Abstract
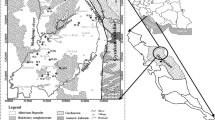
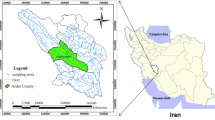
The present study on chemistry, environmetrics and quality index of 116 groundwater samples collected in pre- and post-monsoon periods in the years of 2014 and 2015 from the drought-prone Rajshahi City Corporation area, Bangladesh, is carried out for its drinking suitability from management perspective. According to the Bangladesh Drinking Water Standards (2005), parameters like pH, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, Fe(total) and Mn2+ exceed the desirable limit, but within permissible limit without adverse effect except Mg2+ concentration, which accounts for 45% in pre-monsoon period and makes groundwater unsafe for drinking purposes. The groundwater belongs to alkaline earth elements (Ca2++Mg2+) and exceed alkali elements (Na++K+), and weak acids (HCO3−) exceed the strong acids (SO42−) where Ca2+ and HCO3− are dominant ions, and attribute to temporary hardness of groundwater. The groundwater of the aquifer is of Ca2+–Mg2+–HCO3− type. The source of different ions is associated with partial ion exchanges, weathering of calcareous nodules and clay minerals, flow of groundwater system through aquifer lithology, municipal sewerage, anthropogenic influence, etc. The drinking water quality index also reveals that groundwater mostly falls in ‘good’ category having suitability for drinking purposes round the year. But increasing population and water demand in the area may create threat of quality hazard in near future, and regular groundwater quality monitoring should be carried out periodically for supplying safe drinking water to city dwellers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M. S. (2016). Hydrochemical characterization and identification of groundwater quality zones suitable for drinking and domestic purposes in Rajshahi City Corporation Area using GIS Technique. Ph. D. Thesis (Unpublished), University of Rajshahi, Bangladesh.
APHA (American Public Health Association). (1995). Standard methods for the examination for water and wastewater (19th ed.). Washington: Byrd Press.
BDWS (Bangladesh Drinking Water Standard). (2005). Bangladesh water quality standard, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Craig, E., & Anderson, M. P. (1979). The effect of urbanization of groundwater quality—A case study. Groundwater,17, 456–482.
Davis, J. C. (1973). Statistics and data analysis in geology (pp. 1–646). New York: Wiley.
Garrels, R. M. (1967). Genesis of some groundwater from igneous rocks. In P. H. Abelson (Ed.), Research in geochemistry (Vol. 2, pp. 405–420). New York: Wiley.
Haque, M. L. M., Jahan, C. S., Mazumder, Q. H., Nawaz, S. M. S., Mirdha, G. C., Mamud, P., et al. (2012). Hydrogeological condition and assessment of groundwater resource using visual modflow modelling, Rajshahi City Aquifer, Bangladesh. Journal of Geological Society of India,79, 77–84.
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a Blackfoot diseases area in Taiwan. The Science of the Total Environment,313, 77–89.
Lloyed, J. W., & Heathcote, J. A. (1985). Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater: An introduction (pp. 131–133). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
MacDonald, & Partners, M. (1981). Northwest Bangladesh groundwater modeling study. First phase model report for Bangladesh. Cambridge: Agricultural Development Corporation.
Mehta, B. C., Das, S., Srivastava, S. K. (1994). Environmental hazard of high iron in groundwater of Bhubaneshwar, Orissa. In Regional workshop on environmental aspect of groundwater development, IAH, Roorkee.
Morgan, J. P., & McIntire, W. G. (1959). Quaternary geology of the Bengal Basin, East Pakistan and India. Geological Society of America Bulletin,70, 319–342.
Piper, A. M. (1953). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis, US Geological Survey Groundwater Note 12.
Ramakrishnaiah, C. R., Sadashivaiah, C., & Ranganna, G. (2009). Assessment of water quality index for the groundwater in Tumkur Taluk. Karnataka state, India, E-journal of Chemistry,6, 523–530.
RDA (Rajshahi Development Authority) (2002) Structural plan, master plan and detailed area development plan for Rajshahi Metropolitan City, Draft Interim Report, Development Design Consultants Ltd. Dhaka, Ministry of Housing and Public Works, Government of the Peoples’ Republic of Bangladesh.
Simeonov, V. J., Stratis, C. J., Samara, G. J., Zachariadis, D., Voutsa, A., Anthemidis, M., et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research,37(17), 4119–4124.
Simsek, C., & Gunduz, O. (2007). IWQ index: A GIS-integrated technique to assess irrigation water quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,128, 277–300.
Srivastava, S. K., & Ramanathan, A. L. (2008). Geochemical assessment of groundwater quality in vicinity of Bhaiswa landfill, Delhi, India using graphical and multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Geology,53, 1509–1528.
Wai, W. W., Alkarkhi, A. F. M., & Azhar, M. E. (2010). Comparing biosorbent ability of modified citrus and durian rind pectin. Carbohydrate Polymer,79(3), 584–589.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahaman, M.F., Ali, M.S., Arefin, R. et al. Assessment of drinking water quality characteristics and quality index of Rajshahi city, Bangladesh. Environ Dev Sustain 22, 3957–3971 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00366-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00366-9