Abstract
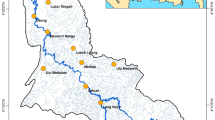
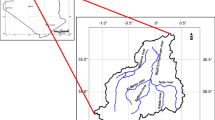
Precipitation is the principal component of the hydrologic cycle. This study examines the spatial and temporal rainfall variability in Gabes Catchment (southeastern Tunisia) by analyzing annual precipitation data in nine stations during the period extending from 1977 to 2015. Several multivariate statistical tools, essentially principal component analysis (PCA), hierarchical clustering analysis and multiple linear regression, are used to characterize spatial variability of rainfall and identify its major controlling factors. PCA resulted in four principal components explaining 70% of the total variance. Stations were clustered into three different groups based on topography, the proximity to the Mediterranean Sea, continentality and seasonality. Hierarchical clustering, applying Ward method, classified variables into two groups. A multiple regression model including 13 variables was developed, representing a suitable tool for predicting precipitation of the different stations spread throughout Gabes Catchment. The proposed model displays acceptable efficiency with an absolute prediction error of approximately 87%.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
The data used in this paper are provided by the Ministry of Agriculture of Tunisia Directorate General of Water Resources.
Abbreviations
- HCA:
-
Hierarchical Clustering Analysis
- P:
-
Annual rainfall
- Paut:
-
Autumn rainfall
- PC:
-
Principal component
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- Pspr:
-
Spring rainfall
- Psum:
-
Summer rainfall
- Pwin:
-
Winter rainfall
- Lat:
-
Latitude
- Lon:
-
Longitude
- Alt:
-
Altitude
- dProx.Sea:
-
Distance to the Mediterranean Sea
- P1, P2, P3, P4:
-
Classes of precipitation defined according to the number of rainy days of given rainfall depths
- NjPtot:
-
Number of total rainy days
- \({\Delta P}_{c}\) :
-
Rainfall variability for calibration model
- MLR:
-
Multiple linear regressions
References
Abdi, H., & Williams, L. J. (2010). Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Computational Statistics, 2, 433–459.
Alotaibi, K., Ghumman, A. R., Haider, H., Ghazaw, Y., & Shafiquzzaman, M. (2018). Future predictions of rainfall and temperature using GCM and ANN for Arid Regions: A case study for the Qassim Region Saudi Arabia. Water, 10, 1260.
Arslan, O. (2009). A GIS-based spatial-multivariate statistical analysis of water quality data in the Porsuk River, Turkey. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 44(3), 279–293.
Bodian, A., Ndiayeb, O., & Dacostac, H. (2016). Evolution des Caractéristiques des Pluies Journalières dans le Bassin Versant du Fleuve Sénégal: Avant et Après Rupture. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 61(5), 905–913.
Bravo Cabrera, J. L., Azpra Romero, E., Zarraluqui Such, V., Gay García, C., & Estrada Porrúa, F. (2012). Cluster analysis for validated climatology stations using precipitation in Mexico. Atmósfera, 25(4), 339–354.
Chifurira, R., & Chikobvu, D. (2014). A weighted multiple regression model to predict rainfall patterns: Principal component analysis approach. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 5(7), 34–42.
Choubin, B., Malekian, A., Samadi, S., Khalighi-Sigaroodi, S., & Sajedi-Hosseini, F. (2017). An ensemble forecast of semi-arid rainfall using large-scale climate predictors. Meteorological Applications, 24(3), 376–386. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1635
Darand, M., & Daneshvar, M. R. M. (2014). Regionalization of precipitation regimes in iran using principal component analysis and hierarchical clustering analysis. Environmental Processes, 1(4), 517–532.
DGRE. (1977–2015). Rainfall variability reports in Tunisia. Technical report. General Directorate of Water Resources, Tunisian Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources, Tunisia.
Djibo, A. G., Karambiri, H., Seidou, O., Sittichok, K., Philippon, N., Paturel, J. E., & Saley, H. M. (2015). Linear and non-linear approaches for statistical seasonal rainfall forecast in the Sirba Watershed Region (SAHEL). Climate, 3(3), 727–752.
Ellouze, M., Azri, C., & Abida, H. (2009). Spatial variability of monthly and annual rainfall data over Southern Tunisia. Journal of Atmospheric Research, 93(4), 832–839.
Fowdur, S. C., Rughooputh, S. D. D. V., Cheeneebash, J., Boojhawon, R., & Gopaul, A. (2014). Rainfall analysis over Mauritius using principal component analysis. Environmental Management and Sustainable Development, 3(2), 94–108.
Fragoso, M., & Gomes, P. T. (2008). Classification of daily abundant rainfall patterns and associated large-scale atmospheric circulation types in Southern Portugal. International Journal of Climatology, 28(4), 537–544.
Gilbert, R. O. (1987). Statistical methods for environmental pollution monitoring. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company Inc. (pp. 320). New York. ISBN 0-442-23050-8.
Gonzalez, M. H., SkansiI, M. M., & Losano, F. (2010). A statistical study of seasonal winter rainfall prediction in the Comahue region (Argentina). Atmósfera, 23(3), 277–294.
IBM Corp. (2012). IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows,” Version 21.0. Armonk, NY.
Jemai, S., Ellouze, M., & Abida, H. (2017). Variability of precipitation using the wavelet approach: Case study of Watershed of Gabes in South-East Tunisia. Atmosphere, 8(9), 1–16.
Jemai, S., Ellouze, M., Agoubi, B., & Abida, H. (2016). Drought intensity and spatial variability in Gabes Watershed, south-eastern Tunisia. Journal of Water and Land Development, 31, 63–72.
Jemai, S., Kallel, A. & Abida, H. (2018). Drought distribution using the standardized precipitation index: case of Gabes Basin, South Tunisia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4053-x.
Kadioglu, M. (2000). Regional variability of seasonal precipitation over Turkey. International Journal of Climatology, 20, 1743–1760.
Kendall, M.G. (1975). Rank correlation methods. 4th Edition, Charles Griffin, (pp. 202). London.
Kipkorior, E. C. (2002). Analysis of rainfall climate on the Njemps Flats, Baringo District, Kenya. Journal of Arid Environments, 50(3), 445–458.
Kouassi, A. M., Kouamé, K. F., Koffi, Y. B., et al. (2010). Analyse de la variabilité climatique et de ses influences sur les régimes pluviométriques saisonniers en Afrique de l’Ouest : cas du bassin versant du N’zi (Bandama) en Côte d’Ivoire. Cybergeo: European Journal of Geography, Environnement, Nature, Paysage, 513, 29, http://journals.openedition.org/cybergeo/23388. Accessed 28 mai 2020.
Kovilage, M. P. (2020). Influence of lean-green practices on organizational sustainable performance. Journal of Asian Business and Economic Studies. https://doi.org/10.1108/JABES-11-2019-0115
Kumar, M., & Padhy, P. K. (2014). Multivariate statistical techniques and water quality assessment: Discourse and review on some analytical models. International Journal of Environmental Science, 5(3), 607–626.
Lyra, G. B., Oliveira-Júnior, J. F., & Zeri, M. (2014). Cluster analysis applied to the spatial and temporal, variability of monthly rainfall in Alagoas state, Northeast of Brazil. International Journal of Climatology, 34, 3546–3558.
Manatsa, D., & Mukwada, G. (2015). Rainfall Mechanisms for the Dominant Rainfall Mode over Zimbabwe Relative to ENSO and/or IODZM. The Scientific World Journal, 2012, 1–15.
Mann, H. B. (1945). Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica, 13, 163–171.
Mehta, D., & Yadav, S. M. (2021). An analysis of rainfall variability and drought over Barmer District of Rajasthan, Northwest India. Water Science and Technology Water Supply. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2021.053
Mourato, S., Moreira, M., & Corte-Real, J. (2009). Interannual variability of precipitation distribution patterns in Southern Portugal. International Journal of Climatology, 30(12), 1784–1794.
Muñoz-Díaz, D., & Rodrigo, F. S. (2004). Spatio-temporal patterns of seasonal rainfall in Spain (1912–2000) using cluster and principal component analysis: Comparison. Annals of Geophysics, 22, 1435–1448.
Nair, A., Joseph, K. A., & Nair, K. S. (2014). Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall trends over a maritime state (Kerala) of India during the last 100 years. Atmospheric Environment, 88, 123–132.
Nasir, M. A., Huynh, T. L. D., & Tram, H. T. X. (2019). Role of financial development, economic growth & foreign direct investment in driving climate change: A case of emerging ASEAN. Journal of Environmental Management, 242, 131–141.
Navid, M., & Niloy, N. H. (2018). Multiple linear regressions for predicting rainfall for Bangladesh. Communications, 6(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.com.20180601.11
Nouaceur, Z., & Musrrescu, O. (2016). Rainfall Variability and Trend Analysis of Annual Rainfall in North Africa. International Journal of Atmospheric Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7230450
Osmana, Y. Z., & Abdellatif, M. E. (2016). Improving accuracy of downscaling rainfall by combining predictions of different statistical downscale models. Water Science, 30(2), 61–75.
Pingale, S. M., Khare, D., Jat, M. K., & Adamowski, J. (2014). Spatial and temporal trends of mean and extreme rainfall and temperature for the 33 urban centers of the arid and semi-arid state of Rajasthan, India. Atmospheric Research, 138, 73–90.
Randall, D. A., Wood, R. A., Bony, S., Colman, R., Fichefet, T., Fyfe, J., Kattsov, V., Pitman, A., Shukla, J., Srinivasan, J., Stouffer, R., Sumi, A., & Taylor, K. (2007). Climate models and their evaluation,” In: S. Solomon, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K. Averyt, M. Tignor & H. Miller, (Eds.) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/ New York.
Refonaa, J., Lakshmi, M., Abbas, R., & Raziullha, M. (2019). Rainfall prediction using regression model. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering., 8(2S3), 2277–3878. https://doi.org/10.35940/ijrte.B1098.0782S319
Rencher, A. C. (1998). Multivariate statistical inference and applications. Wiley.
Singh, C. V. (2006). Pattern characteristics of Indian monsoon rainfall using principal component analysis (PCA). Elsevier Atmospheric Research, 79(3–4), 317–326.
Soares dos Santos, T., Mendes, D., & Rodrigues Torres, R. (2016). Artificial neural networks and multiple linear regression model using principal components to estimate rainfall over South America. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics, 23(1), 13–20.
Soltani, S., & Modarres, R. (2006). Classification of Spatio-Temporal pattern of rainfall in iran using a hierarchical and divisive cluster analysis. Journal of Spatial Hydrology, 6(2), 1–12.
Tatli, H., Dalfes, N., & Mente, S. (2004). A statistical downscaling method for monthly total precipitation over Turkey. International Journal of Climatology, 24, 161–188.
Tatli, H., Dalfes, N., & Mente, S. (2005). Surface air temperature variability over Turkey and its connection to large scale upper air circulation via multivariate techniques. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 331–350.
Vrochidou, A. E. K., & Tsanis, I. K. (2012). Assessing precipitation distribution impacts on droughts on the island of Crete. Natural Hazards and Earth Systems Sciences, 12, 1159–1171.
Ward, J. H. (1963). Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 58(301), 236–244.
Wilks, D. S. (1995) Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences: An Introduction. Academic Press. (pp. 467). New York.
Wilson, L. J., & Vallée, M. (2002). The Canadian updateable model output statistics (UMOS) system: Design and development tests. Weather and Forecasting, 17, 206–222.
WMO. (1990). Guide to Climatological Practices. Publication No. 100. World Meteorological Organization, Geneva.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jemai, S., Kallel, A., Agoubi, B. et al. Spatial and temporal rainfall variability and its controlling factors under an arid climate condition: case of Gabes Catchment, Southern Tunisia. Environ Dev Sustain 24, 5496–5513 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01668-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01668-7