Abstract
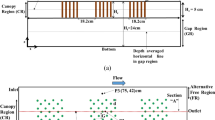
Urban lakes provide many ecosystem services, e.g., flood control, nature protection, coolness island, recreation. Hydrodynamic models will increasingly be used to enhance these benefits. We present the first validation of a three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic model on a small shallow lake with high resolution and high frequency measurements. Lake Créteil, France (area 0.4 km2, mean depth 4.5 m, and catchment area 1 km2) is a former gravel pit and now part of a regional park. The model Delft3D-FLOW was calibrated on a one-month period, with continuous measurements of temperature at five depths at the center of the lake and at three depths at two other stations, and with current speed profiles at the centre of the lake. The model was then verified on 18 1-month periods with similar temperature measurements. The model reproduced very well the temperature dynamics, including the alternation between mixing and stratification periods and internal wave patterns. The mean absolute errors over the five depths at the central point remained below 0.55∘C in spring and summer, the most favorable seasons for phytoplankton growth. Horizontal temperature differences, which rose up to 3∘C at the beginning of stratification periods, were also well reproduced, as well as current speeds. These results are very promising for assessing nutrient and pollutant diffusion, settling and resuspension, as well as for understanding how phytoplankton blooms start in small shallow lakes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meybeck, M. (1995). Global distribution of lakes. In Lerman, A, Imboden, D, & Gat, J (Eds.), Physics and chemistry of lakes (pp. 1–35). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Downing, J., Prairie, Y., Cole, J., Duarte, C., Tranvik, L., Striegl, R., McDowell, W., Kortelainen, P., Caraco, N., Melack, J., & Middelburg, J. (2006). The global abundance and size distribution of lakes, ponds, and impoundments. Limnology and Oceanography, 51(5), 2388–2397.
Catherine, A., Troussellier, M., & Bernard, C. (2008). Design and application of a stratified sampling strategy to study the regional distribution of cyanobacteria (Ile-de-France, France). Water Research, 42, 4989–5000.
Stepanenko, V.M., Martynov, A., Johnk, K.D., Subin, Z.M., Perroud, M., Fang, X., Beyrich, F., Mironov, D., & Goyette, S. (2012). A one-dimensional model intercomparison study of thermal regime of a shallow turbid midlatitude lake. Geosci Model Dev Discuss, 5, 3993–4035.
Medrano, E.A., Uittenbogaard, R.E., Pires, L.M.D., van de Wiel, B.J.H., & Clercx, H.J.H. (2013). Coupling hydrodynamics and buoyancy regulation in Microcystis aeruginosa for its vertical distribution in lakes. Ecological Modelling, 248, 41–56.
Chanudet, V., Fabre, V., & van der Kaaij, T. (2012). Application of a three-dimensional hydrodynamic model to the Nam Theun 2 Reservoir (Lao PDR). Journal of Great Lakes Research, 38(2), 260–269.
Zhu, Y., Yang, J., Hao, J., & Shen, H. (2009). Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic characteristics and water quality in Yangchenghu Lake. Advances in Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering, 1-6, 710–715.
Fabian, J., & Budinski, L. (2013). Horizontal mixing in the shallow Palic Lake caused by steady and unsteady winds. Environmental Modeling and Assessment, 18(4), 427–438.
Kopmann, R., & Markofsky, M. (2000). Three-dimensional water quality modelling with TELEMAC-3D. Hydrological Processes, 14(13), 2279–2292.
Garnier, J. (1992). Typical and atypical features of phytoplankton in a changing environment - 8 years of oligotrophication in a recently created sand-pit lake (creteil lake, paris suburb, france). Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie, 125 (4), 463–478.
Deltares. (2013). Delft3D-FLOW user manual. The Netherlands: Delft.
Gill, A.E. (1982). Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics (International Geophysics Series, Volume 30). Academic Press.
Lane, A. (1989). The heat balance of the North Sea. Birkenhead, Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory, 46pp. Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory, Report No. 8.
UNESCO. (1981). Tenth report of the joint panel on oceanographic tables and standards, Technical papers in marine science 36. Paris: France.
Taylor, K.E. (2001). Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 106, 7183–7192.
Bocaniov, S.A., Ullmann, C., Rinke, K., Lamb, K.G., & Boehrer, B. (2014). Internal waves and mixing in a stratified reservoir:Insights from three-dimensional modeling. Limnologica - Ecology and Management of Inland Waters, 49(0), 52–67.
Curtarelli, M.P., Alcantara, E., Renno, C.D., Assireu, A.T., Bonnet, M.P., & Stech, J.L. (2014). Modelling the surface circulation and thermal structure of a tropical reservoir using three-dimensional hydrodynamic lake model and remote-sensing data. Water and Environment Journal, 28(4), 516–525.
Wahl, B., & Peeters, F. (2014). Effect of climatic changes on stratification and deep-water renewal in Lake Constance assessed by sensitivity studies with a 3D hydrodynamic model. Limnology & Oceanography, 59(3), 1035–1052.
Zhao, L., Li, Y.Z., Zou, R., He, B., Zhu, X., Liu, Y., Wang, J.S., & Zhu, Y.G. (2013). A three-dimensional water quality modeling approach for exploring the eutrophication responses to load reduction scenarios in Lake Yilong (China). Environmental Pollution, 177, 13–21.
Missaghi, S., & Hondzo, M. (2010). Evaluation and application of a three-dimensional water quality model in a shallow lake with complex morphometry. Ecological Modelling, 221(11), 1512–1525.
Jin, K.R., Hamrick, J.H., & Tisdale, T. (2000). Application of three-dimensional hydrodynamic model for Lake Okeechobee. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering-Asce, 126(10), 758–771.
Jin, K.R., Ji, Z.G., & Hamrick, J.H. (2002). Modeling winter circulation in Lake Okeechobee, Florida. Journal of Waterway Port Coastal and Ocean Engineering-Asce, 128(3), 114– 125.
Jin, K.R., & Ji, Z.G. (2005). Application and validation of three-dimensional model in a shallow lake. Journal of Waterway Port Coastal and Ocean Engineering-Asce, 131(5), 213– 225.
Acknowledgements
The research presented in this paper was funded by grants from École des Ponts ParisTech, Région Île-de-France (research project PLUMMME), the Climate KIC (Blue Green Dream project), École doctorale SIE (Université Paris-Est). We acknowledge the French National Research Agency (ANR, research project PULSE) and the OSU EFLUVE for equiment funding. We also acknowledge the nke team for the sensor technical assistance and Département du Val de Marne, Ville de Créteil and Base de loisirs du lac de Créteil for their logical support in the field campaigns. The University of São Paulo (Brazil) supported the sabbatical stay of José R. Scarati Martins at Leesu/École des Ponts ParisTech. Finally we would like to thank Rob Uittenbogaard (DELTARES) and Frans Van de Ven (TU Delft) for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soulignac, F., Vinçon-Leite, B., Lemaire, B.J. et al. Performance Assessment of a 3D Hydrodynamic Model Using High Temporal Resolution Measurements in a Shallow Urban Lake. Environ Model Assess 22, 309–322 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-017-9548-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-017-9548-4