Abstract
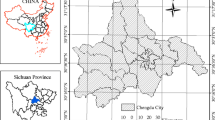
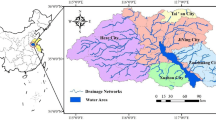
The provision capacity of ecosystem services is affected by land-use/land-cover (LULC) change and biophysical and socio-economic characteristics. Studies related to ecosystem service values (ESVs) and their impact factors can provide a good reference for natural capital management. In this paper, the temporal and spatial dynamics of LULC and ESVs in the Nansihu Lake basin, China, since the reform and opening of China were analyzed by a combined method of spatial analysis and correlation analysis, and the factors that influence ESV changes were discussed. The results indicated that the main LULC changes were the enormous loss of cultivated land and rapid urban land expansion since the policy of reformation and opening in 1978. The ESVs in the basin decreased by 1.64% (1.70 × 108 US$) from 1975 to 2015, and the main impact factors of this temporal change in ESVs were the changes in waterbodies and cultivated land. Spatial patterns of ESVs were significantly influenced by socio-economic factors in the basin, such as population density and intensity of land use. This research provides alternatives and robust information for policy-making processes for the Nansihu Lake basin, and similar work can be conducted in other parts of the country.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arowolo, A. O., Deng, X., Olatunji, O. A., & Obayelu, A. E. (2018). Assessing changes in the value of ecosystem services in response to land-use/land-cover dynamics in Nigeria. Science of the Total Environment, 636, 597–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.277.
Board, M. E. A. (2005). Millenium ecosystem assessment - ecosystem and human well-being: synthesis. Physics Teacher, 34(9), 534–534.
Bren d’Amour, C., Reitsma, F., Baiocchi, G., Barthel, S., Güneralp, B., Erb, K.-H., Haberl, H., Creutzig, F., & Seto, K. C. (2017). Future urban land expansion and implications for global croplands. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(34), 8939. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1606036114.
Costanza, R. (1997). The value of ecosystem service and nature capital in the world. Nature, 387(15), 235–260.
Costanza, R., de Groot, R., Sutton, P., van der Ploeg, S., Anderson, S. J., Kubiszewski, I., Farber, S., & Turner, R. K. (2014). Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Global Environmental Change, 26, 152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.04.002.
Estoque, R. C., & Murayama, Y. (2012). Examining the potential impact of land use/cover changes on the ecosystem services of Baguio city, the Philippines: A scenario-based analysis. Applied Geography, 35(1-2), 316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2012.08.006.
Foley, J. A., DeFries, R., Asner, G. P., Barford, C., Bonan, G., Carpenter, S. R., Chapin, F. S., Coe, M. T., Daily, G. C., Gibbs, H. K., Helkowski, J. H., Holloway, T., Howard, E. A., Kucharik, C. J., Monfreda, C., Patz, J. A., Prentice, I. C., Ramankutty, N., & Snyder, P. K. (2005). Global consequences of land use. Science, 309(5734), 570–574. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1111772.
Gashaw, T., Tulu, T., Argaw, M., Worqlul, A. W., Tolessa, T., & Kindu, M. (2018). Estimating the impacts of land use/land cover changes on Ecosystem Service Values: the case of the Andassa watershed in the Upper Blue Nile basin of Ethiopia. Ecosystem Services, 31, 219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.05.001.
Groot, R. D., Brander, L., Ploeg, S. V. D., Costanza, R., Bernard, F., Braat, L., Christie, M., Crossman, N., Ghermandi, A., & Hein, L. (2012). Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units. Ecosystem Services, 1(1), 50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2012.07.005.
Hu, H., Hao, J., & An, J. (2013). Spatio-temporal variation in the value of ecosystem services and its response to land use intensity in an urbanized watershed. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(8), 2565–2576.
Lawler, J. J., Lewis, D. J., Nelson, E., Plantinga, A. J., Polasky, S., Withey, J. C., Helmers, D. P., Martinuzzi, S., Pennington, D., & Radeloff, V. C. (2014). Projected land-use change impacts on ecosystem services in the United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(20), 7492. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1405557111.
Liang, J., Zhong, M., Zeng, G., Chen, G., Hua, S., Li, X., Yuan, Y., Wu, H., & Gao, X. (2017). Risk management for optimal land use planning integrating ecosystem services values: a case study in Changsha, Middle China. Science of the Total Environment, 579, 1675–1682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.184.
Liu, J., Kuang, W., Zhang, Z., Xu, X., Qin, Y., Ning, J., Zhou, W., Zhang, S., Li, R., Yan, C., Wu, S., Shi, X., Jiang, N., Yu, D., Pan, X., & Chi, W. (2014). Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 24(2), 195–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-014-1082-6.
Lyv, X., Shi, Y. Y., Huang, X. J., Sun, X. F., & Miao, Z. W. (2016). Geo-spectrum characteristics of land use change in Jiangsu Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, (04), 1077–1084.
MA. (2005). Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. In Ecosystem and human wellbeing: synthesis. Washington, DC: Island Press. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2137465.
Maes, W. H., Heuvelmans, G., & Muys, B. (2009). Assessment of land use impact on water-related ecosystem services capturing the integrated terrestrial-aquatic system. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(19), 7324–7330. https://doi.org/10.1021/es900613w.
Metzger, M. J., Rounsevell, M. D. A., Acosta-Michlik, L., Leemans, R., & Schrotere, D. (2006). The vulnerability of ecosystem services to land use change. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 114(1), 69–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2005.11.025.
Pandey, B., & Seto, K. C. (2015). Urbanization and agricultural land loss in India: Comparing satellite estimates with census data. Journal of Environmental Management, 148, 53–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.05.014.
Song, W., & Deng, X. (2017). Land-use/land-cover change and ecosystem service provision in China. Science of the Total Environment, 576, 705–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.078.
Sun, X. Y., Guo, H. W., Lian, L. S., Liu, F., & Li, B. F. (2017). The spatial pattern of water yield and its driving factors in Nansi Lake basin. Journal of Natural Resources, 32(04), 669–679.
Tolessa, T., Senbeta, F., & Kidane, M. (2017). The impact of land use/land cover change on ecosystem services in the central highlands of Ethiopia. Ecosystem Services, 23, 47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2016.11.010.
Wang, Y., Gao, J., Wang, J., & Qiu, J. (2014). Value assessment of ecosystem services in nature reserves in Ningxia, China: a response to ecological restoration. PLoS One, 9(2), e89174. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089174.
Wang, X., Dong, X., Liu, H., Wei, H., Fan, W., Lu, N., Xu, Z., Ren, J., & Xing, K. (2017). Linking land use change, ecosystem services and human well-being: a case study of the Manas River Basin of Xinjiang, China. Ecosystem Services, 27, 113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2017.08.013.
Xie, G., Zhen, L., Lu, C., Xiao, Y., & Chen, G. (2008). Expert knowledge based valuation method of ecosystem service in China. Journal of Natural Resources, 23(5), 911–919.
Xie, G., Zhang, C., Zhang, C., Xiao, Y., & Lu, C. (2015a). The value of ecosystem services in China. Resources Science, 37(9), 1740–1746.
Xie, G., Zhang, C., Zhang, L., Chen, W., & Li, S. (2015b). Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area. Journal of Natural Resources, 30(8), 1243–1254.
Zank, B., Bagstad, K. J., Voigt, B., & Villa, F. (2016). Modeling the effects of urban expansion on natural capital stocks and ecosystem service flows: a case study in the Puget Sound, Washington, USA. Landscape and Urban Planning, 149, 31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.01.004.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Ministry of Education of Humanities and Social Science Project (No. 14YJCZH138), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 41471389, 41501542), and the Science Foundation of Qufu Normal University (No. XJ201202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Sun, X., Liu, F. et al. Spatio-temporal variation of land use and ecosystem service values and their impact factors in an urbanized agricultural basin since the reform and opening of China. Environ Monit Assess 191, 739 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7896-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7896-z