partial resistance to coffee leaf rust, Hemileia vastarix. A segregating F 2 population derived from a cross between the susceptible Coffea arabica cv. Caturra and a C. canephora-introgressed Arabica line exhibiting high partial resistance was analyzed. Rust resistance measured as rust incidence (RI) and defoliation (DEF) was evaluated in field conditions in three consecutive years (2003–2005). During the 2003 season, which was characterized by favorable conditions for a rust epidemic, the F 2 plants exhibited different levels of resistance ranging from very susceptible (50.1% for DEF and 49.5% for RI) to highly partial resistance (9.1% for DEF and 3.7% for RI). Molecular analysis enabled identification of seven polymorphic markers (5 AFLP and 2 SSR) exhibiting significant association with partial resistance. Coexistence of resistance homozygous alleles (RR) at codominant SSR loci was correlated with high resistance. This study is the first attempt to develop PCR-based sequence specific markers linked to partial rust resistance in coffee.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarado G (2005) Evolution of Hemileia vastatrix virulence in Colombia. In: Zambolim L, Zambolim EM, Várzea VMP (eds) Durable resistance to coffee leaf rust. UFV Viçosa, Brasil, pp 99–115
Alvarado G, Castillo J (1996) Progreso de la roya del cafeto sobre genotipos resistentes y susceptibles a Hemileia vastatrix. Cenicafe 47:42–52
Alvarado G, Moreno LG, Cortina H (2002) Caracteres agronómicos y resistencia incompleta a Hemileia vastatrix de progenies da Caturra x Híbrido de Timor. Cenicafe 53:7–24
Baruah A, Naik V, Hendre PS, Rajkumar R, Rajendrakumar P, Aggarwal RK (2003) Isolation and characterization of nine microsatellite markers from Coffea arabica L., showing wide cross-species amplifications. Mol Ecol Notes 3:647–650. doi:10.1046/j.1471-8286.2003.00544.x
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng ZB (1997) QTL cartographer: a reference manual and tutorial for QTL mapping. Department of Statistics, NC State Univ Raleigh
Bernatsky R, Tanksley S (1986) Toward saturated linkage map in tomato based on isoenzymes and random cDNA sequences. Genetics 112:887–898
Bettencourt AJ (1983) Caracteristicas agronómicas de selecçoes derivadas de cruzamentos entre Híbrido de Timor e as variedades Caturra, Villa Sarchi e Catuaí. In: Simpósio sobre Ferrugens do Cafeeiro, Oeiras, Portugal, 373 pp
Bettencourt AJ, Rodrigues CJ Jr (1988) Principles and practice of coffee breeding for resistance to rust and other diseases. In: Clarke RJ, Macrae R (eds) Coffee, vol 4. Elsevier, London, pp 199–234
Bhat PR, Krishnakumar V, Hendre PS, Rajendrakumar P, Varshney RK, Aggarwal RK (2005) Identification and characterization of expressed sequence tags-derived simple sequence repeat markers from robusta coffee variety ‘C × R’ (an interspecific hybrid of Coffea canephora × Coffea congensis). Mol Ecol Notes 5:80–83. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2004.00839.x
Castillo J, Alvarado G (1997) Resistencia incompleta de genotipos de café a la roya bajo condiciones de campo en la region central de Colombia. Cenicafe 48:40–58
Chaimovitsh D, Didai N, Putievsky E (2006) Inheritance of resistance to Fusarium wilt in sweet Brasil. Plant Dis 90:58–60. doi:10.1094/PD-90-0058
Combes MC, Andrzejewski S, Anthony F, Bertrand B, Rovelli P, Graziosi MC, Lashermes P (2000) Characterization of microsatellite loci in Coffea arabica and related coffee species. Mol Ecol 9:1178–1180. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.00954-5.x
Eskes AB (1983) Incomplete resistance to coffee leaf rust. PhD thesis, Agricultural University of Wageningen, Landbouwhogeschool, p 135
Eskes AB (1989) Resistance. In: Kushalappa AC, Eskes AB (eds) Coffee rust: epidemiology, resistance, management, chap 6. CRC Press, Boca Raton USA, pp 171–291
Eskes AB (2005) Phenotypic expression of resistance to coffee leaf rust and its possible relationship with durability. In: Zambolim L, Zambolim EM, Várzea VMP (eds) Durable resistance to coffee leaf rust. UFV Viçosa, Brasil, pp 305–332
Eskes AB, Souza EA (1981) Ataque da ferrugem em ramos com e sem produçao de plantas do cultivar Catuai. IX Congr Bras Pesq Caf, IBC, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, p 186
Fjellstrom R, McClung AM, Shank AR (2006) SSR markers closely linked to the Pi-z locus are useful for selection of blast resistance in a broad array of rice germplasm. Mol Breed 17:149–157. doi:10.1007/s11032-005-4735-4
Flor HH (1942) Inheritance of pathogenicity in Melampsora lini. Phytopathology 32:653–669
Jafary H, Szabo LJ, Niks RE (2006) Innate nonhost immunity in barley to different heterologous rust fungi is controlled by sets of resistance genes with different and overlapping specificities. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:1270–1279. doi:10.1094/MPMI-19-1270
Julio E, Verrier JL, de Borne DF (2006) Development of SCAR markers linked to three disease resistances based on AFLP within Nicotiana tabacum L. Theor Appl Genet 112:335–346. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0132-y
Lander SE, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M, Lincoln S, Newburg L (1987) Mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genetics 1:174–181
Lashermes P, Agwnada CO, Anthony F, Combes MC, Trouslot P, Charrier A (1997) Molecular marker-assisted selection: a powerful approach for coffee improvement. In: Proceedings of the 13th international conference on coffee science (ASIC), Nairobi, pp 474–480
Lashermes P, Andrzejewski S, Bertrand B, Combes MC, Dussert S, Graziosi G, Trouslot P, Anthony F (2000) Molecular analysis of introgressive breeding in coffee (Coffea arabica L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:139–146. doi:10.1007/s001220050019
Lefèvre F, Goué-Mourier MC, Faivre-Rampant P, Villar M (1998) A single gene cluster controls incompatibility and partial resistance to various Melampsora larici-populina races in hybrid poplars. Phytopathology 88:156–163. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.1998.88.2.156
Lillemo M, Skinnes H (2006) Genetic analysis of partial resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat line Saar. Plant Dis 90:225–228. doi:10.1094/PD-90-0225
Lin C, Mueller LA, McCarthy J, Crouzillat D, Pétiard V, Tanksley SD (2005) Coffee and tomato share common gene repertoires as revealed by deep sequencing of seed and cherry transcripts. Theor Appl Genet 112:114–130. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0112-2
Mahé L, Combes MC, Lashermes P (2007) Comparison between a coffee single copy chromosomal region and Arabidopsis duplicated counterparts evidenced high level synteny between the coffee genome and the ancestral Arabidopsis genome. Plant Mol Biol 64:699–711. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9191-6
Mahé L, Combes MC, Varzea VMP, Guilhaumon C, Lashermes P (2008) Development of sequence characterized DNA markers linked to leaf rust (Hemileia vastatrix) resistance in coffee (Coffea arabica L.). Mol Breed 21:105–113. doi:10.1007/s11032-007-9112-z
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.21.9828
Mienie CMS, Fourie H, Smit MA, Van Standen J, Botha FC (2002) Identification of AFLP markers in soybean linked to resistance to Meloidogyne javanica and conversion to sequence characterized amplified regions (SCARs). Plant Growth Regul 37:57–166. doi:10.1023/A:1020585023976
Moncada P, McCouch S (2004) Simple sequence repeat diversity in diploid and tetraploid Coffea species. Genome 47:501–509. doi:10.1139/g03-129
Poncet V, Hamon P, Minier J, Carasco C, Hamon S, Noirot M (2004) SSR cross-amplification and variation within coffee trees (Coffea spp.). Genome 47:1071–1081. doi:10.1139/g04-064
Prakash NS, Combes MC, Naveen KS, Lashermes P (2002) AFLP analysis of introgression in coffee cultivars (Coffea arabica L.) derived from a natural interspecific hybrid. Euphytica 124:265–271. doi:10.1023/A:1015736220358
Prakash NS, Marques DV, Varzea VMP, Silva MC, Combes MC, Lashermes P (2004) Introgression analysis of a leaf rust resistance gene from Coffea liberica into C. arabica. Theor Appl Genet 109:1311–1317. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1748-z
Qi X, Niks RE, Stam P, Lindhout P (1998) Identification of QTLs for partial resistance to leaf rust (Puccinia hordei) in barley. Theor Appl Genet 96:1205–1215. doi:10.1007/s001220050858
Rivillas CA, Leguizamón JE, Gil LF, Duque H (2005) Recomendaciones para el manejo de la roya en Colombia. Boletin técnico No 19, Cenicafe—Gerencia técnica FNC, Colombia, p 36
Rodriguez CJ Jr, Bettencourt AJ, Rijo L (1975) Races of pathogen and resistance to coffee rust. Ann Rev Phytopathol 13:49–70. doi:10.1146/annurev.py.13.090175.000405
Schuster I, Damiao-Cruz C (2004) Estatistica genómica aplicada a populaçoes derivadas de cruzamentos controlados. UFV Editora, Vicosa, pp 348–390
Silva MC, Várzea V, Guimaraes LG, Azinheira HG, Fernandez D, Petitot AS, Bertrand B, Lashermes P, Nicole M (2006) Coffee resistance to the main diseases: leaf rust and coffee berry disease. Braz J Plant Physiol 18:119–147. doi:10.1590/S1677-04202006000100010
Silva-Acuña R, Maffia LA, Zambolim L, Berger RD (1999) Incidence-severity relationship in the pathosystem Coffea arabica-Hemileia vastatrix. Plant Dis 83:186–188. doi:10.1094/PDIS.1999.83.2.186
Suenaga K, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, William HM (2003) Microsatellite markers for genes Lr34/Yr18 and other quantitative trait loci for leaf rust and stripe rust resistance in bread wheat. Phytopathology 93:881–890. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.2003.93.7.881
Van der Vossen HAM (2001) Coffee breeding practices. In: Clarke RJ, Vitzthum OG (eds) Coffee: recent developments. Oxford-Balckwell Science, UK, pp 184–201
Van der Vossen HAM (2005) State-of-the-art of developing durable resistance to biotrophic pathogens in crop plants, such as coffee leaf rust. In: Zambolim L, Zambolim EM, Várzea VMP (eds) Durable resistance to coffee leaf rust. UFV Viçosa, Brasil, pp 1–30
Zambolim L, Vale FXR, Pereira AA, Chaves GM (1999) Manejo integrado das doenças do cafeeiro. In: Zambolim L (ed) Produçao de café com qualidades. UFV Viçosa, Brasil, pp 134–215
Zhang ZJ, Yang GH, Li GH, Jin SL, Yang XB (2001) Transgresive segregation, heritability, and number of genes controlling durable resistance to stripe rust in one Chinese and two Italian wheat cultivars. Phytopathology 91:680–686. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.2001.91.7.680
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development of Colombia through a collaborative project between the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD, France) and the National Center of Coffee Research (CENICAFE, Colombia). We are grateful to JC Montoya and O Taborda for technical assistance. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for helpful comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera P., J.C., Alvarado A., G., Cortina G., H.A. et al. Genetic analysis of partial resistance to coffee leaf rust (Hemileia vastatrix Berk & Br.) introgressed into the cultivated Coffea arabica L. from the diploid C. canephora species. Euphytica 167, 57–67 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9860-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9860-9