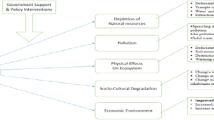
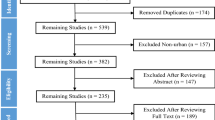
Abstract
The Mediterranean region attracts annually more than 400 million tourists. In recent decades, quad tourism has grown, favoured by poor regulations. Environmental impacts of off-road vehicles have been widely studied in the USA, but not in the Mediterranean. This paper addresses that gap through a literature review on the impacts of motorized recreation, and an analysis of the current implementation of quad tourism in the region and of advertising topics. Main impacts were reported on soils, vegetation and wildlife. We have registered 337 quad agencies in 20 Mediterranean countries, with important concentrations in some regions. Half agencies promote their tours with images driving out of the trails, 22% crossing rivers, 9% driving on the beach, 7% on dunes and 23% sell the activity as an extreme adventure. It is necessary a stronger authorization framework, including the environmental impact assessment of these activities, more involvement of tour operators in environmental protection and greater education of the participants about the impacts of off-road driving and the importance of their behaviour. Further research in the region is also convenient.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Information used in the research is included as supplementary data.
References
Albritton, R., & Stein, T. V. (2011). Integrating social and natural resource information to improve planning for motorized recreation. Applied Geography, 31(1), 85–97.
Anders, F. J., & Leatherman, S. P. (1987). Disturbance of beach sediment by off-road vehicles. Environmental Geology and Water Sciences, 9(3), 183–189.
Andreyashkina, N. I. (2012). Composition of plant communities in natural and technogenically disturbed ecotopes on watersheds of the Yamal Peninsula: Floristic diversity. Russian Journal of Ecology, 43(1), 19–23.
Araujo, V. D., Reyes-Pérez, Y. A., Freire, R. C., Gauw, D. S., Santos, D. A. S., Fracasso, P., et al. (2006). Monitoring methods of dunefield susceptible to human activities in the Nísia Floresta area, eastern coast of the State of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment, 88, 387–396.
Arp, C. D., & Simmons, T. (2012). Analyzing the impacts of off-road vehicle (ORV) trails on watershed processes in Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve. Alaska. Environmental Management, 49(3), 751–766.
Assaeed, A. M., Al-Rowaily, S., El-Bana, M., Abood, A. A. A., Dar, B. A. M., & Hegazy, A. K. (2019). Impact of off-road vehicles on soil and vegetation in a desert rangeland in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 26(6), 1187–1193.
Attum, O. (2007). Can landscape use be among the factors that potentially make some ungulates species more difficult to conserve? Journal of Arid Environments, 69(3), 410–419.
Banha, F., Marques, M., & Anastácio, P. M. (2014). Dispersal of two freshwater invasive macroinvertebrates, Procambarus clarkii and Physella acuta, by off-road vehicles. Aquatic Conservation, 24(5), 582–591.
Barr, S., Shaw, G., Coles, T., & Prillwitz, J. (2010). A holiday is a holiday: Practicing sustainability, home and away. Journal of Transport Geography, 18(3), 474–481.
Barton, D. C., & Holmes, A. L. (2007). Off-highway vehicle trail impacts on breeding songbirds in northeastern California. Journal of Wildlife Management, 71(5), 1617–1620.
Belnap, J. (1995). Surface disturbances: Their role in accelerating desertification. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 37(1–3), 39–57.
Berno, T., Moore, K., Simmons, D., & Hart, V. (1996). The nature of the adventure experience in Queenstown. Australian Leisure, 8(1), 21–25.
Bissix, G. (2012). Nova Scotia’s shared-use trails policy on abandoned rail corridors: An integrative assessment. Leisure/Loisir, 36(3–4), 289–308.
Blackwell, D. R., Miniard, W. P., & Engel, F. J. (2006). Consumer behaviour. Mason: South-Western.
Bonnet, M., Wehbe-Herrera, C. D., & Lobo, Á. (2018). Analysis of the regulation of active tourism in Spain. Revista de Estudios Empresariales, 2, 28–56.
Brodhead, J. M., & Godfrey, P. J. (1977). Off road vehicle impact in Cape Cod national seashore: Disruption and recovery of dune vegetation. International Journal of Biometeorology, 21(3), 299–306.
Brooks, M. L. (1995). Benefits of protective fencing to plant and rodent communities of the western Mojave Desert, California. Environmental Management, 19(1), 65–74.
Buckley, R. C. (2003). Adventure tourism and the clothing, fashion and entertainment industries. Journal of Ecotourism, 2(2), 126–134.
Buckley, R. (2007). Adventure tourism products: Price, duration, size, skill, remoteness. Tourism Management, 28, 1428–1433.
Budeanu, A. (2007). Sustainable tourist behaviour—A discussion of opportunities for change. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 31(5), 499–508.
Buick, A. M., & Paton, D. C. (1989). Impact of off-road vehicles on the nesting success of hooded plovers Charadrius rubricollis in the Coorong Region of South Australia. Emu, 89(3), 159–172.
Burgin, S., & Hardiman, N. (2012). Extreme sports in natural areas: Looming disaster or a catalyst for a paradigm shift in land use planning? Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 55(7), 921–940.
Busack, S. D. (1975). Some effects of off-road vehicles and sheep grazing on lizard populations in the Mojave Desert. Biological Conservation, 6, 179–183.
Butler, R. W. (1991). Tourism, environment, and sustainable development. Environmental Conservation, 18(3), 201–209.
Cater, C. I. (2006). Playing with risk? Participant perceptions of risk and management implications in adventure tourism. Tourism Management, 27(1), 317–325.
Cloke, P., & Perkins, H. V. (1998). “Cracking the canyon with the awesome foursome”: Representations of adventure tourism in New Zealand. Environment and Planning D: Society and Space, 16, 185–218.
Dávid, L., Lontai-Szilágyi, Z., & Baros, Z. (2010). The impact of tourism and sports activities. In J. Szabó, L. Dávid, & D. Lóczy (Eds.), Anthropogenic geomorphology: A guide to man-made landforms (pp. 233–254). Berlin: Springer.
Davies, R., Speldewinde, P. C., & Stewart, B. A. (2016). Low level off-road vehicle (ORV) traffic negatively impacts macroinvertebrate assemblages at sandy beaches in south-Western Australia. Scientific Reports, 6, 24899.
Dewidar, K., Thomas, J., & Bayoumi, S. (2016). Detecting the environmental impact of off-road vehicles on Rawdat Al Shams in central Saudi Arabia by remote sensing. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 396.
Dickson, T. L., Wilsey, B. J., Busby, R. R., & Gebhart, D. L. (2008). Grassland plant composition alters vehicular disturbance effects in Kansas, USA. Environmental Management, 41(5), 676–684.
Duniway, M. C., Pfennigwerth, A. A., Fick, S. E., Nauman, T. W., Belnap, J., & Barger, N. N. (2019). Wind erosion and dust from US drylands: A review of causes, consequences, and solutions in a changing world. Ecosphere, 10(3), e02650.
Foltz, R. B., & Yanosek, K. A. (2005). Impacts of all terrain vehicles (ATV) on National Forest lands and Grasslands. In G. E. Moglen (Ed.), Managing watersheds for human and natural impacts: Engineering, ecological, and economic challenges (pp. 1023). Proceedings of the 2005 Watershed Management Conference. American Society of Civil Engineers. July 19–22, 2005, Williamsburg, VA.
Forbes, B. C. (1992). Tundra disturbance studies, I: Long-term effects of vehicles on species richness and biomass. Environmental Conservation, 19(1), 48–58.
Foster-Smith, J., Birchenough, A. C., Evans, S. M., & Prince, J. (2007). Human impacts on Cable Beach, Broome (Western Australia). Coastal Management, 35(2–3), 181–194.
Gilbertson, D. D. (1981). The impact of past and present land use on a major coastal barrier system. Applied Geography, 1(2), 97–119.
Goossens, D., & Buck, B. (2009). Dust dynamics in off-road vehicle trails: Measurements on 16 arid soil types, Nevada, USA. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(11), 3458–3469.
Grant, T. J., & Doherty, P. F. (2009). Potential mortality effects of off-highway vehicles on the flat-tailed horned lizard (Phrynosoma mcallii): A manipulative experiment. Environmental Management, 43(3), 508–513.
Groom, J. D., McKinney, L. B., Ball, L. C., & Winchell, C. S. (2007). Quantifying off-highway vehicle impacts on density and survival of a threatened dune-endemic plant. Biological Conservation, 135(1), 119–134.
Hambleton, J., & Drescher, A. (2008). Soil damage models for off-road vehicles. In K. R. Reddy, M. V. Khire, & A. N. Alshawabkeh (Eds.), Geocongress 2008: Geosustainability and Geohazard Mitigation (pp. 562–569). Virginia: ASCE.
Hernández-Yáñez, H., Kos, J. T., Bast, M. D., Griggs, J. L., Hage, P. A., Killian, A., et al. (2016). A systematic assessment of threats affecting the rare plants of the United States. Biological Conservation, 203, 260–267.
Hicks, D., Grzebieta, R., Mongiardini, M., Rechnitzer, G., Simmons, K., & Olivier, J. (2018). Investigation of when quad bikes rollover in the farming environment. Safety Science, 106, 28–34.
Hillman, M. D., Karpanty, S. M., Fraser, J. D., & DeRose-Wilson, A. (2015). Effects of aircraft and recreation on colonial waterbird nesting behavior. Journal of Wildlife Management, 79(7), 1192–1198.
Hosier, P. E., & Eaton, T. E. (1980). The impact of vehicles on dunes and grassland vegetation on a south-eastern North Carolina barrier beach. Journal of Applied Ecology, 17(1), 173–182.
Hosier, P. E., & Kochhar, M. (1981). Off-road vehicle and pedestrian track effects on the sea-approach of hatchling loggerhead turtles. Environmental Conservation, 8(2), 158–161.
Jones, G. K. (2015). Changes in distribution and abundance of Australian pied and sooty oystercatchers on highly disturbed beaches of the south-eastern fleurieu Peninsula, South Australia. Stilt, 68, 31–39.
Jones, A. S., Anderson, J. J., Dickson, B. G., Boe, S., & Rubin, E. S. (2017). Off-highway vehicle road networks and kit fox space use. Journal of Wildlife Management, 81(2), 230–237.
Juvan, E., & Dolnicar, S. (2014). The attitude-behaviour gap in sustainable tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 48, 76–95.
Juvan, E., Ring, A., Leisch, F., & Dolnicar, S. (2016). Tourist segments’ justifications for behaving in an environmentally unsustainable way. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 24(11), 1506–1522.
Kavallinis, I., & Pizam, A. (1994). The environmental impacts of tourism—Whose responsibility is it anyway? The case study of Mykonos. Journal of Travel Research, 33(2), 26–32.
Kinugasa, T., & Oda, S. (2014). Effects of vehicle track formation on soil seed banks in grasslands with different vegetation in the Mongolian steppe. Ecological Engineering, 67, 112–118.
Knisley, C. B., Gowan, C., & Fenster, M. S. (2018). Effects of off-highway vehicles on sandy habitat critical to survival of a rare beetle. Insect Conservation and Diversity, 11(2), 185–193.
Knisley, C. B., & Hill, J. M. (2001). Biology and conservation of the Coral Pink Sand Dunes tiger beetle, Cicindela limbata albissima Rumpp. Western North American Naturalist, 61(4), 381–394.
Kobryn, H. T., Beckley, L. E., Cramer, V., & Newsome, D. (2017). An assessment of coastal land cover and off-road vehicle tracks adjacent to Ningaloo Marine Park, north-western Australia. Ocean and Coastal Management, 145, 94–105.
Lei, S. A. (2004). Soil compaction from human trampling, biking, and off-road motor vehicle activity in a blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima) shrubland. Western North American Naturalist, 64(1), 125–130.
Lerdsuchatavanich, P., Pradatsundarasar, A., Pattanakiat, S., & Utarasakul, T. (2017). Impact assessment of off-road activities for sustainable tourism management in khao krajome, Thailand. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 10(4), 197–205.
Lucrezi, S., & Schlacher, T. A. (2010). Impacts of off-road vehicles (ORVs) on burrow architecture of ghost crabs (Genus Ocypode) on sandy beaches. Environmental Management, 45(6), 1352–1362.
Martin, S. R., Onuf, C. P., & Dunton, K. H. (2008). Assessment of propeller and off-road vehicle scarring in seagrass beds and wind-tidal flats of the southwestern Gulf of Mexico. Botanica Marina, 51(2), 79–91.
Masini, N., & Lasaponara, R. (2020). Satellite and close range analysis for the surveillance and knowledge improvement of the Nasca geoglyphs. Remote Sensing of Environment, 236, 111447.
McGowan, C. P., & Simons, T. R. (2006). Effects of human recreation on the incubation behavior of American oystercatchers. Wilson Journal of Ornithology, 118(4), 485–493.
McGrann, A. M., McGrann, M. C., & Dial, R. (2005). Off-highway vehicle impact on Astragalus magdalenae var. peirsonii, and other critical plant species of the Algodones Dunes, California. California Fish and Game, 91(2), 61–82.
McKercher, B. (1993). Some fundamental truths about tourism: Understanding tourism’s social and environmental impacts. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 1(1), 6–16.
McKercher, B., & Prideaux, B. (2011). Are tourism impacts low on personal environmental agendas? Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 19(3), 325–345.
Melvin, S. M., Hecht, A., & Griffin, C. R. (1994). Piping plover mortalities caused by off-road vehicles on Atlantic coast beaches. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 22(3), 409–413.
Miniat, C. F., Clinton, P. P., & Everage, L. K. (2019). The effects of off-highway vehicle trails and use on stream water quality in the north fork of the broad river. Transactions of the ASABE, 62(2), 539–548.
Morgan, N., & Pritchard, A. (2000). Advertising in tourism and leisure. London: Routledge.
Müller, C. W., Otte, D., Stübig, T., Brand, S., Oszwald, M., Frink, M., et al. (2010). Quad-Fahren ein lebensgefährlicher Spaß? Eine medizinische und technische Unfallanalyse. Zeitschrift für Orthopädie und Unfallchirurgie, 148(5), 573–578.
Nauman, T. W., Duniway, M. C., Webb, N. P., & Belnap, J. (2018). Elevated aeolian sediment transport on the Colorado Plateau, USA: The role of grazing, vehicle disturbance, and increasing aridity. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 43(14), 2897–2914.
Navas, A. L., Herrera, M. A., Dalmasso, A. D., & Barros, A. (2019). Quad bike impacts on vegetation and soil physicochemical properties in an arid ecosystem. Acta Oecologica, 97, 14–22.
Onyeanusi, A. E. (1986). Measurements of impact of tourist off-road driving on grasslands in Masai Mara National Reserve, Kenya: A simulation approach. Environmental Conservation, 13(4), 325–329.
Padgett, P. E., Meadows, D., Eubanks, E., & Ryan, W. E. (2008). Monitoring fugitive dust emissions from off-highway vehicles traveling on unpaved roads and trails using passive samplers. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 144(1–3), 93–103.
Pauli, B. P., Spaul, R. J., & Heath, J. A. (2017). Forecasting disturbance effects on wildlife: Tolerance does not mitigate effects of increased recreation on wildlands. Animal Conservation, 20(3), 251–260.
Petch, N., Maguire, G. S., Schlacher, T. A., & Weston, M. A. (2018). Motivations and behavior of off-road drivers on sandy beaches. Ocean and Coastal Management, 163, 82–91.
Preisler, H. K., Ager, A. A., & Wisdom, M. J. (2013). Analyzing animal movement patterns using potential functions. Ecosphere, 4(3), 1–13.
Rickard, C. A., McLachlan, A., & Kerley, G. I. H. (1994). The effects of vehicular and pedestrian traffic on dune vegetation in South Africa. Ocean and Coastal Management, 23(3), 225–247.
Schlacher, T. A., & Morrison, J. M. (2008). Beach disturbance caused by off-road vehicles (ORVs) on sandy shores: Relationship with traffic volumes and a new method to quantify impacts using image-based data acquisition and analysis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56(9), 1646–1649.
Schlacher, T. A., Thompson, L., & Price, S. (2007). Vehicles versus conservation of invertebrates on sandy beaches: Mortalities inflicted by off-road vehicles on ghost crabs. Marine Ecology, 28, 354–367.
Scoullos, M. (2020). Environmental and sustainable development components of a European strategy for the Mediterranean in 2010. In S. Scoullos & E. Ferragina (Eds.), Environmental and sustainable development in the Mediterranean (pp. 13–51). Girona-Paris: European Institute of the Mediterranean and Institute for Security Studies.
Shilling, F., Boggs, J., & Reed, S. (2012). Recreational system optimization to reduce conflict on public lands. Environmental Management, 50, 381–395.
Slaughter, C. W., Racine, C. H., Walker, D. A., Johnson, L. A., & Abele, G. (1990). Use of off-road vehicles and mitigation of effects in Alaska permafrost environments: A review. Environmental Management, 14, 63–72.
Stebbins, R. C. (1974). Off-road vehicles and the fragile desert. American Biology Teacher, 36(5), 294–304.
Steg, L., & Vlek, C. (2009). Encouraging pro-environmental behaviour: An integrative review and research agenda. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 29, 309–317.
Steiner, A. J., & Leatherman, S. P. (1981). Recreational impacts on the distribution of ghost crabs Ocypode quadrata Fab. Biological Conservation, 20(2), 111–122.
Stern, P. C. (1999). Information, incentives, and proenvironmental consumer behavior. Journal of Consumer Policy, 22(4), 461–478.
St-Louis, A., Hamel, S., Mainguy, J., & Côté, S. D. (2013). Factors influencing the reaction of mountain goats towards all-terrain vehicles. Journal of Wildlife Management, 77(3), 599–605.
Styles, D., Schönberger, H., & Galvez, J. L. (2013). JRC scientific and policy report on best environmental management practice in the tourism sector. Luxembourg: European Commission.
Switalski, A. (2018). Off-highway vehicle recreation in drylands: A literature review and recommendations for best management practices. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 21, 87–96.
Tarr, N. M., Simons, T. R., & Pollock, K. H. (2010). An experimental assessment of vehicle disturbance effects on migratory shorebirds. Journal of Wildlife Management, 74(8), 1776–1783.
Vogt, G. (1979). Adverse effects of recreation on sand dunes: A problem for coastal zone management. Coastal Zone Management Journal, 6(1), 37–68.
Waight, C. F., & Bath, A. J. (2014). Factors influencing attitudes among all-terrain vehicle users on the island portion of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, 5–6, 27–36.
Walker, S. J., & Schlacher, T. A. (2011). Impact of a pulse human disturbance experiment on macrofaunal assemblages on an Australian sandy beach. Journal of Coastal Research, 27(6), 184–192.
Webb, R. H., Esque, T. C., Nussear, K. E., & Sturm, M. (2013). Disruption rates for one vulnerable soil in Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, Arizona, USA. Journal of Arid Environments, 95, 75–83.
Whitbeck, D. C., & Fehmi, J. S. (2016). Variables influencing law enforcement off-road route proliferation on an arid site. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 3, 45–52.
Williams, Paul., & Soutar, Geoffrey. N. (2009). Value, satisfaction and behavioral intentions in an adventure tourism context. Annals of Tourism Research, 36(3), 413–438.
Wilshire, H. G. (1983). Off-road vehicle recreation management policy for public lands in the United States: A case history. Environmental Management, 7(6), 489–499.
Wilshire, H. G., Nakata, J. K., Shipley, S., & Prestegaard, K. (1978). Impacts of vehicles on natural terrain at seven sites in the San Francisco Bay area. Environmental Geology, 2(5), 295–319.
Wolcott, T. G., & Wolcott, D. L. (1984). Impact of off-road vehicles on macroinvertebrates of a mid-atlantic beach. Biological Conservation, 29(3), 217–240.
WTO. (2019). International tourism highlights, 2019 edition. Madrid: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO). https://doi.org/10.18111/9789284421152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enríquez-de-Salamanca, Á. The impact of quad tourism: a preventive action for the Mediterranean. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 9454–9476 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01036-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01036-x