Abstract
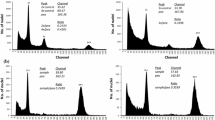
The possibility to induce embryo development after pollination of F1 interspecific cotton hybrids (Gossypium barbadense × Gossypium. hirsutum) with pollen from Abelmoschus esculentus was investigated to determine if wide-cross hybrid, haploid or other types of progeny might result. Small numbers of progeny (Pa) were indeed recovered after numerous alien pollinations and in-planta development or in-vitro culture. The Pa plants were characterized phenotypically and studied cytogenetically and microscopically to help establish their origin documenting their reproductive basis. Root-tip chromosome counts and meiotic Metaphase-I analyses revealed that chromosome numbers among cells of the Pa plants ranged from 33 to 44 and that the differences in chromosome number among cells of the same plant ranged from 1 to 3, indicating somatic instability. Flow cytometric analysis also indicated the aneuploid nature of Pa plants. Although the reproductive mechanisms need to be characterized more extensively by cytological and molecular means, the observations suggest that alien pollinations may have resulted in parthenogenetic (Pa) egg cell development, or some other unusual reproductive events. The production of wide-crosses and high degrees of aneuploidy could be of use for several types of genomic studies, e.g., functional genomic characterization of genome shock, deletion mapping, and germplasm introgression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajaj YPS, Gill MS (1996) In-vitro induction of haploidy in cotton. In: Jain SM, Sopory SK, Veilleux RE (eds) In-vitro haploid production in higher plants. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 165–174
Brown MS (1947) A case of spontaneous reduction of chromosome number in somatic tissue of cotton. Am J Botany 34:384–388
Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (2001) RFLP diversity in cotton. In: Jenkins JN, Saha S (eds) Genetic improvement of cotton, emerging technologies. Science Publisher, Inc, Enfield, NH, pp 81–101
Galanopoulou-Sendouca S, Roupakias D (1999) Performance of cotton F1 hybrids and its relation to the mean yield of advanced bulk generations. Eur J Agron 11:53–62
Gao W, Chen ZJ, Yu JZ, Raska D, Kohel RJ, Womack JE, Stelly DM (2004) Wide-Cross whole-genome radiation hybrid mapping of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Genetics 167:1317–1329
Goodin JR, Trolinder NL (1990) The in-vitro production of cotton (Gossypium) fibers. VIIth interantional congress on plant tissue and cell culture, Amsterdam, June 24–29
Kohel RJ, Endrizzi JE, White TG (1977) An evaluation of Gossypium barbadense L. chromosomes 6 and 17 in the G. hirsutum L. genome. Crop Sci 17:404–406
Lacape JM, Nguyen TB, Courtois B, Belot JL, Giband M, Gourlot JP, Gawryziak G, Roques S, Hau B (2005) QTL analysis of cotton fiber quality using multiple Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense backcross generations. Crop Sci 45:123–140
Martin FM (1959) Staining and observing pollen tubes by means of fluorescence. Stain Technol 34:436–437
Mavromatis AG, Roupakias DG (1994) Biotechnology: A hope for a partial interspecific hybrid in cotton (Gossypium spp.). In: Peeters MC (ed) Cotton biotechnology. Proceedings of a meeting of the working group on cotton biotechnology. Leuven, Belgium, 22–23 October 1993. FAO, Rome, 1994. FAO-Technical Series 32:29–36
Mavromatis AG, Roupakias DG (1995) Haploid production via intergenetic pollination and inovule culture in cotton (Gossypium spp.). Proceedings 2nd meeting of the WG Cotton biotechnology of the FAO-Int. cooperative res network on cotton, 31st March and 1st April 1995, Thessaloniki, Greece, pp.179–184
Mavromatis AG, Kantartzi SK, Vlachostergios DN, Xynias IN, Skarakis GN, Roupakias (2005) Induction of embryo development and fixation of partial Interspecific lines after pollination of F1 cotton interspecific hybrids (Gossypium barbadense × Gossypium hirsutum) with pollen from Hibiscus cannabinus. Aust J Agric Res (accepted Volume 10, October 2005)
Natsiou-Vozike T, Roupakias DG, Galanopoulou-Sendouca S, Tsaftaris A (1988) Interspecific hybrids between Gossypium hirsutum L. and Gossypium barbadense L. in the F1 and the following generations. Proc second meeting of the Greek Plant Breed Soc, 20–21 October 1988, Thessaloniki, pp 267–273
Paterson AH, Smith R (1999) Future horizons: Biotechnology for cotton imporvement, In: Smith CW, Cothren JT (eds) Cotton. origin, history, technology and production. John Wiley & sons, New York p. 415–432
Roupakias DG, Gouli-Vavdinoudi E, Koutsika-Sotiriou M, Galanopoulou S, Mavromatis AG (1998) “Heterosis in Cotton” In: Bajaj YSP (ed) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry, vol 42. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 140–172
Saha S, Wu J, Jenkins JN, McCarty JC, Gutierrez Jr OA, Stelly DM, Percy RG, Raska DA (2004) Effect of chromosome substitutions from Gossypium barbadense L. 3–79 into G.hirsutum L. TM-1 on agronomic and fiber traits. J Cotton Sci 8:162–169
Stewart JMcD, Hsu CL (1978) Hybridization of diploid and tetraploid cottons through in ovule embryo culture. J Hered 69:404–408
Susin I, Alvarez JM (1997) Fertility and pollen tube growth in polyploid melons (Cucumis melo L.). Euphytica 93:369–373
Turaev AM, Shamina ZB (1986) Optimization of the medium for cotton anther culture. Sov Plant Physiol 33:439–444
Vroh Bi I, Baudoin JP, Hau B, Mergeai G (1999) Development of high gossypol cotton plants with low gossypol seeds using trispecies bridge crosses and in-vitro culture of seed embryos. Euphytica 106:243–251
White TG, Richmond TR, Lewis CF (1967) Use of cotton monosomes in developing interspecific substitution lines. Crops Research, ARS 34–91. pp 3–15
Wise RR, Sassenrath-Cole GF, Percy R (2000) A comparison of leaf anatomy in field-grown Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense. Ann Bot 86:731–738
Zhou SQ (2003) Viewing the difference between the diploid and the polyploid in the light of the upland cotton aneuploid. Hereditas 138:65–72
Zhou SQ, Qian DQ, Cao XY (1991) Induction of parthenogenesis and chromosome behavior in plants of parthenogenetic origin in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Genome 34:255–260
Zhou SQ, Qian DQ, Cao XY (1992) Inheritance of characters and chromosome number in aneusomatic progeny of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) of parthenogenetic origin. Genome 35:35–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kantartzi, S., Roupakias, D.G. Production of aneuploids of the cotton hybrid G. barbadense × G. hirsutum L. via intergeneric pollination with Abelmoschus esculentus . Euphytica 161, 319–327 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9550-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9550-z