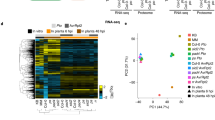
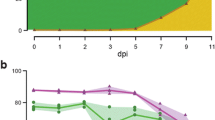
Summary
The use of in silico and in vivo transcriptomic tools have revolutionized the way biological processes are studied. These technologies provide a global approach that is well suited for the analysis of plant–pathogen interactions, in which complex gene networks are regulated. Most of the available studies involving gene arrays were reported in Arabidopsis thaliana, but recent evidence showed that the information gained on this model plant may not always be extrapolated to legumes. Transcriptomic data generated specifically from legume–pathogen pathosystems are therefore needed to improve our understanding of the mechanisms underlying resistance of host plants and pathogenicity of their invaders. This review focuses on the few available studies that describe the characterisation of compatible or incompatible interactions between legumes and parasites through transcriptomic approaches, and summarizes various strategies that can increase our knowledge in this domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- dpi:
-
day post inoculation
- DGE:
-
differential gene expression
- ET:
-
ethylene
- EST:
-
expressed sequence tag
- hpi:
-
hour post inoculation
- JA:
-
jasmonic acid
- LOX:
-
lipoxygenase
- SA:
-
salicylic acid
- SAR:
-
systemic acquired resistance
- SDS:
-
sudden death symptom
- SSH:
-
suppression subtractive hybridization
- TC:
-
tentative consensus sequence
References
Asamizu, E., Y. Nakamura, S. Sato & S. Tabata, 2004. Characteristics of the Lotus Japonicus gene repertoire deduced from large-scale expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis. Plant Mol Biol 54: 405–414.
Birch, P.R.J. & S. Kamoun, 2000. Studying interaction transcriptomes: coordinated analyses of gene expression during plant–microorganism interactions. In: E.S.R. Wood (Ed.), New Technologies for Life Sciences: A Trends Guide, pp. 77–82. Elsevier Science, London.
Borevitz, J.O., D. Liang, D. Plouffe, H.S. Chang, T. Zhu, D. Weigel, C.C. Berry, E. Winzeler & J. Chory, 2003. Large-scale identification of single-feature polymorphisms in complex genomes. Genome Res 13: 513–523.
Brazma, A., P. Hingamp, J. Quackenbush, G. Sherlock, P. Spellman, C. Stoeckert, J. Aach, W. Ansorge, C.A. Ball, H.C. Causton, T. Gaasterland, P. Glenisson, F.C. Holstege, I.F. Kim, V. Markowitz, J.C. Matese, H. Parkinson, A. Robinson, U. Sarkans, S. Schulze-Kremer, J. Stewart, R. Taylor, J. Vilo & M. Vingron, 2001. Minimum information about a microarray experiment (MIAME)-toward standards for microarray data. Nat Genet 29: 365–371.
Broughton, W.J., G. Hernandez, M. Blair, S. Beebe, P. Gepts & J. Vanderleyden, 2003. Beans (Phaseolus spp.); model food legumes. Plant Soil 252: 55–128.
Buckhout, T.J. & O. Thimm, 2003. Insights into metabolism obtained from microarray analysis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6: 288–296.
Cheong, Y.H., H.S. Chang, R. Gupta, X. Wang, T. Zhu & S. Luan, 2002. Transcriptional profiling reveals novel interactions between wounding, pathogen, abiotic stress, and hormonal responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129: 661–677.
Cho, S. & F.J. Muehlbauer, 2004. Genetic effect of differentially regulated fungal response genes on resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 64: 57–66.
Cluzet, S., C. Torregrosa, C. Jacquet, C. Lafitte, J. Fournier, L. Mercier, S. Salamagne, X. Briand, M.T. Esquerre-Tugaye & B. Dumas, 2004. Gene expression profiling and protection of Medicago truncatula against a fungal infection in response to an elicitor from green algae Ulva spp. Plant Cell Environ 27: 917–928.
Colebatch, G., S. Kloska, B. Trevaskis, S. Freund, T. Altmann & M.K. Udvardi, 2002. Novel aspects of symbiotic nitrogen fixation uncovered by transcript profiling with cDNA arrays. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15: 411–420.
Constantin, G.D., B.N. Krath, S.A. MacFarlane, M. Nicolaisen, I. Elisabeth Johansen & O.S. Lund, 2004. Virus-induced gene silencing as a tool for functional genomics in a legume species. Plant J 40: 622–631.
Cook, D.R., 1999. Medicago truncatula, a model in the making! Curr Opin Plant Biol 2: 301–304.
d’Erfurth, I., V. Cosson, A. Eschstruth, H. Lucas, A. Kondorosi & P. Ratet, 2003. Efficient transposition of the Tnt1 tobacco retrotransposon in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant J 34: 95–106.
Diatchenko, L., Y.F. Lau, A.P. Campbell, A. Chenchik, F. Moqadam, B. Huang, S. Lukyanov, K. Lukyanov, N. Gurskaya, E.D. Sverdlov & P.D. Siebert, 1996. Suppression subtractive hybridization: A method for generating differentially regulated or tissue-specific cDNA probes and libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 6025–6030.
Dixon, R.A., L. Achnine, P. Kota, C.-J. Liu, M.S.S. Reddy & L. Wang, 2002. The phenylpropanoid pathway and plant defence – a genomic perspective. Mol Plant Pathol 3: 371–390.
Donson, J., Y. Fang, G. Espiritu-Santo, W. Xing, A. Salazar, S. Miyamoto, V. Armendarez & W. Volkmuth, 2002. Comprehensive gene expression analysis by transcript profiling. Plant Mol Biol 48: 75–97.
El Yahyaoui, F., H. Kuster, B. Ben Amor, N. Hohnjec, A. Puhler, A. Becker, J. Gouzy, T. Vernie, C. Gough, A. Niebel, L. Godiard & P. Gamas, 2004. Expression profiling in Medicago truncatula identifies more than 750 genes differentially expressed during nodulation, including many potential regulators of the symbiotic program. Plant Physiol 136: 3159–3176.
Eulgem, T., V.J. Weigman, H.-S. Chang, J.M. McDowell, E.B. Holub, J. Glazebrook, T. Zhu & J.L. Dangl, 2004. Gene expression signatures from three genetically separable resistance gene signaling pathways for downy mildew resistance. Plant Physiol 135: 1129–1144.
Fedorova, M., J. van de Mortel, P.A. Matsumoto, J. Cho, C.D. Town, K.A. VandenBosch, J.S. Gantt & C.P. Vance, 2002. Genome-wide identification of nodule-specific transcripts in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 130: 519–537.
Foster-Hartnett, D., S. Penuela, D. Danesh, K.A. Sharapova, K.A. VandenBosch, N.D. Young & D.A. Samac, 2004. Histochemical and transcriptome analysis of the interactions between Medicago truncatula and the pathogens Colletotrichum trifolii and Erisyphe pisi. Legumes for the benefit of agriculture, nutrition and the environment. In: Proceedings of Second International Conference on Legume Genomics and Genetics, 7–11 June 2004, Dijon, p. 239.
Gamas, P., F. de Billy & G. Truchet, 1998. Symbiosis-specific expression of two Medicago truncatula nodulin genes, MtN1 and MtN13, encoding products homologous to plant defense proteins. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11: 393–403.
Graham, M.A., K.A.T. Silverstein, S.B. Cannon & K.A. VandenBosch, 2004. Computational identification and characterization of novel genes from legumes. Plant Physiol 135: 1179–1197.
Green, C.D., J.F. Simons, B.E. Taillon & D.A. Lewin, 2001. Open systems: Panoramic views of gene expression. J Immunol Methods 250: 67–79.
Hammond-Kosack, K.E. & J.E. Parker, 2003. Deciphering plant–pathogen communication: Fresh perspectives for molecular resistance breeding. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14: 177–193.
Handberg, K. & J. Stougaard, 1992. Lotus japonicus, an autogamous, diploid legume species for classical and molecular genetics. Plant J 2: 487–492.
Harmer, S.L. & S.A. Kay, 2000. Microarrays: Determining the balance of cellular transcription. Plant Cell 12: 613–616.
Hays, D.B. & D.Z. Skinner, 2001. Development of an expressed sequence tag (EST) library for Medicago sativa. Plant Sci 161: 517–526.
Hazen, S.P. & S.A. Kay, 2003. Gene arrays are not just for measuring gene expression. Trends Plant Sci 8: 413–416.
Hofte, H., T. Desprez, J. Amselem, H. Chiapello, P. Rouze, M. Caboche, A. Moisan, M.F. Jourjon, J.L. Charpenteau, P. Berthomieu, et al., 1993. An inventory of 1152 expressed sequence tags obtained by partial sequencing of cDNAs from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 4: 1051–1061.
Huitema, E., V.G.A.A. Vleeshouwers, D.M. Francis & S. Kamoun, 2003. Active defence responses associated with non-host resistance of Arabidopsis thaliana to the oomycete pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Mol Plant Pathol 4: 487–500.
Iqbal, M., S. Yaegashi, V. Njiti, R. Ahsan, K. Cryder & D. Lightfoot, 2002. Resistance locus pyramids alter transcript abundance in soybean roots inoculated with Fusarium solani f.sp. glycines. Mol Genet Genomics 268: 407–417.
Iqbal, M., S. Yaegashi, R. Ahsan, K.L. Shopinski, T.M. Nair & D. Lightfoot, 2004. Root response to Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines: Temporal accumulation of transcripts in partially resistant and susceptible soybean. Legumes for the benefit of agriculture, nutrition and the environment. In: Proceedings of Second International Conference on Legume Genomics and Genetics, 7–11 June 2004, Dijon, p. 234.
Journet, E.-P., D. van Tuinen, J. Gouzy, H. Crespeau, V. Carreau, M.-J. Farmer, A. Niebel, T. Schiex, O. Jaillon, O. Chatagnier, L. Godiard, F. Micheli, D. Kahn, V. Gianinazzi-Pearson & P. Gamas, 2002. Exploring root symbiotic programs in the model legume Medicago truncatula using EST analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 30: 5579–5592.
Kazan, K., P.M. Schenk, I. Wilson & J.M. Manners, 2001. DNA microarrays: New tools in the analysis of plant defence responses. Mol Plant Pathol 2: 177–185.
Kuester, H., N. Hohnjec, F. Krajinski, Y.F. El, K. Manthey, J. Gouzy, M. Dondrup, F. Meyer, J. Kalinowski, L. Brechenmacher, D. van Tuinen, V. Gianinazzi-Pearson, A. Puhler, P. Gamas & A. Becker, 2004. Construction and validation of cDNA-based Mt6k-RIT macro- and microarrays to explore root endosymbioses in the model legume Medicago truncatula. J Biotechnol 108: 95–113.
Kuester, H. & A. Bendahmane, 2004. New genomics tools and resources. Grain Legumes 40: 15.
Lee, S., S.Y. Kim, E. Chung, Y.H. Joung, H.S. Pai, C.G. Hur & D. Choi, 2004. EST and microarray analyses of pathogen-responsive genes in hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) non-host resistance against soybean pustule pathogen (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. glycines). Funct Integr Genomics 4: 196–205.
Liu, C.J., D. Huhman, L.W. Sumner & R.A. Dixon, 2003. Regiospecific hydroxylation of isoflavones by cytochrome p450 81E enzymes from Medicago truncatula. Plant J 36: 471–484.
Maleck, K., A. Levine, T. Eulgem, A. Morgan, J. Schmid, K.A. Lawton, J.L. Dangl & R.A. Dietrich, 2000. The transcriptome of Arabidopsis thaliana during systemic acquired resistance. Nat Genet 26: 403–410.
Marshall, E., 2004. Getting the noise out of gene arrays. Science 306: 630–631.
Moy, P., D. Qutob, B.P. Chapman, I. Atkinson & M. Gijzen, 2004. Patterns of gene expression upon infection of soybean plants by Phytophthora sojae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17: 1051–1062.
Narusaka, Y., M. Narusaka, M. Seki, J. Ishida, M. Nakashima, A. Kamiya, A. Enju, T. Sakurai, M. Satoh, M. Kobayashi, Y. Tosa, P. Park & K. Shinozaki, 2003. The cDNA microarray analysis using an Arabidopsis pad3 mutant reveals the expression profiles and classification of genes induced by Alternaria brassicicola attack. Plant Cell Physiol 44: 377–387.
Narusaka, Y., M. Narusaka, P. Park, Y. Kubo, T. Hirayama, M. Seki, T. Shiraishi, J. Ishida, M. Nakashima, A. Enju, T. Sakurai, M. Satou, M. Kobayashi & K. Shinozaki, 2004. RCH1, a locus in Arabidopsis that confers resistance to the hemibiotrophic fungal pathogen Colletotrichum higginsianum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17: 749–762.
Nyamsuren, O., F. Colditz, S. Rosendahl, M. Tamasloukht, T. Bekel, F. Meyer, H. Kuester, P. Franken & F. Krajinski, 2003. Transcriptional profiling of Medicago truncatula roots after infection with Aphanomyces euteiches (oomycota) identifies novel genes upregulated during this pathogenic interaction. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 63: 17–26.
Perry, J.A., T.L. Wang, T.J. Welham, S. Gardner, J.M. Pike, S. Yoshida & M. Parniske, 2003. A TILLING reverse genetics tool and a web-accessible collection of mutants of the legume Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol 131: 866–871.
Qutob, D., P.T. Hraber, B.W. Sobral & M. Gijzen, 2000. Comparative analysis of expressed sequences in Phytophthora sojae. Plant Physiol 123: 243–254.
Sawbridge, T., E.-K. Ong, C. Binnion, M. Emmerling, K. Meath, K. Nunan, M. O’Neill, F. O’Toole, J. Simmonds & K. Wearne, 2003. Generation and analysis of expressed sequence tags in white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Plant Sci 165: 1077–1087.
Scheideler, M., N.L. Schlaich, K. Fellenberg, T. Beissbarth, N.C. Hauser, M. Vingron, A.J. Slusarenko & J.D. Hoheisel, 2002. Monitoring the switch from housekeeping to pathogen defense metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana using cDNA arrays. J Biol Chem 277: 10555–10561.
Schenk, P.M., K. Kazan, I. Wilson, J.P. Anderson, T. Richmond, S.C. Somerville & J.M. Manners, 2000. Coordinated plant defense responses in Arabidopsis revealed by microarray analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 11655–11660.
Schenk, P.M., K. Kazan, J.M. Manners, J.P. Anderson, R.S. Simpson, I.W. Wilson, S.C. Somerville & D.J. Maclean, 2003. Systemic gene expression in Arabidopsis during an incompatible interaction with Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Physiol 132: 999–1010.
Schoor, S. & B.A. Moffatt, 2004. Applying high throughput techniques in the study of adenosine kinase in plant metabolism and development. Front Biosci 9: 1771–1781.
Shoemaker, R., P. Keim, L. Vodkin, E. Retzel, S.W. Clifton, R. Waterston, D. Smoller, V. Coryell, A. Khanna, J. Erpelding, X. Gai, V. Brendel, C. Raph-Schmidt, E.G. Shoop, C.J. Vielweber, M. Schmatz, D. Pape, Y. Bowers, B. Theising, J. Martin, M. Dante, T. Wylie & C. Granger, 2002. A compilation of soybean ESTs: generation and analysis. Genome 45: 329–338.
Suzuki, H., L. Achnine, R. Xu, S.P. Matsuda & R.A. Dixon, 2002. A genomics approach to the early stages of triterpene saponin biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula. Plant J 32: 1033–1048.
Tao, Y., Z. Xie, W. Chen, J. Glazebrook, H.S. Chang, B. Han, T. Zhu, G. Zou & F. Katagiri, 2003. Quantitative nature of Arabidopsis responses during compatible and incompatible interactions with the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Cell 15: 317–330.
Thomma, B., K. Eggermont, I. Penninckx, B. Mauch-Mani, R. Vogelsang, B.P.A. Cammue & W.F. Broekaert, 1998. Separate jasmonate-dependent and salicylate-dependent defense-response pathways in Arabidopsis are essential for resistance to distinct microbial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15107–15111.
Tian, A.-G., J. Wang, P. Cui, Y.-J. Han, H. Xu, L.-J. Cong, X.-G. Huang, X.-L. Wang, Y.-Z. Jiao, B.-J. Wang, Y.-J. Wang, J.-S. Zhang & S.-Y. Chen, 2004. Characterization of soybean genomic features by analysis of its expressed sequence tags. Theor Appl Genet 108: 903–913.
Torregrosa, C., S. Cluzet, J. Fournier, T. Huguet, P. Gamas, J.M. Prosperi, M.T. Esquerre-Tugaye, B. Dumas & C. Jacquet, 2004. Cytological, genetic, and molecular analysis to characterize compatible and incompatible interactions between Medicago truncatula and Colletotrichum trifolii. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17: 909–920.
Tuteja, J.H., S.J. Clough, W.C. Chan & L.O. Vodkin, 2004. Tissue-specific gene silencing mediated by a naturally occurring chalcone synthase gene cluster in Glycine max. Plant Cell 16: 819–835.
van Wees, S.C., H.S. Chang, T. Zhu & J. Glazebrook, 2003. Characterization of the early response of Arabidopsis to Alternaria brassicicola infection using expression profiling. Plant Physiol 132: 606–617.
VandenBosch, K.A. & G. Stacey, 2003. Summaries of legume genomics projects from around the globe. Community resources for crops and models. Plant Physiol 131: 840–865.
Vodkin, L.O., A. Khanna, R. Shealy, S.J. Clough, D.O. Gonzalez, R. Philip, G. Zabala, F. Thibaud-Nissen, M. Sidarous, M.V. Stromvik, E. Shoop, C. Schmidt, E. Retzel, J. Erpelding, R.C. Shoemaker, A.M. Rodriguez-Huete, J.C. Polacco, V. Coryell, P. Keim, G. Gong, L. Liu, J. Pardinas & P. Schweitzer, 2004. Microarrays for global expression constructed with a low redundancy set of 27,500 sequenced cDNAs representing an array of developmental stages and physiological conditions of the soybean plant. BMC Genomics 5: 73.
Wan, J., F.M. Dunning & A.F. Bent, 2002. Probing plant–pathogen interactions and downstream defense signaling using DNA microarrays. Funct Integr Genomics 2: 259–273.
Zhu, H., D.J. Kim, J.M. Baek, H.K. Choi, L.C. Ellis, H. Kuester, W.R. McCombie, H.M. Peng & D.R. Cook, 2003. Syntenic relationships between Medicago truncatula and Arabidopsis reveal extensive divergence of genome organization. Plant Physiol 131: 1018–1026.
Zou, J., S. Rodriguez-Zas, D.O. Gonzales, L. Vodkin & S.J. Clough, 2004. Gene expression profiling of soybean response during compatible and incompatible interactions with the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Legumes for the benefit of agriculture, nutrition and the environment In: Proceedings of Second International Conference on Legume Genomics and Genetics, 7–11 June 2004, Dijon, p. 245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ameline-Torregrosa, C., Dumas, B., Krajinski, F. et al. Transcriptomic approaches to unravel plant–pathogen interactions in legumes. Euphytica 147, 25–36 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-6767-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-6767-1