Abstract
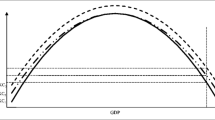
This study attempts to investigate the presence of a regional Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) in selected South Asian countries, namely, Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka for the period 1984–2008. In addition, it also intends to inspect the impact of corruption on environmental degradation in this region. The Fixed Effect results confirm the existence of the regional EKC in these countries. Furthermore, the results indicate that corruption do affect environment in the manner that it delays the turning point in EKC. It is found that, in the presence of corruption, the per capita GDP at the turning point is USD 998, which is USD 128 higher from the value that would have been in the absence of corruption. Based on these results, the study suggests appropriate policy measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The socially optimal point here refers to the per capita GDP at the turning point in the absence of corruption.
However, the effect of corruption on the turning point in EKC has not been studied sufficiently.
References
Abler, D. G., Rodriguez, A. G., & Shortle, J. S. (1999). Trade liberalization and the environment in Costa Rica. Environment and Development Economics, 4, 357–373.
Abosedra, S., & Baghestani, H. (1989). New evidence on the causal relationship between United States energy consumption and gross national product. Journal of Energy and Development, 14, 285–292.
Akarca, A. T., & Long, T. V. (1980). On the relationship between energy and GNP: A reexamination. Journal of Energy and Development, 5, 326–331.
Altinay, G., & Karagol, E. (2004). Structural break, unit root, and the causality between energy consumption and GDP in Turkey. Energy Economics, 26(6), 985–994.
Antweiler, W., Copeland, B. R., & Taylor, M. S. (2001). Is free trade good for the environment? American Economic Review, 91(4), 877–908.
Aqeel, A., & Butt, M. S. (2001). The relationship between energy consumption and economic growth in Pakistan. Asia Pacific Development Journal, 8(2), 101–110.
Beghin, J., Bowland, B., Dessus, S., Roland-Holst, D., & Mensbrugghe, D. V. D. (2011). Trade integration, environmental degradation, and public health in Chile: Assessing the linkages. Environment and Development Economics, 7, 241–267.
Belloumi, M. (2009). Energy consumption and GDP in Tunisia: Cointegration and causality analysis. Energy Policy, 37(7), 2745–2753.
Bhattarai, M., & Hamming, M. (2001). Institutions and the Environmental Kuznets curve for deforestation: A cross-country analysis for Latin America, Africa and Asia. World Development, 29(6), 995–1010.
Bimonte, S. (2002). Information access, income distribution and the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Ecological Economics, 41, 145–156.
Birdsall, N., & Wheeler, D. (1993). Trade policy and industrial pollution in Latin America: Where are the pollution Havens? Journal of Environment and Development, 2(1), 137–149.
Bowden, N., & Payne, J. E. (2009). The causal relationship between US energy consumption and real output: A disaggregated analysis. Journal of Policy Modeling, 31(2), 180–188.
Cheng, B. S. (1999). Causality between energy consumption and economic growth in India: An application of cointegration and error-correction modeling. Indian Economic Review, 34, 39–49.
Cole, M. A. (2007). Corruption, income and the environment: An empirical analysis. Ecological Economics, 62, 637–647.
Damania, R., Fredriksson, P. G., & List, J. A. (2003). Trade liberalization, corruption, and environmental policy formation: Theory and evidence. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 46, 490–512.
Deacon, R. T., & Norman, C. S. (2004). Does the Environmental Kuznets Curve describe how individual countries behave? Land Economics, 82(2), 291–315.
Dinda, S. (2005). A theoretical basis for the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Ecological Economics, 53, 403–413.
Fredriksson, P. G., & Svensson, J. (2003). Political instability, corruption and policy formation: The case of environmental policy. Journal of public economics, 87(7–8), 1383–1405.
Fredriksson, P. G., Neumayer, E., Damania, R., & Gates, S. (2005). Environmentalism, democracy, and pollution control. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 49(2), 343–365.
Grether, J. M., Mathys, N. A., & Melo, J. D. (2007). Is trade bad for the environment? Decomposing world-wide SO2 emissions 1990–2000. Discussion Paper. University of Geneva.
Grossman, G., & Krueger, A. (1991). Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement. National Bureau of Economics Research. Working Paper 3194.
Grossman, G. M., & Krueger, A. B. (1991). Environmental Impacts of a North American free trade agreement. National Bureau of Economic Research. Working Paper 3914.
Ho, C. Y., & Siu, K. W. (2007). A dynamic equilibrium of electricity consumption and GDP in Hong Kong: An empirical investigation. Energy Policy, 35(4), 2507–2513.
Hwang, D., & Gum, B. (1991). The causal relationship between energy and GNP: The case of Taiwan. Journal of Energy and Development, 16, 219–226.
International Country Risk Guide. (2009). ADB Institute.
Jalil, A., & Mahmud, S. F. (2009). Environment Kuznets Curve for CO2 emissions: A Cointegration analysis for china. Energy Policy, 37, 5167–5172.
Jobert, T., & Karanfil, F. (2007). Sectoral energy consumption by source and economic growth in Turkey. Energy Policy, 35, 5447–5456.
Karanfil, F. (2008). Energy consumption and economic growth revisited: Does the size of unrecorded economy matter? Energy Policy, 36(8), 3029–3035.
Khanna, N., & Plassmann, F. (2004). The demand for environmental quality and the environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis. Ecological Economics, 51, 225–236.
Leitao, A. (2010). Corruption and the environmental Kuznets Curve: Empirical evidence for sulfur. Ecological Economics, 69, 2191–2201.
Mauro, P. (1995). Corruption and growth. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 110(3), 681–712.
Mo, P. H. (2001). Corruption and economic growth. Journal of Comparative Economics, 29(1), 66–79.
Nasir, M., & Rehman, F. U. (2011). Environmental Kuznets Curve for carbon emissions in Pakistan: An empirical investigation. Energy Policy, 39(3), 1857–1864.
Oh, W., & Lee, K. (2004). Causal relationship between energy consumption and GDP: The case of Korea 1970–1999. Energy Economics, 26(1), 51–59.
Panayotou, T. (1997). Demystifying the Environmental Kuznets Curve: Turning a black box into a policy tool. Environment and Development Economics, 2(4), 465–484.
Paul, S., & Bhattacharya, R. N. (2004). Causality between energy consumption and economic growth in India: A note on conflicting results. Energy Economics, 26(6), 977–983.
Pellegrini, L. (2003). Corruption, economic development and environmental policy. IVM, The Netherlands: Political Economy of the Environment, Institute for Environmental Studies.
Pellegrini, L., & Gerlagh, R. (2006a). Corruption and environmental policies: What are the implications for the enlarged EU? European Environment, 16, 139–154.
Pellegrini, L., & Gerlagh, R. (2006b). Corruption, democracy, and environmental policy: An empirical contribution to the debate. The Journal of Environment & Development, 15, 332–354.
Rehman, F. U., Ali, A., & Nasir, M. (2007). Corruption, trade openness, and environmental quality: A panel data analysis of selected South Asian countries. Pakistan Development Review, 46(4), 673–688.
Siddiqui, R. (2004). Energy and economic growth in Pakistan. The Pakistan Development Review, 43, 175–200.
Soytas, U., & Sari, R. (2009). Energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon emissions: Challenges faced by an EU candidate member. Ecological Economics, 68(6), 1667–1675.
Stern, D. I. (1993). Energy and economic growth in the USA. A multivariate approach. Energy Economics, 15, 137–150.
Torras, M., & Boyce, J. K. (1998). Income, inequality and pollution: Reassessment of the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Ecological Economics, 25(2), 147–160.
Welsch, H. (2004). Corruption, growth, and the environment: A cross-country analysis. Environment and Development Economics, 9, 663–693.
World Bank. (2010). The World Development Indicators 2009 (WDI) Database.
Yu, E. S. H., & Hwang, B. K. (1984). The relationship between energy and GNP: Further results. Energy Economics, 6, 186–190.
Yu, E. S. H., & Jin, J. C. (1992). Cointegration tests of energy consumption, income, and employment. Resources and Energy, 14, 259–266.
Zarzoso, I. M., & Morancho, A. B. (2003). Pooled mean group estimation of an environmental Kuznets curve for CO2. Economics Letters, 82, 121–126.
Zhang, X. P., & Cheng, X. M. (2009). Energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth in China. Ecological Economics, 68(10), 2706–2712.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehman, F.U., Nasir, M. & Kanwal, F. Nexus between corruption and regional Environmental Kuznets Curve: the case of South Asian countries. Environ Dev Sustain 14, 827–841 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-012-9356-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-012-9356-6